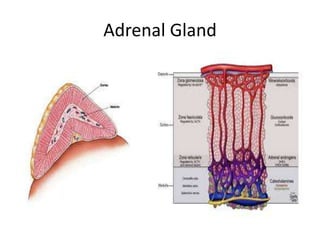
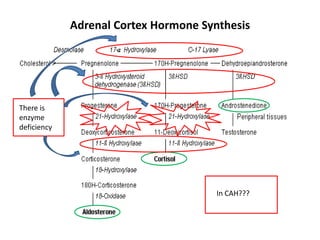
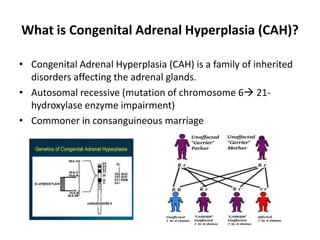
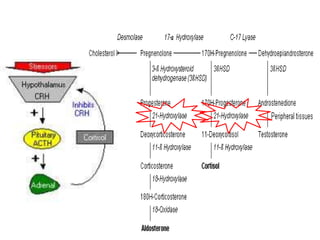
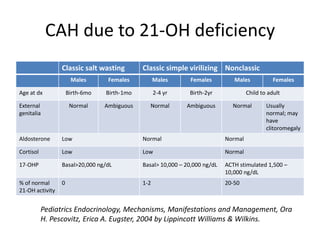
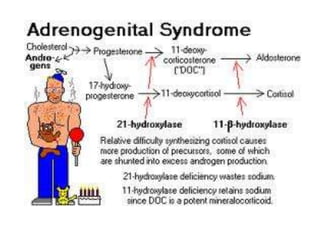
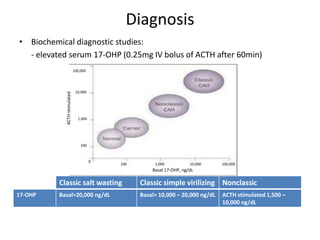
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) is a family of inherited disorders affecting the adrenal glands caused by a deficiency in enzymes involved in cortisol and aldosterone production. The most common type (over 90% of cases) is 21-hydroxylase deficiency, which is autosomal recessive and can cause ambiguous genitalia in females and other symptoms. Clinical manifestations include salt wasting, low blood sugar, and excessive male hormone production leading to virilization. Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure hormone levels before and after stimulation with ACTH. Treatment consists of glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid hormone replacement, monitoring of hormone levels, and surgery to correct ambiguous genitalia.