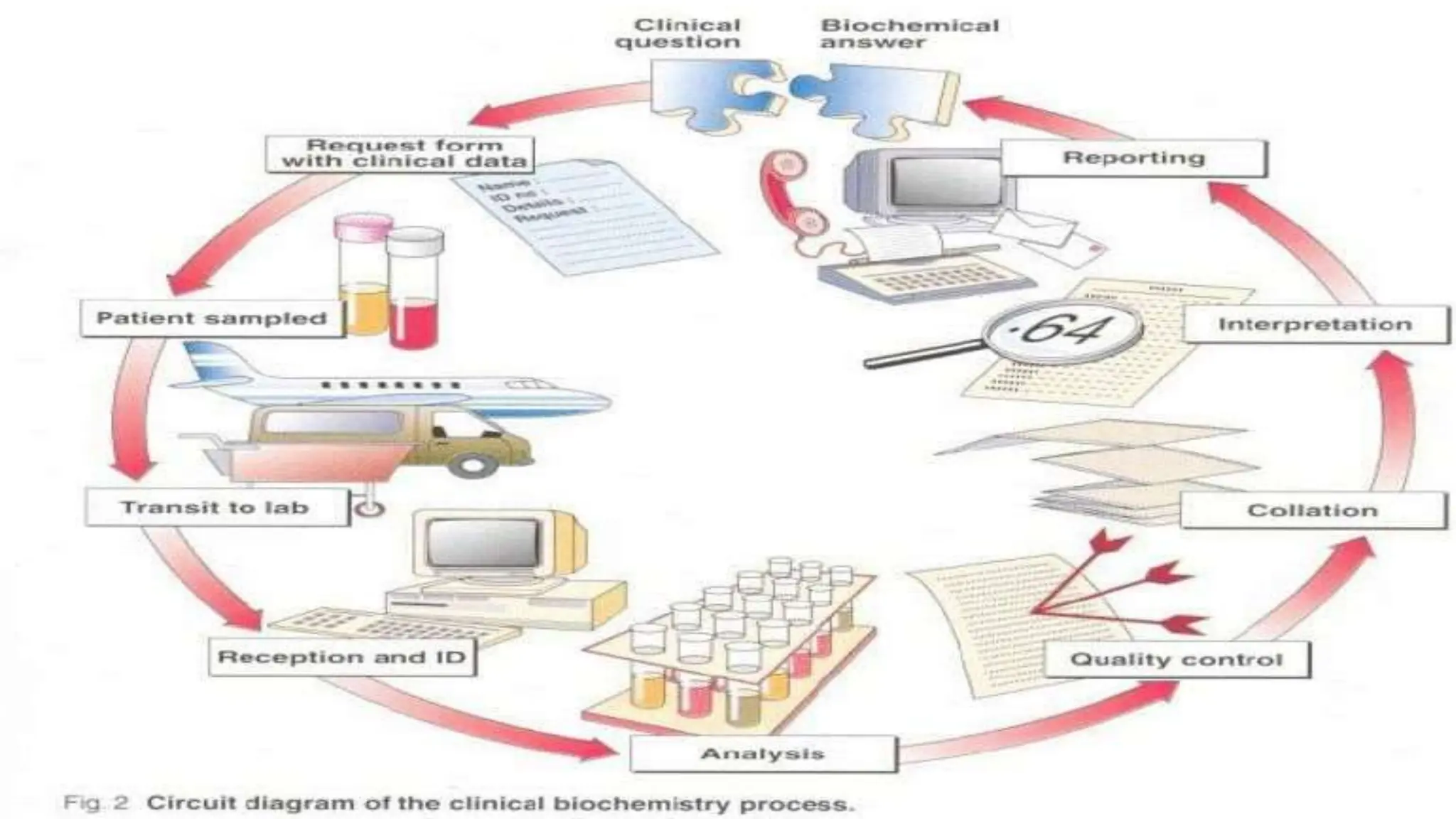
