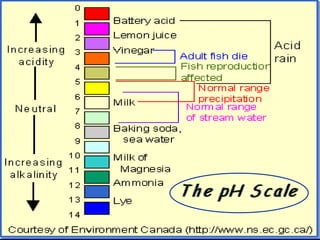
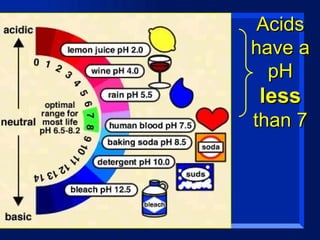
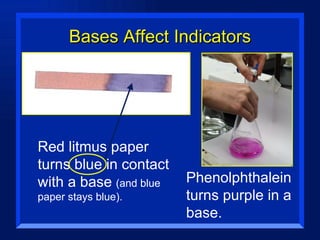
Acids have a pH below 7 and react with bases to form salts and water. Common acids include hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, and acetic acid. Bases have a pH above 7 and react with acids in neutralization reactions. Common bases are sodium hydroxide, calcium hydroxide, and potassium hydroxide. Indicators are used to test whether a solution is acidic or basic by changing color in different pH ranges.


















![The pH concept – from 0 to 14 pH = pouvoir hydrogene (Fr.) “hydrogen power” definition: pH = -log[H + ] in neutral pH = 7 in acidic solution=< 7 pH < -log(10 -7 ) pH < 7 (from 0 to 7 is the acid range) in base , pH > 7 (7 to 14 is base range)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter19acidsbasesandsaltsprobe-111208073917-phpapp01/85/Chapter-19-acids-bases-and-salts-probe-21-320.jpg)