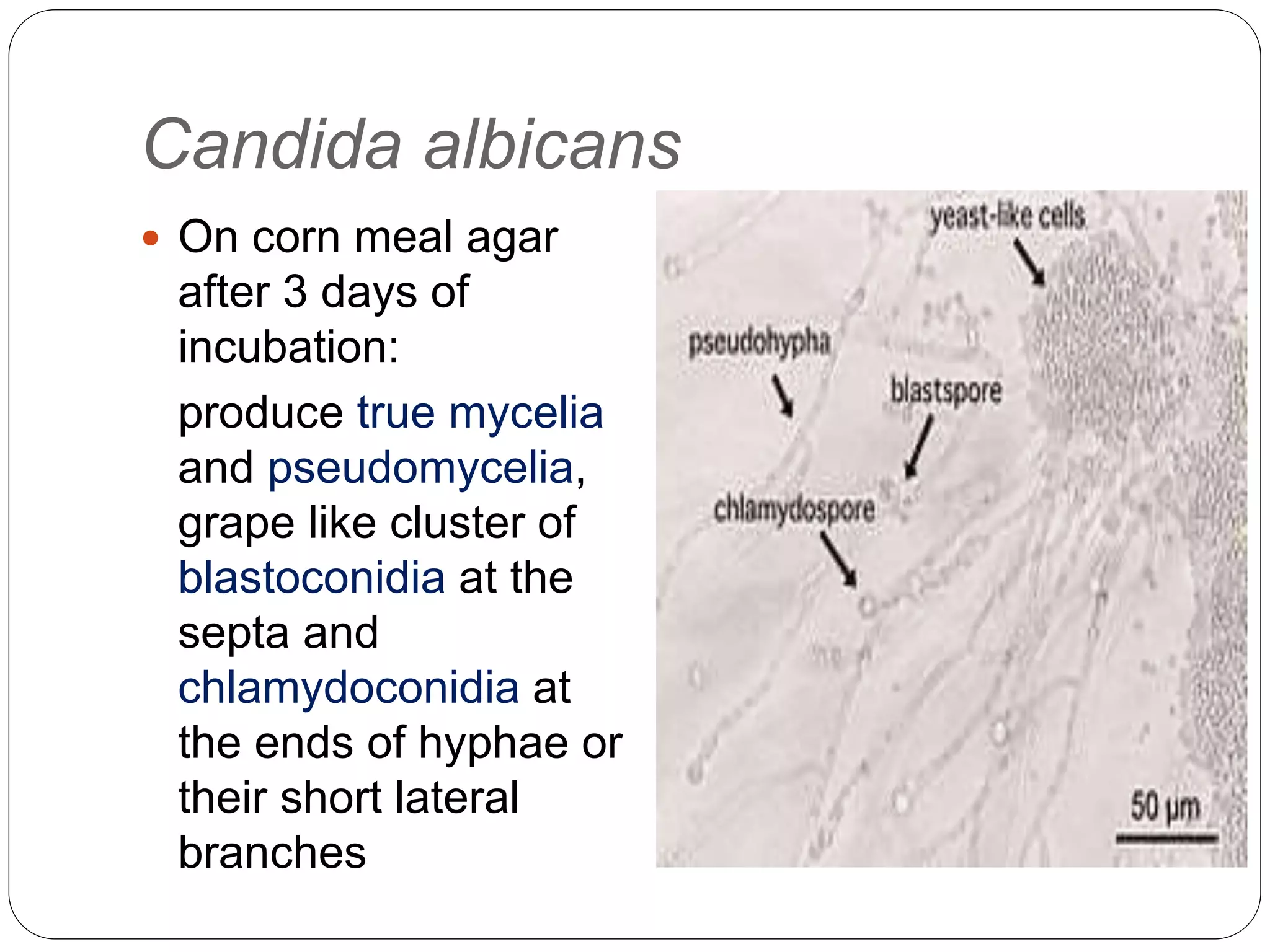
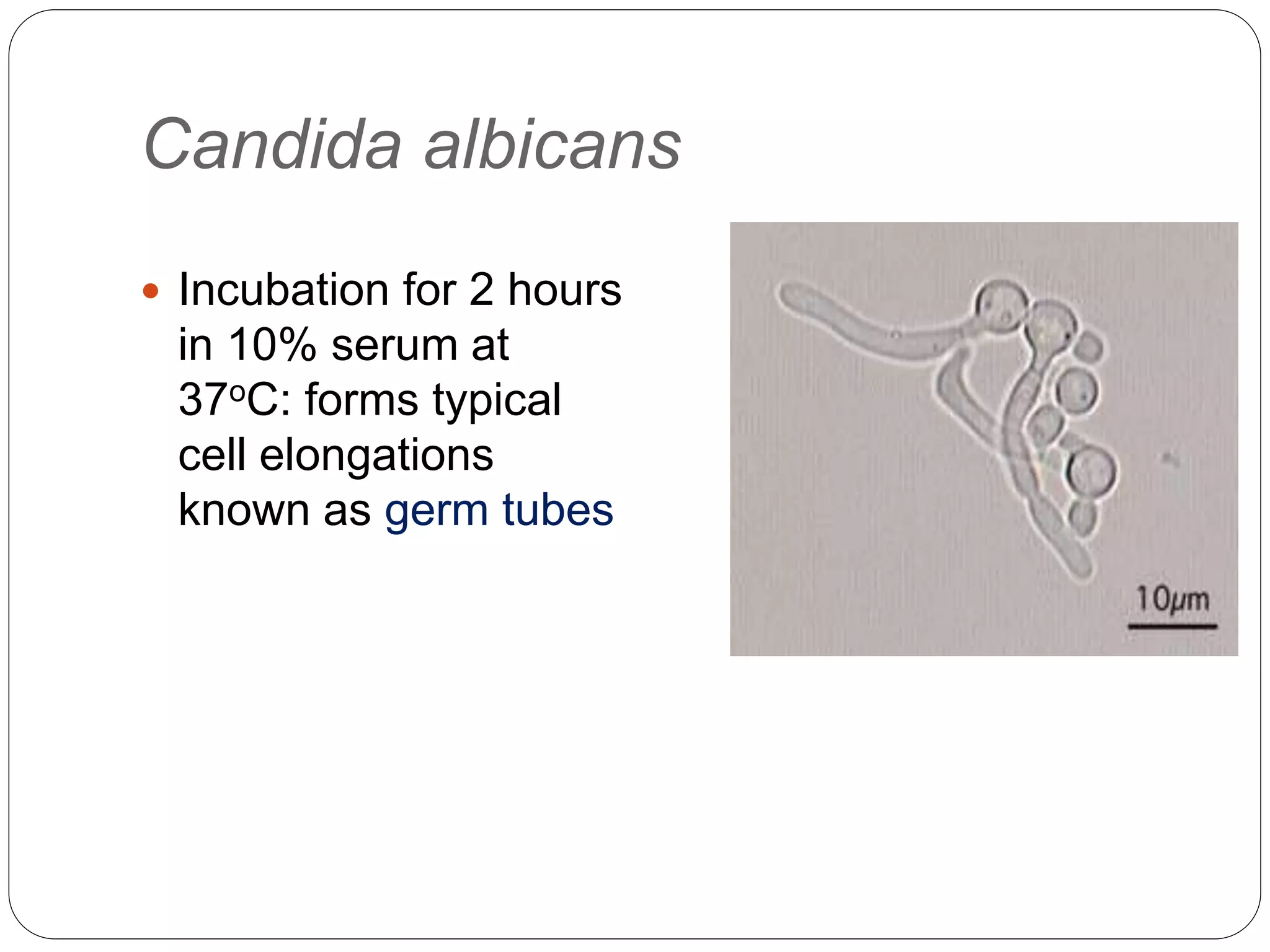
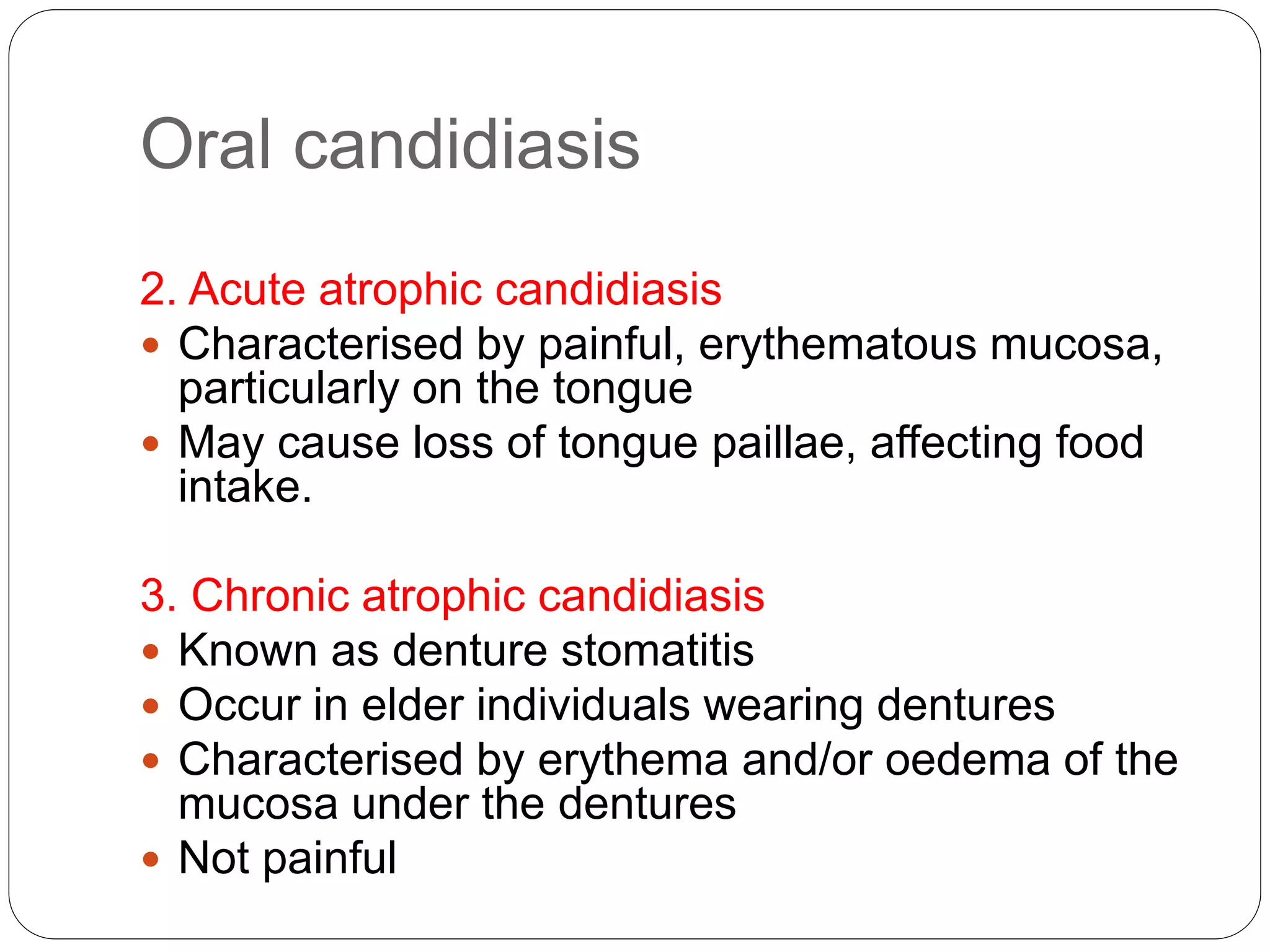
