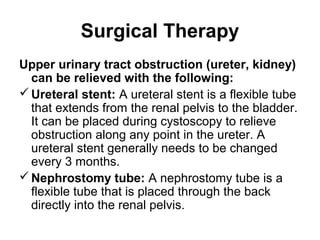
Obstructive uropathy can affect people of all ages and has varied presentations depending on the site and degree of obstruction. It can be caused by mechanical factors like congenital anomalies, inflammation, tumors, or stones, as well as functional issues related to neurological or muscular disorders. Common symptoms include pain, hematuria, and hydronephrosis. Diagnostic workup involves lab tests, imaging like ultrasound, CT, IVP, and procedures like cystoscopy. Treatment aims to relieve the obstruction through catheters, stents, or other surgeries, while also treating infections or other complications. Complete or solitary kidney obstructions require urgent intervention to prevent serious issues like renal failure.