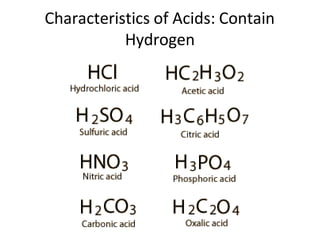
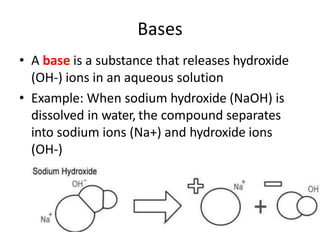
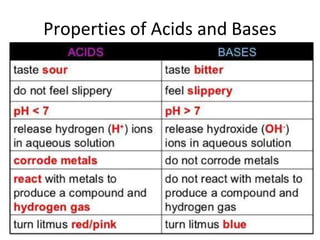
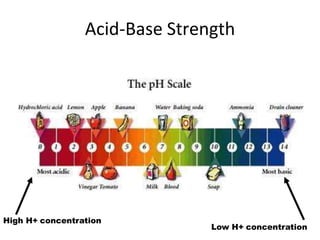
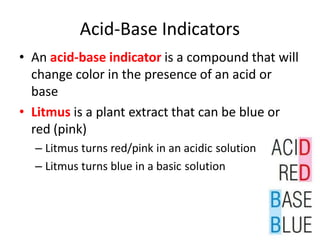
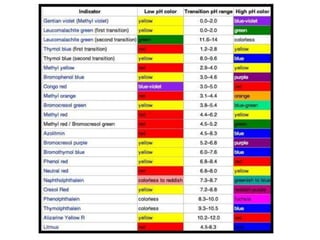
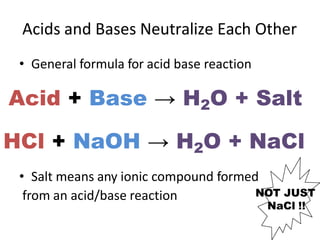
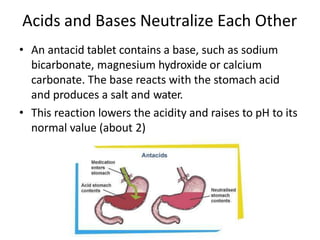
Acids and bases are defined by whether they release H+ or OH- ions in water. Strong acids and bases dissociate completely, while weak ones only partially dissociate. Acids taste sour, react with carbonates and metals to produce gas, and contain hydrogen. Bases taste bitter, feel slippery, and contain hydroxide ions. The pH scale measures acidity and alkalinity, with values below 7 indicating acids and above 7 indicating bases. Acid-base indicators change color at specific pH levels, allowing identification of acids and bases. When acids and bases neutralize, they form water and salts.