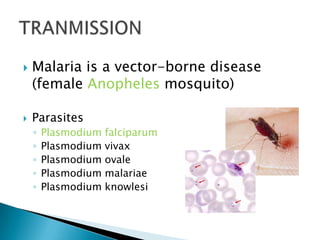
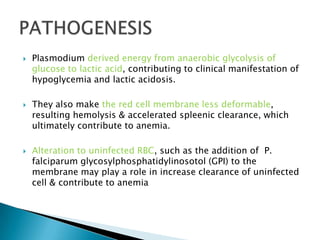
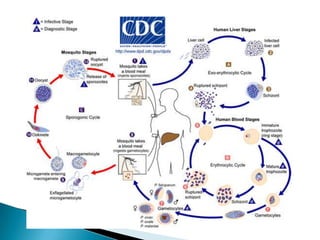
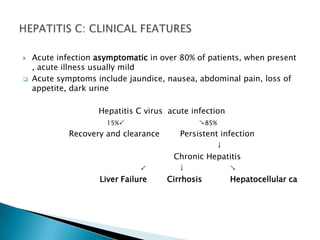
Hepatitis is inflammation of the liver that is commonly caused by viral hepatitis A, B, and C. Hepatitis A virus is transmitted through the fecal-oral route or contaminated food/water while hepatitis B and C viruses are transmitted through blood or bodily fluids. The viruses infect liver cells and cause liver damage that leads to symptoms. While hepatitis often resolves on its own, chronic hepatitis B and C infections can develop and increase risk of cirrhosis and liver cancer over time without treatment. Tuberculosis is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis and transmitted via airborne respiratory droplets. It commonly affects the lungs but can spread systemically, especially in immunosuppressed individuals.































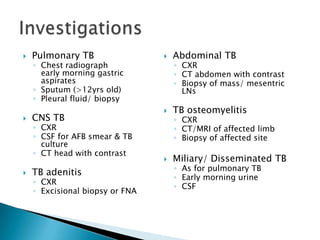



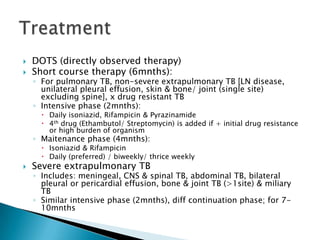








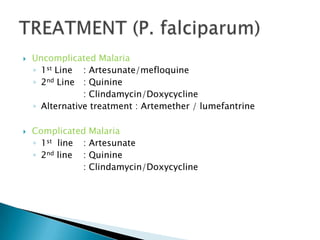
![TreatmentDOTS (directly observed therapy)Short course therapy (6mnths):For pulmonary TB, non-severe extrapulmonary TB [LN disease, unilateral pleural effusion, skin & bone/ joint (single site) excluding spine], x drug resistant TB Intensive phase (2mnths):Daily isoniazid, Rifampicin & Pyrazinamide4th drug (Ethambutol/ Streptomycin) is added if + initial drug resistance or high burden of organismMaitenance phase (4mnths):Isoniazid & RifampicinDaily (preferred) / biweekly/ thrice weeklySevere extrapulmonary TBIncludes: meningeal, CNS & spinal TB, abdominal TB, bilateral pleural or pericardial effusion, bone & joint TB (>1site) & miliary TBSimilar intensive phase (2mnths), diff continuation phase; for 7-10mnths](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-chronicinfection-110107203831-phpapp02/85/3-chronic-infection-49-320.jpg)