This document discusses surgical jaundice, including:
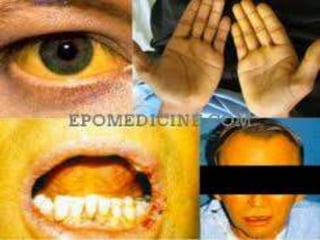
1. It defines jaundice and surgical jaundice, and classifies jaundice into pre-hepatic, hepatic, and post-hepatic types.
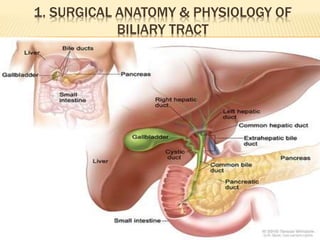
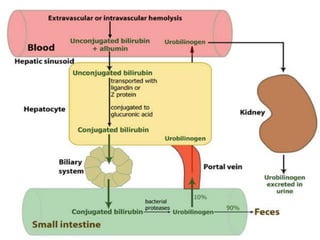
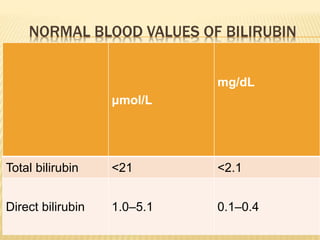
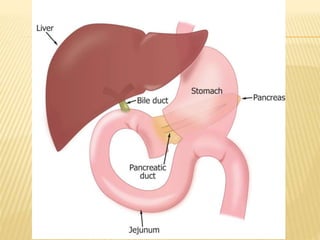
2. It describes the anatomy and physiology of the biliary tract and bilirubin metabolism.
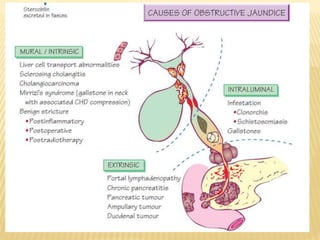
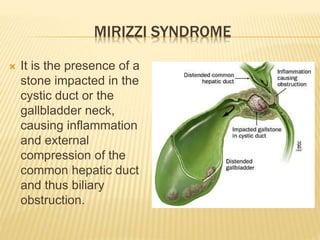
3. Common causes of obstructive jaundice include gallstones, cancer, strictures, and inflammation. A thorough history and physical exam can help identify the cause.
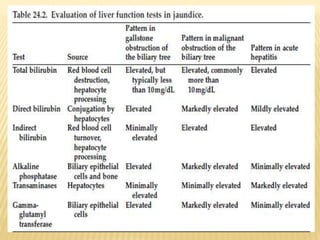
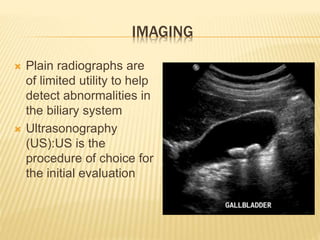
4. Investigations include blood tests, imaging like ultrasound and MRCP, and procedures like ERCP. The goal is to determine the specific cause and level of obstruction.
5. Treatment depends on the