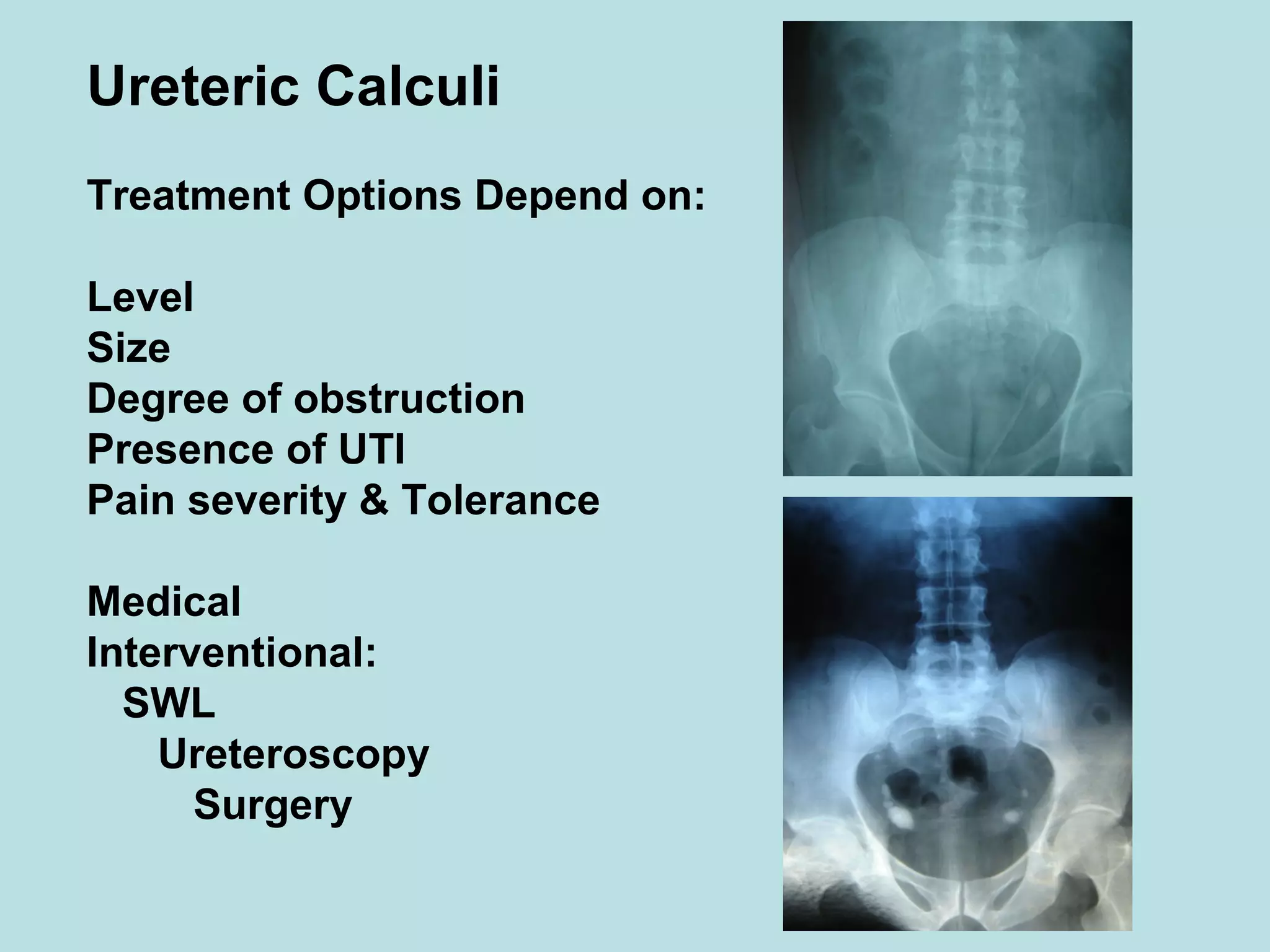
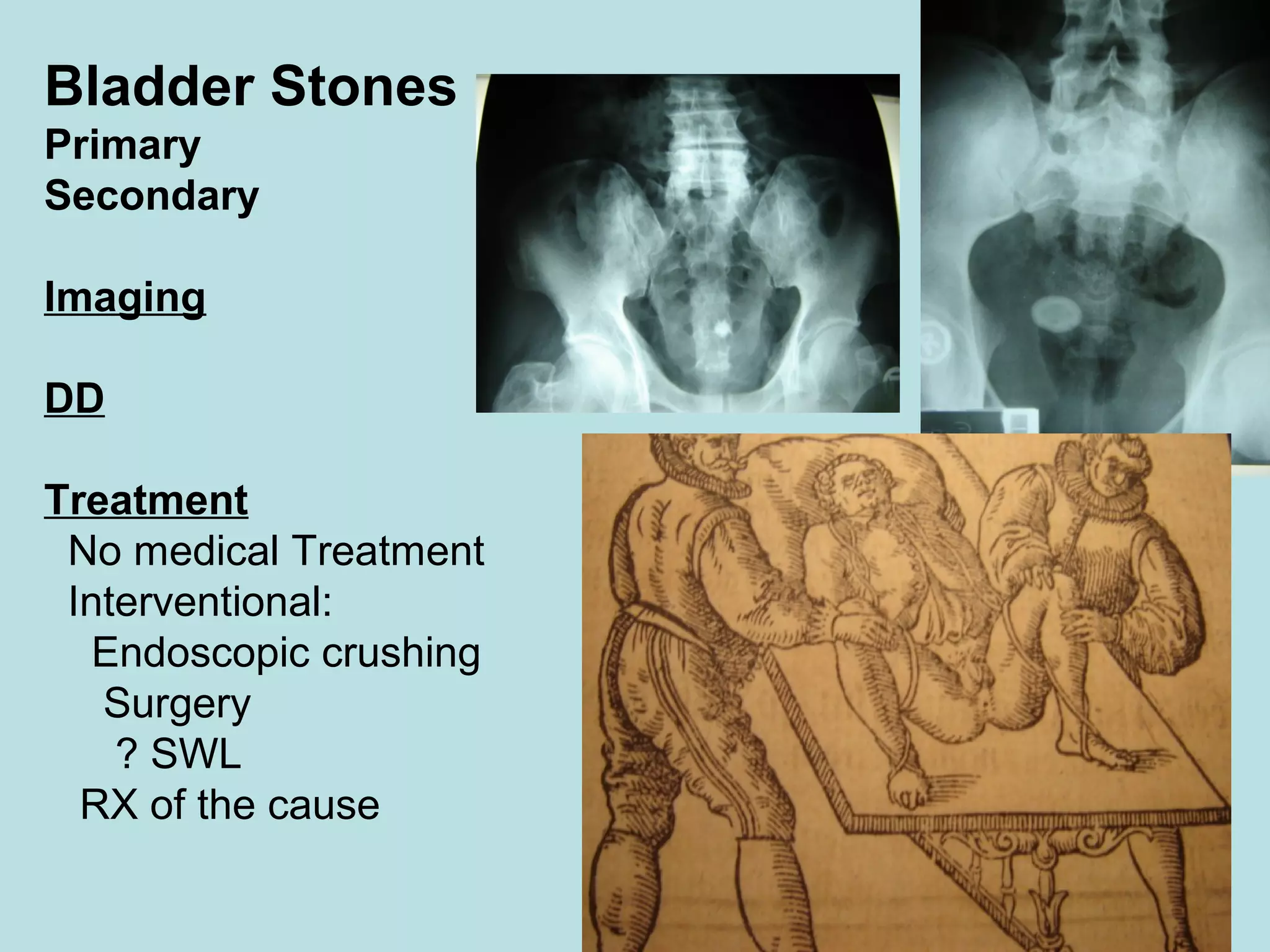
