More Related Content
PPTX
PPT
Acids-and-Alkalis-KS3-interactive-lesson.ppt PPT
acids and alkailies, definition and properties.ppt PPT
Acids-and-Alkalis-KS3-interactive-lesson.ppt PPT
Acids and Bases and use of indicators to find the nature of substances PPTX
AS 4.1 Acid and base.pptx PPT
PPT
Acids and alkalis final ppt.ppt Similar to Acids and Alkalis.ppt SDCDSdscSDCcCccCASCC
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
PPTX
Acids, Bases and Neutralization PPTX
Introduction to acids,bases and salts PPT
acids and bases, chemical properties.ppt PPTX
KS3 Acids and Alkalis.pptx PPT
PPTX
acids bases and salts for the students 2.pptx PPTX
Acids, Bases and Salts Class 7 Science.pptx PPT
PPTX
Ch- 6 Acids , Bases And Salts PPT,8th std. PPTX
Material changes, Acids, AlKali, neutralization reaction PPTX
PPTX
Ch. 10 -Acids and Alkalis grade 8 helppptx PPTX
Acids, Bases and Salts Class - 10th PPT
BASIC FACTS ABOUT ACIDS AND ALKALIS PPTX
Acids and Bases and Oxides- IGCSE, Chemistry PPTX
Acid-bases-salt-ppt class 7 ncert ..pptx PPT
Recently uploaded
PPTX
How to Manage Product Types in Odoo 18 Sales PPTX
Palta Utsav Open Quiz Prelims Answer.pptx PPTX
VITAMINS CHAPTER NO.05 PHARMACOGNOSY D. PHARMACY PDF
McDowell Technical Community College Early Childhood Program Equitable Workfo... PPTX
ANTISEPTICS AND DISINFECTANTS CHAPTER NO.05.pptx PDF
GIÁO ÁN KẾ HOẠCH BÀI DẠY NĂNG LỰC SỐ MÔN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 10 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUC... PDF
GIÁO ÁN KẾ HOẠCH BÀI DẠY NĂNG LỰC SỐ MÔN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 11 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUC... PPTX
THEORIES OF LEARNING Shilpa Hotakar.pptx PDF
Freshman Geography Chapter 7-Population of Ethiiopia PDF
Types of Artificial Intelligence: Capabilities and Functionality Explained PDF
Freshman Geography Group Work CH7 (1).pdf PPTX
The Creation Pattern Physical Health.pptx PDF
The Unique Wildlife of Ethiopia: From the Simien to the Bale Mountains PPTX
Blood, Blood Composition, Blood Groups, Disorders of Blood.pptx PDF
GIÁO ÁN KẾ HOẠCH BÀI DẠY NĂNG LỰC SỐ MÔN TIẾNG ANH LỚP 12 CẢ NĂM - GLOBAL SUC... PPTX
How to Add or Remove Multiple Followers in a Records PPTX
Insertion of Suppositories..........pptx PDF
Agents in Artificial Intelligence: Types, Architecture and Real-World Examples PDF
BÀI GIẢNG POWERPOINT CHÍNH KHÓA PHIÊN BẢN AI TIẾNG ANH 6 CẢ NĂM, THEO TỪNG BÀ... PPTX
STERILITY INDICATOR Pharmaceutical microbiology Acids and Alkalis.ppt SDCDSdscSDCcCccCASCC
- 1.
- 2.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
What is an acid?
Here are some facts about acids.
• Strong acids are corrosive “eating away” at things like
metal, stone and flesh!
• Weak acids, like lemon juice and vinegar, taste sour.
• Acids turn litmus red.
• Acids have a pH below 7.
• Acids contain hydrogen (but not all things that contain
hydrogen are acids!).
• Acids can be neutralised with alkalis.
- 3.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Some common acids
Three acids are particularly common in the laboratory .
These are strong acids that should be treated with
the greatest respect.
Acid Formula Salts formed
hydrochloric HCl chlorides
sulphuric H2SO4 sulphates
nitric HNO3 nitrates
- 4.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
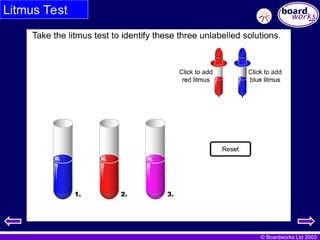
Indicators: acid or alkali?
