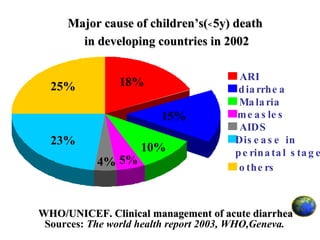
1. Diarrhea is a common disease in childhood that can be caused by infections, non-infectious factors, or a combination of both. Infectious causes include viruses like rotavirus and bacteria like E. coli, while non-infectious causes include improper diet, weather factors, and feeding issues.
2. The pathogenesis of infectious diarrhea involves mechanisms like enterotoxins produced by bacteria that increase intestinal fluid secretion, or viruses and bacteria that directly invade and damage the intestinal mucosa. This leads to reduced nutrient absorption and an osmotic diarrhea.
3. Clinical manifestations of diarrhea range from mild cases involving changes in stool frequency and consistency, to more severe cases accompanied by dehydration