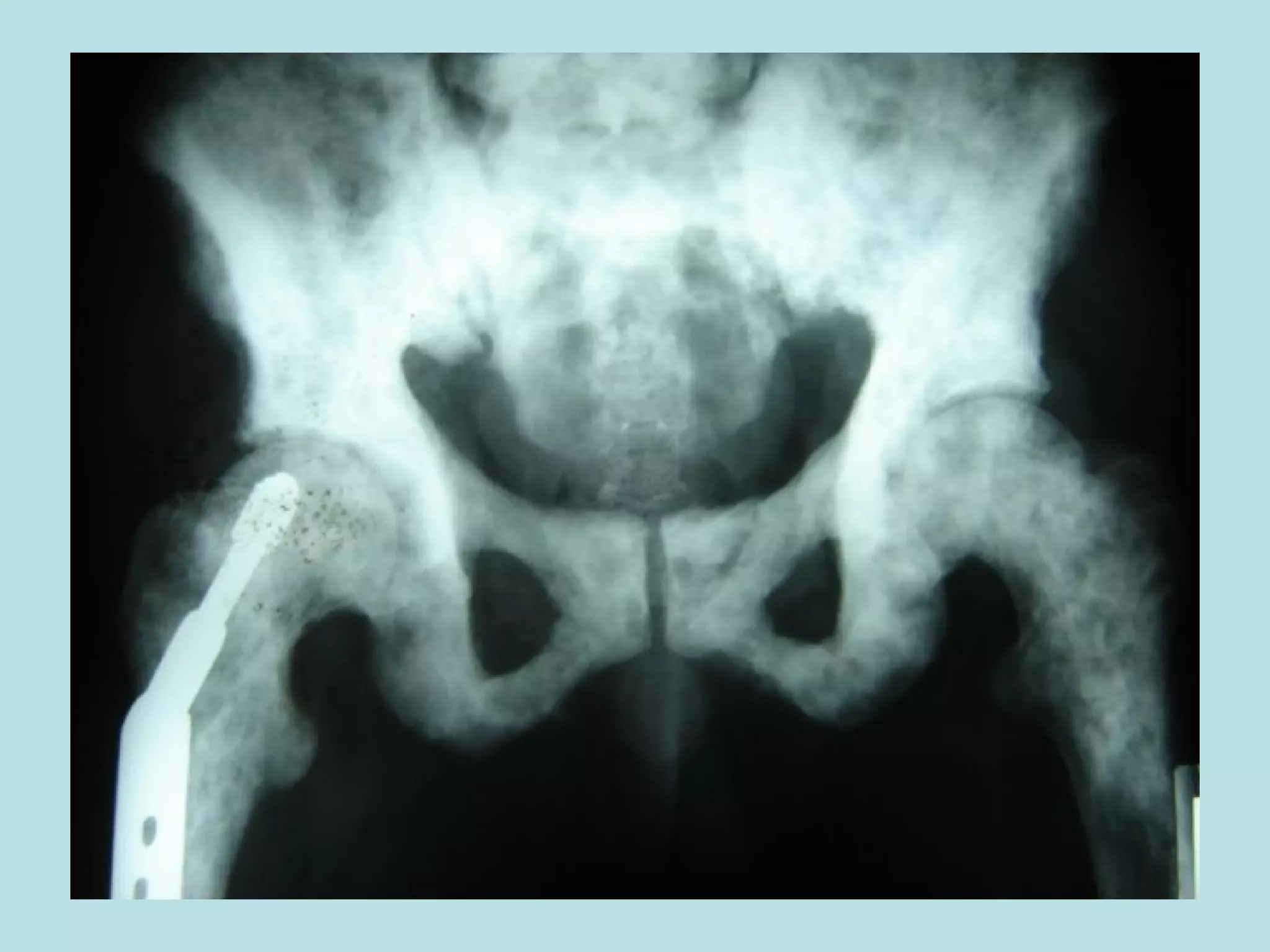
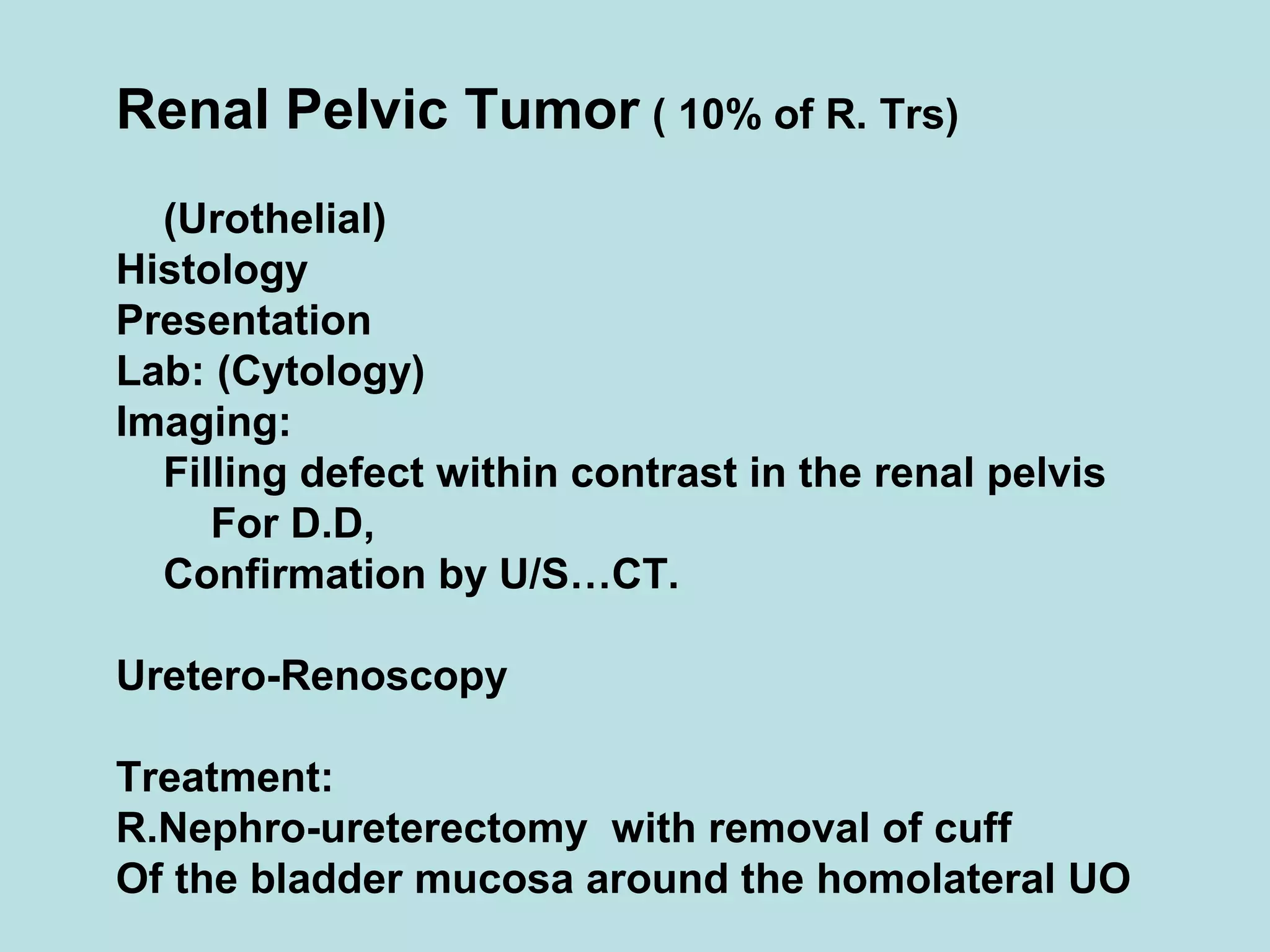
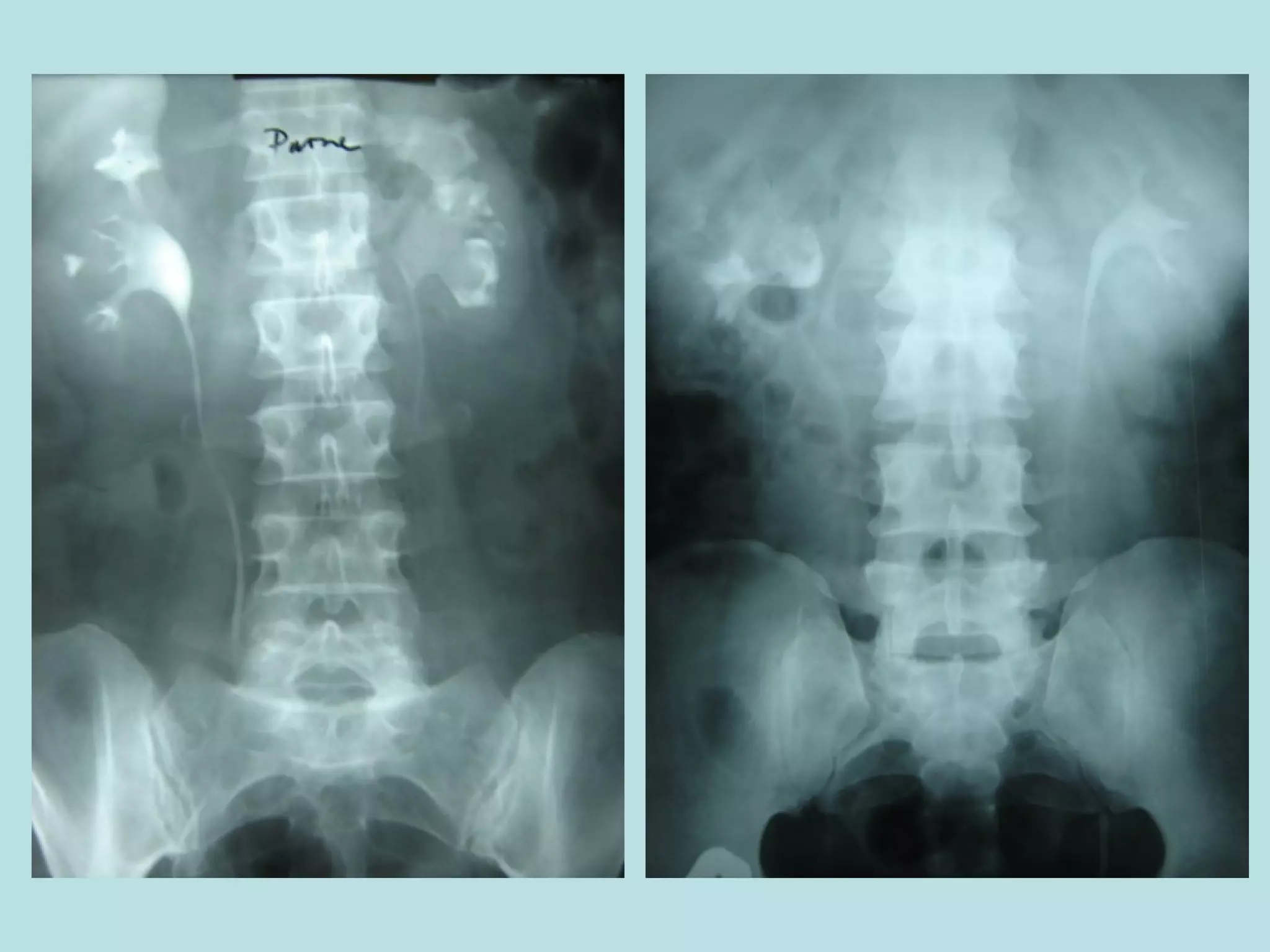