An indicator is a dye which changes colour according to
whether it is in an acidic or alkaline solution.
Litmus is available as a liquid that
can be added to the solution.
For example, litmus is an indicator
that is red in acid and blue in alkali.
It is also available as strips of
paper so that you can add a drop
of the solution to the paper.
- 5.
- 6.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Indicators: how acid or alkali?
Litmus will tell you whether a solution is acid or alkali:
what it won’t tell you is how
how acid or alkali.
Universal indicator has a whole range of colours that tell
us how strong an acid or alkali is.
Strong acid Neutral Strong alkali
Weak acid Weak alkali
More alkali
More acid
- 7.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
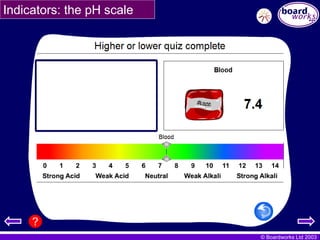
Indicators: the pH scale
This attaches a number called the pH value to each
universal indicator colour.
This means we can quickly say how acid or alkali a
substance is by quoting a single number.
1 2 14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
Strong acid Neutral Strong alkali
Weak acid Weak alkali
•pH7 is neutral
•pH 1 is strongly acid
•pH14 is strongly alkali
- 8.
- 9.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
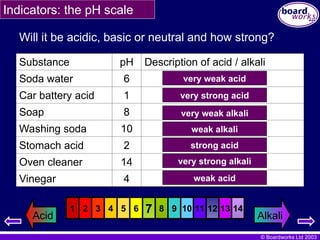
Will it be acidic, basic or neutral and how strong?
1 2 14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
Substance pH Description of acid / alkali
Soda water 6
Car battery acid 1
Soap 8
Washing soda 10
Stomach acid 2
Oven cleaner 14
Vinegar 4
very weak acid
very strong acid
very weak alkali
weak alkali
strong acid
very strong alkali
weak acid
Alkali
Acid
Indicators: the pH scale
- 10.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Bases
Bases are substances that neutralise acids.
Bases are usually:
•Metal hydroxides contain OH
•Metal oxides contain O
•Metal carbonates contain CO3
The following general word equation describes
neutralisations:
acid + base a salt + water
In the case of carbonates we also get carbon dioxide.
- 11.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
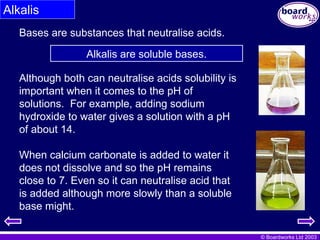
Alkalis
Bases are substances that neutralise acids.
Alkalis are soluble bases.
Although both can neutralise acids solubility is
important when it comes to the pH of
solutions. For example, adding sodium
hydroxide to water gives a solution with a pH
of about 14.
When calcium carbonate is added to water it
does not dissolve and so the pH remains
close to 7. Even so it can neutralise acid that
is added although more slowly than a soluble
base might.
- 12.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
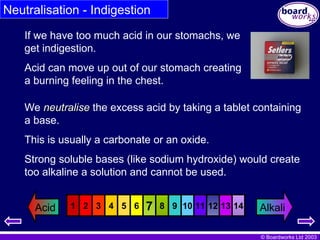
Neutralisation - Indigestion
If we have too much acid in our stomachs, we
get indigestion.
Acid can move up out of our stomach creating
a burning feeling in the chest.
We neutralise
neutralise the excess acid by taking a tablet containing
a base.
This is usually a carbonate or an oxide.
Strong soluble bases (like sodium hydroxide) would create
too alkaline a solution and cannot be used.
Alkali
Acid 1 2 14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
- 13.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
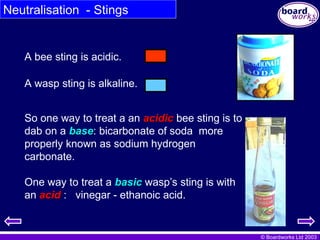
Neutralisation - Stings
A bee sting is acidic.
