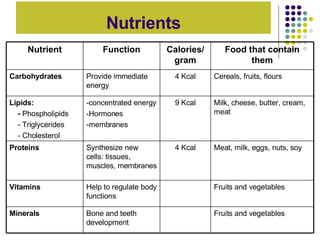
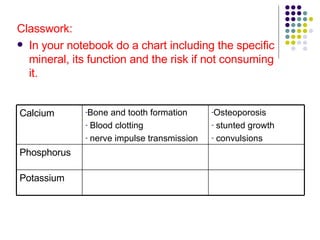
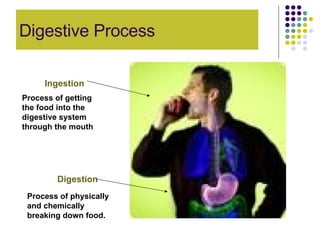
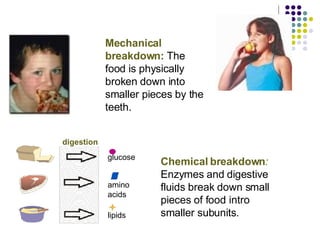
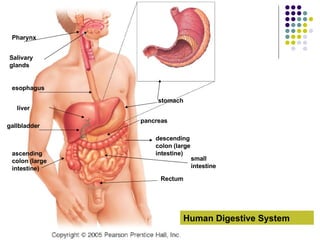
The document discusses the digestive system and nutrition. It defines nutrients, calories, and the main nutrient groups - carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals. It describes the digestive process, including ingestion, mechanical and chemical breakdown, absorption, and elimination. Key organs involved are the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, pancreas, liver, gallbladder, large intestine, and rectum.