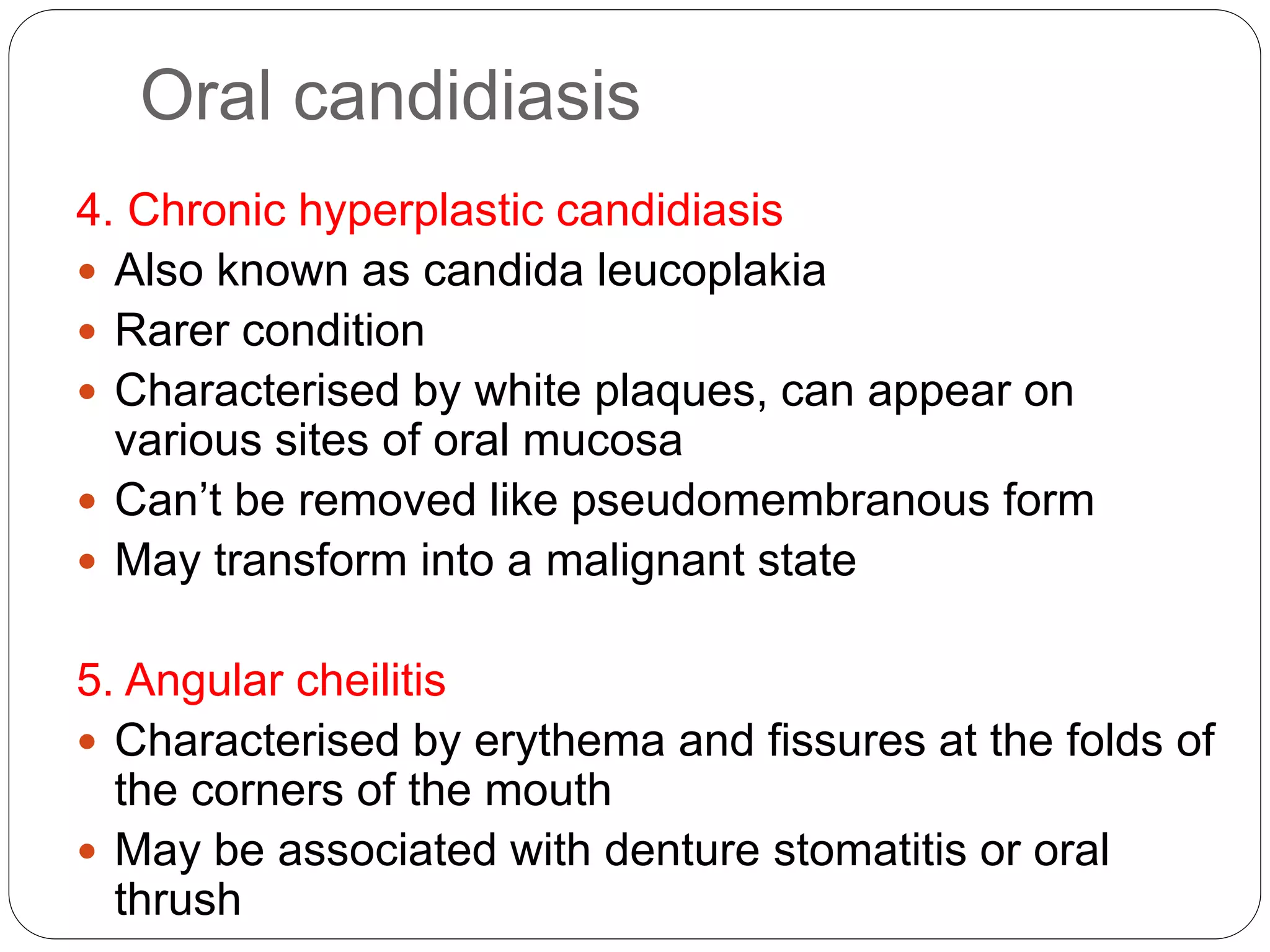
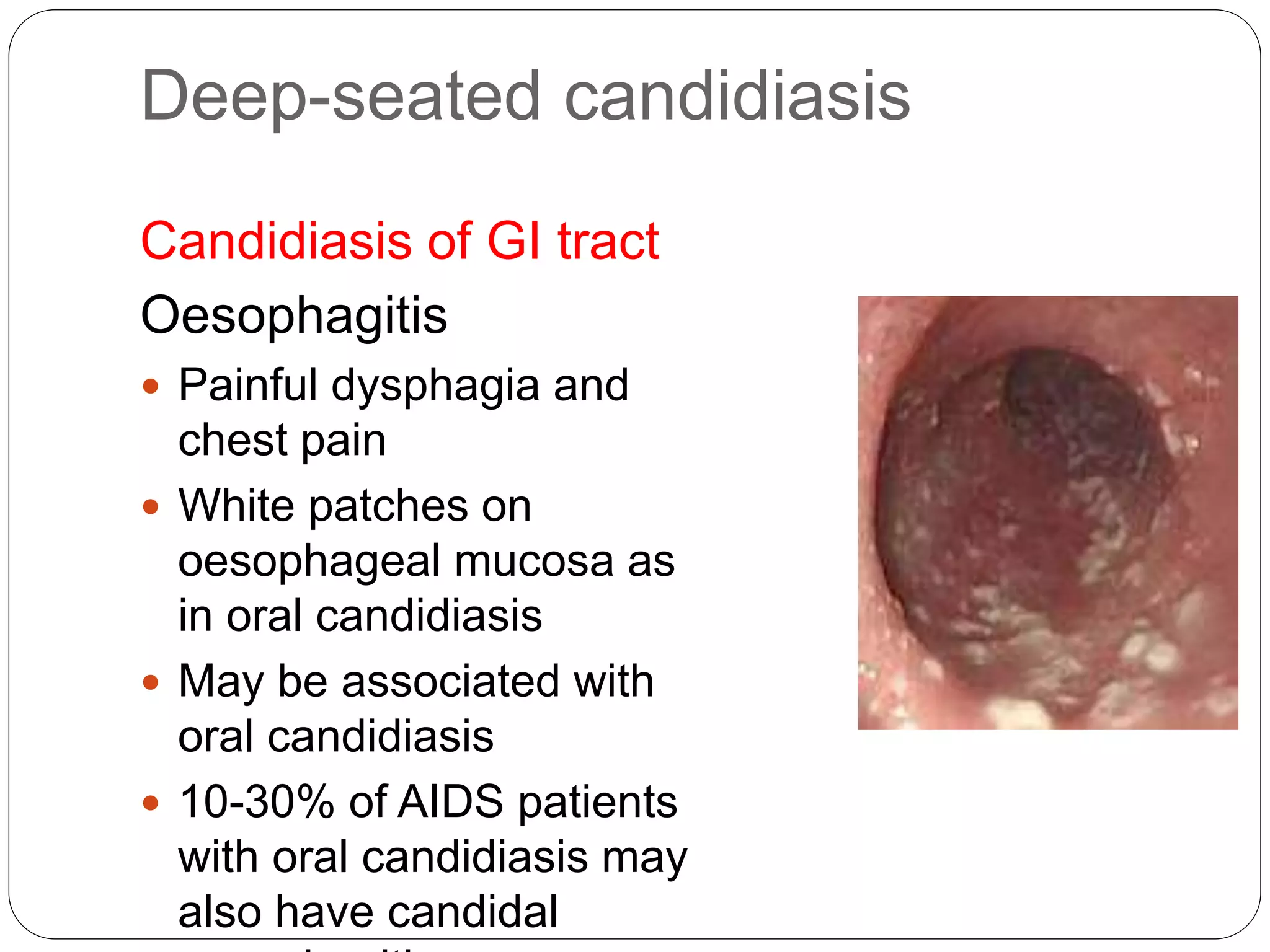
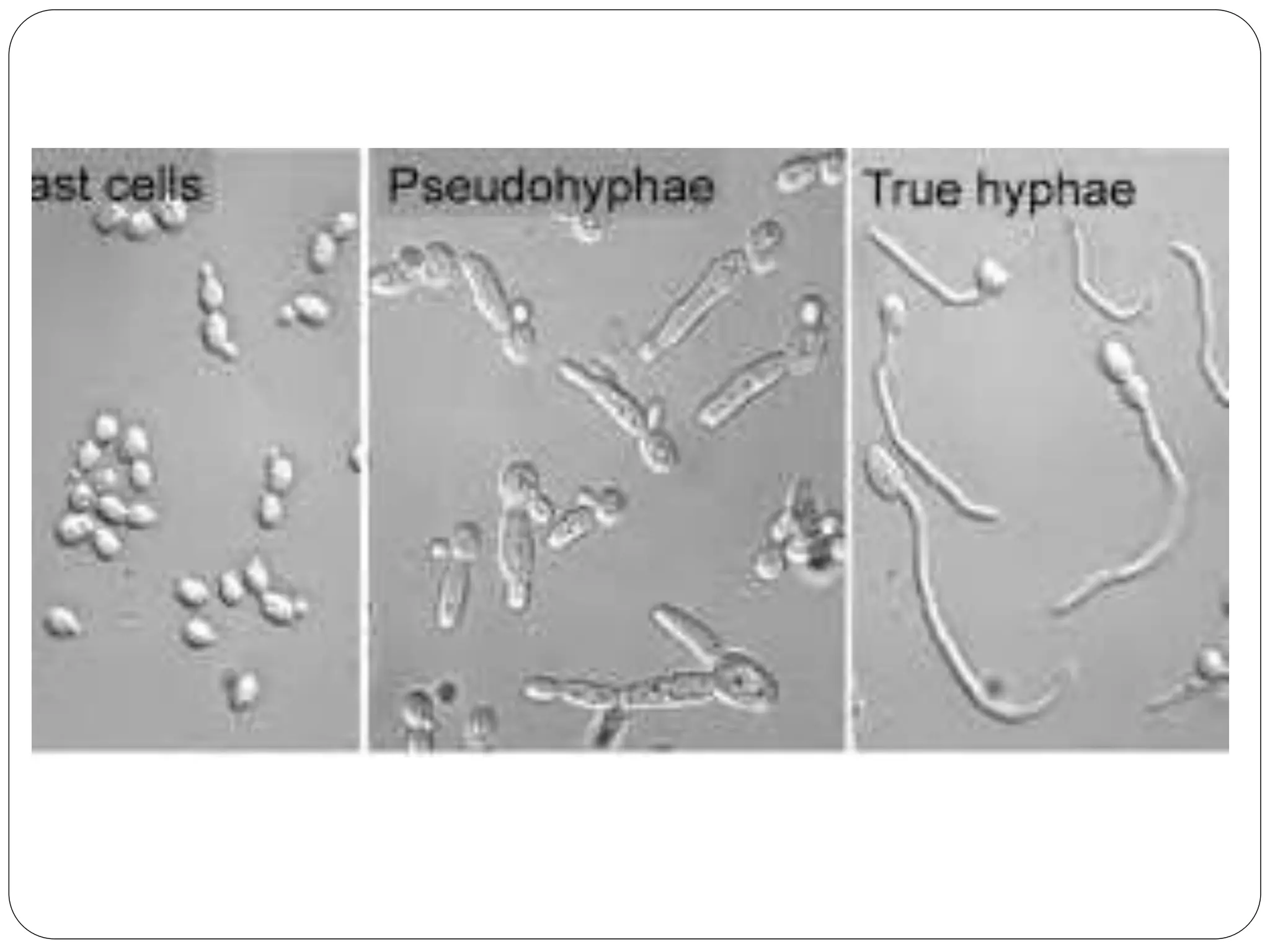
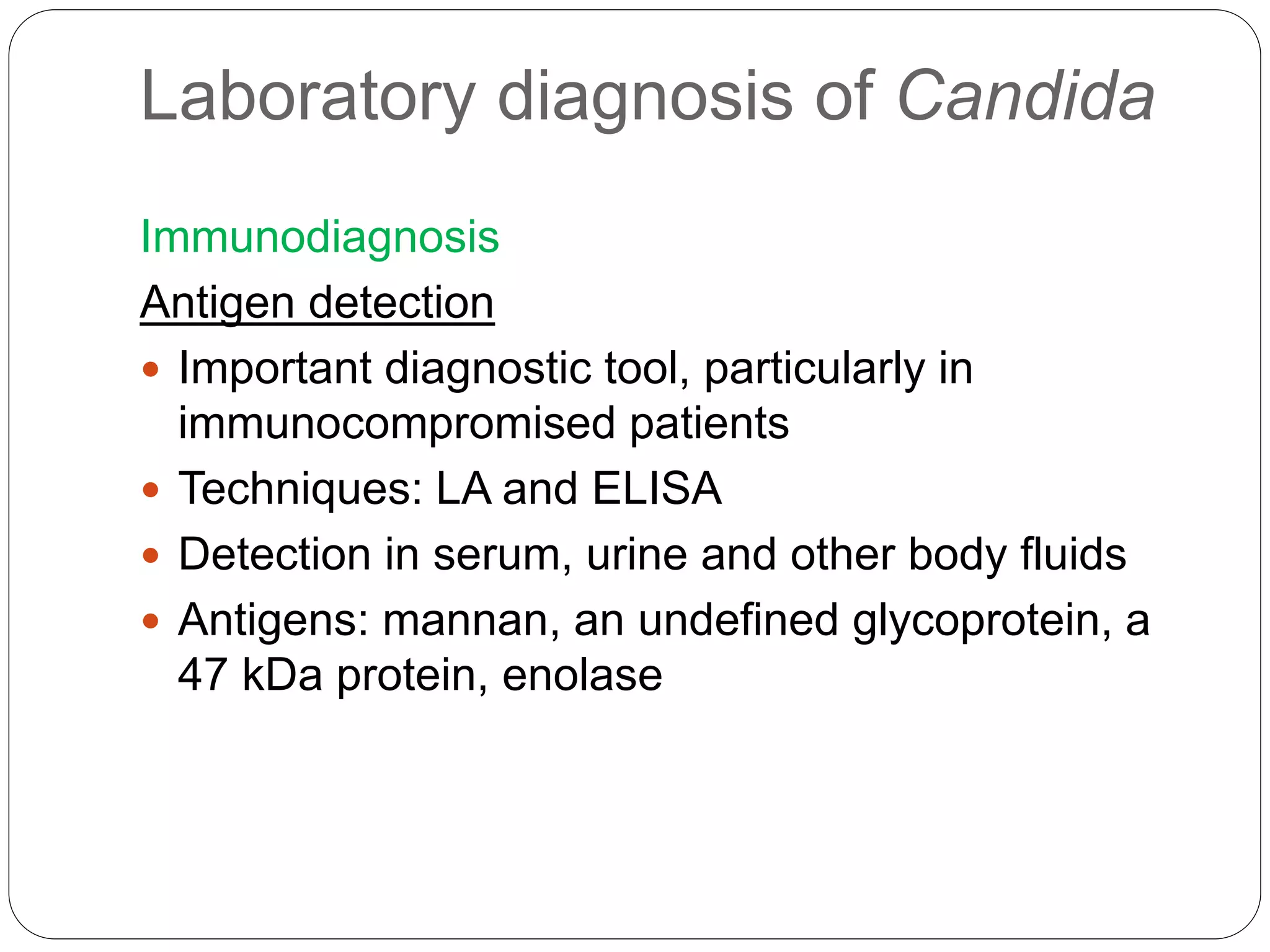
This document discusses the fungus Candida. It notes that Candida includes approximately 200 species, about 20 of which can cause infections in humans. C. albicans is the most common cause of infection. Candida is normally found in the gastrointestinal tract but can cause superficial or deep infections. Superficial infections include oral and vaginal candidiasis. Deep infections involve organs and can become disseminated. Virulence factors that enable Candida pathogenesis include adhesion, dimorphism, and production of enzymes. Laboratory diagnosis involves direct microscopic examination of samples and culture isolation followed by identification of Candida species.