1) Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) in water, turning litmus paper red and having a sour taste, while bases release hydroxide ions (OH-), turning litmus blue and having a bitter taste.
2) The pH scale measures the acidity or alkalinity of solutions, with values from 0-7 being acidic, 7 being neutral, and 7-14 being alkaline. Strong acids and bases fully dissociate in water while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
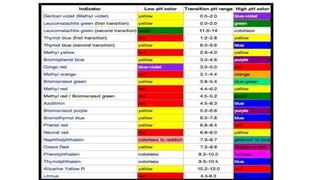
3) Acid-base indicators change color depending on the pH, allowing identification of acids and bases. Litmus is commonly used, turning red in acids and blue in bases. Neutralization occurs