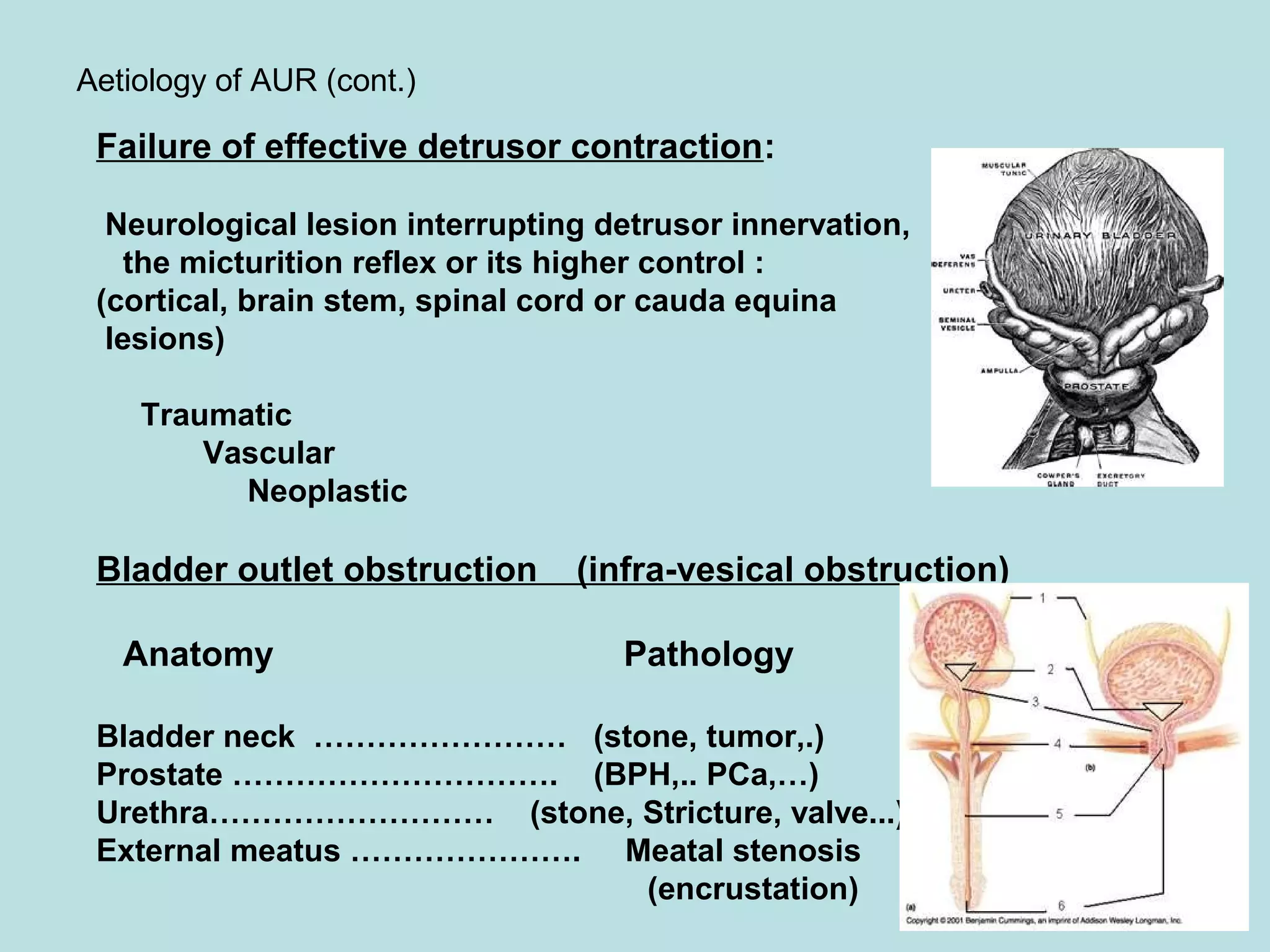
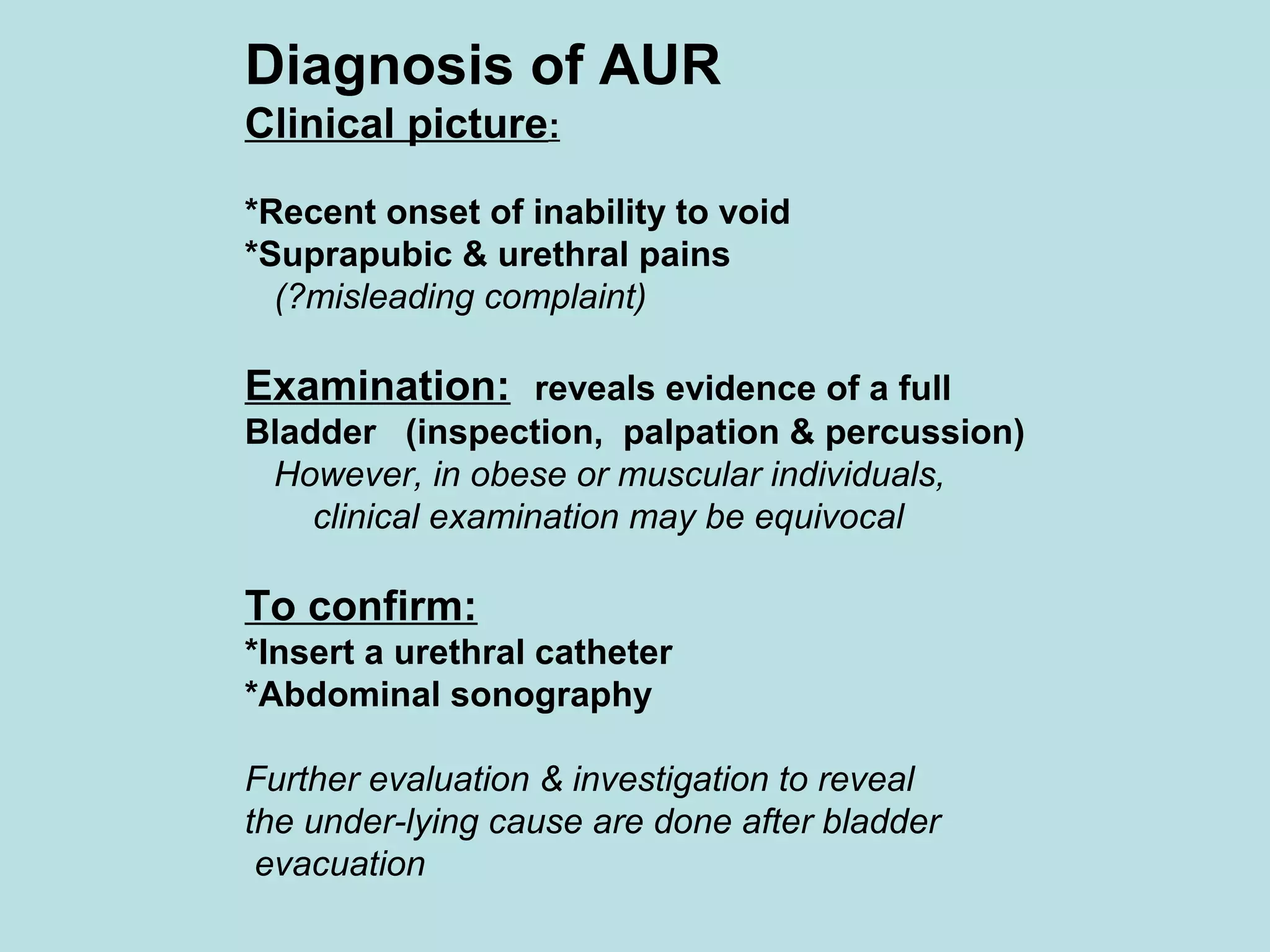
Acute urinary retention (AUR) is the inability to void despite a full bladder. It can be caused by failure of detrusor contraction or bladder outlet obstruction. Diagnosis involves confirmation of a full bladder on exam and insertion of a urethral catheter. Immediate treatment is catheterization to evacuate the bladder. Further evaluation is then done to identify the underlying cause and provide definitive treatment.