One way to treat a basic
basic wasp’s sting is with
an acid
acid : vinegar - ethanoic acid.
So one way to treat a an acidic
acidic bee sting is to
dab on a base
base: bicarbonate of soda more
properly known as sodium hydrogen
carbonate.
A wasp sting is alkaline.
- 14.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Neutralisation – Soil pH
Many plants won’t grow well in acid soil and so
farmers have to regularly check the pH and
adjust it by adding a base.
Plants remove compounds from the soil in a way
that tends to leave the soil acidic.
Calcium carbonate or calcium
hydroxide are cheap and so are
often used for this purpose.
- 15.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Neutralisation – Soil fertilisers
Ammonia is a water soluble gas high in nitrogen and in
some countries it is injected directly into moist soil.
However, because it is a gas much of it is quickly lost.
In the UK ammonia is dissolved in water to give
ammonium hydroxide (an alkali) and this is neutralised
by reacting it with nitric acid to give a solid nitrogen rich
fertiliser.
Plants also remove nitrogen compounds from the soil and
this is often replaced using fertiliser.
water
+
ammonium
nitrate
nitric acid
+
ammonium
hydroxide
NH4OH + HNO3 NH4NO3 + H2O
- 16.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
The gases are “scrubbed”, as much as possible,
of these acidic oxides by reacting them with a
base before releasing them into the air.
Many power stations burn coal containing sulphur.
When this burns it produces acidic sulphur oxides which
can cause acid rain.
Calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide are often
used for this purpose.
Neutralisation - acid gases
- 17.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Steps have been taken to reduce emissions of acidic
sulfur oxides from power stations and nitrogen oxides
from cars.
Even so the atmosphere still contains enough of them to
make the rain from industrial areas quite acidic.
Acid rain – living things
Trees and lakes are badly
affected in many parts of the
world including Northern
Germany and Scandinavia
which suffers from South-West
winds from the UK.
Acid rain damaged tress
- 18.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Acid rain increases the rate of corrosion of metals.
Acid rain – metals and stone
The metal above the
wheel arch of this car
is rusting away
It also greatly accelerates the rate of chemical weathering
of certain stones used in building such as limestone and
marble. (These stones are carbonates. What gas will be
given off as they dissolve?)
CO2
- 19.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
Acid
Alkali
Carbonate
Chloride
Hydrogen
Indicator
Indigestion
Litmus
Metal
Neutralise
Nitrate
Nitrogen
Salt
Water
• There are sixteen
“easy-find” words
in the word square.
• Write a clue for
each word drawing
upon what you have
studied in this unit
of work
I Q W R A C I D Q P S S W K G
N E U T R A L I S E G A R M Y
D P L X S R Q N I T R O G E N
I M S U U B K D X O C G W Y I
G S C H L O R I D E B Z S R F
E W T Y F N S C M E T A L O J
S G K D A A U A L K A L I J O
T S A R T T L T C U W A T E R
I I P O E E F O S D H I M U W
O N K G E E U R A C O W U M D
N O B E B C R C L Q K D S U J
N V J N I T T A T E A J N B B
- 20.
- 21.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A Sodium bicarbonate
B Vinegar
C Litmus
D Salt
1. Which of these is an indicator?
- 22.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A Potassium hydroxide
B Sodium chloride
C Sodium hydroxide
D Sodium
2. Which of these is a salt?
- 23.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A pH 7
B pH 1
C pH 8
D pH 13
3. Which of these is a weak alkali?
A substance with:
- 24.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A Water - pH 7
B Lemon - pH 3
C Oven cleaner - pH 14
D Bicarbonate of Soda – pH 9
4. Which of these might you put on a ant
sting to neutralise the acid in the sting?
- 25.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A Hydrogen
B Sulphur
C Oxygen
D Nitrogen
5. Which of these do all acids contain?
- 26.
© Boardworks Ltd2003
A Silver nitrate
B Sodium hydroxide
C Calcium hydroxide
D Magnesium hydroxide
6. Which of these substances would not
neutralise an acid?
Editor's Notes
- #5 TEACHER’S NOTES
Results of the litmus test are :
alkali
acid
water