Embed presentation
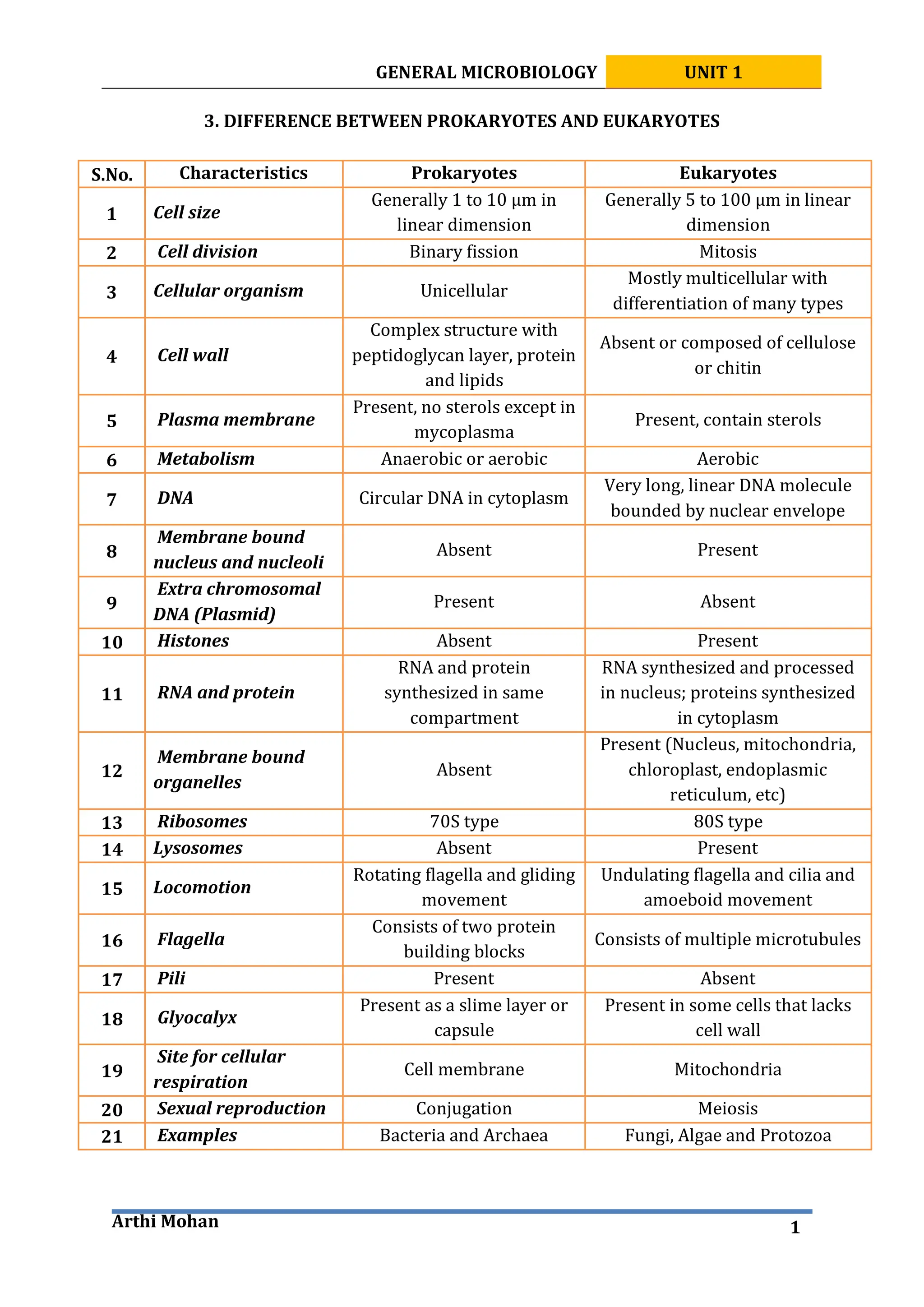
Prokaryotes like bacteria are generally smaller, unicellular, lack membrane-bound organelles, and have circular DNA not confined to a nucleus. In contrast, eukaryotes including fungi and plants are usually larger, often multicellular, with internal membrane-bound structures like the nucleus and mitochondria that contain linear DNA. Major differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes include cell structure, DNA organization, intracellular components, and modes of reproduction.
