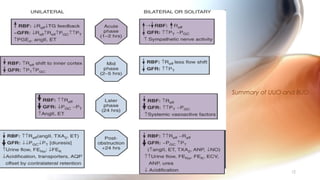
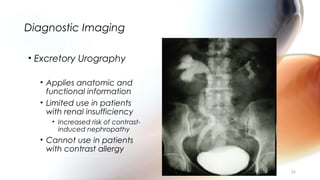
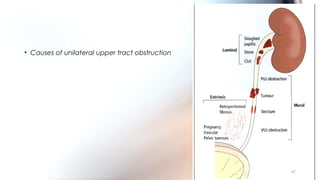
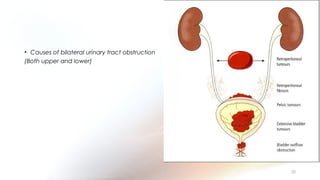
This document provides an overview of obstructive uropathy. It begins by defining obstructive uropathy as the functional or anatomic obstruction of urine flow at any level of the urinary tract. It then discusses the prevalence of obstructive uropathy and how it can be classified based on factors like duration and site of obstruction. Potential causes of obstructive uropathy are then reviewed for different parts of the urinary tract. The pathophysiology and hemodynamic changes that occur with obstruction are explained. Cellular and molecular changes that can lead to fibrosis and tubular cell death are described. Management of patients is discussed including diagnostic imaging, issues in patient care like hypertension and pain management, and considerations for surgical intervention.