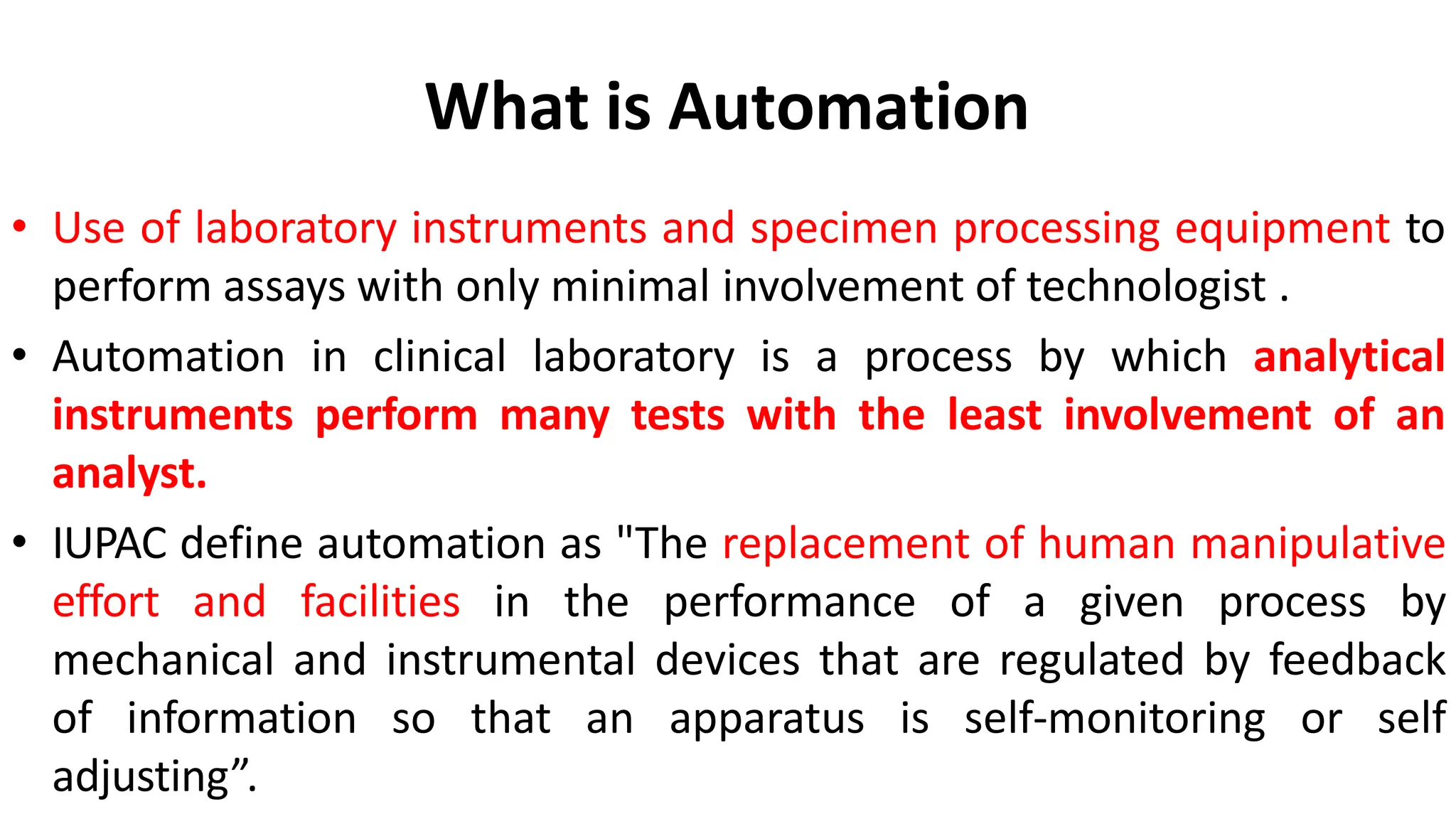
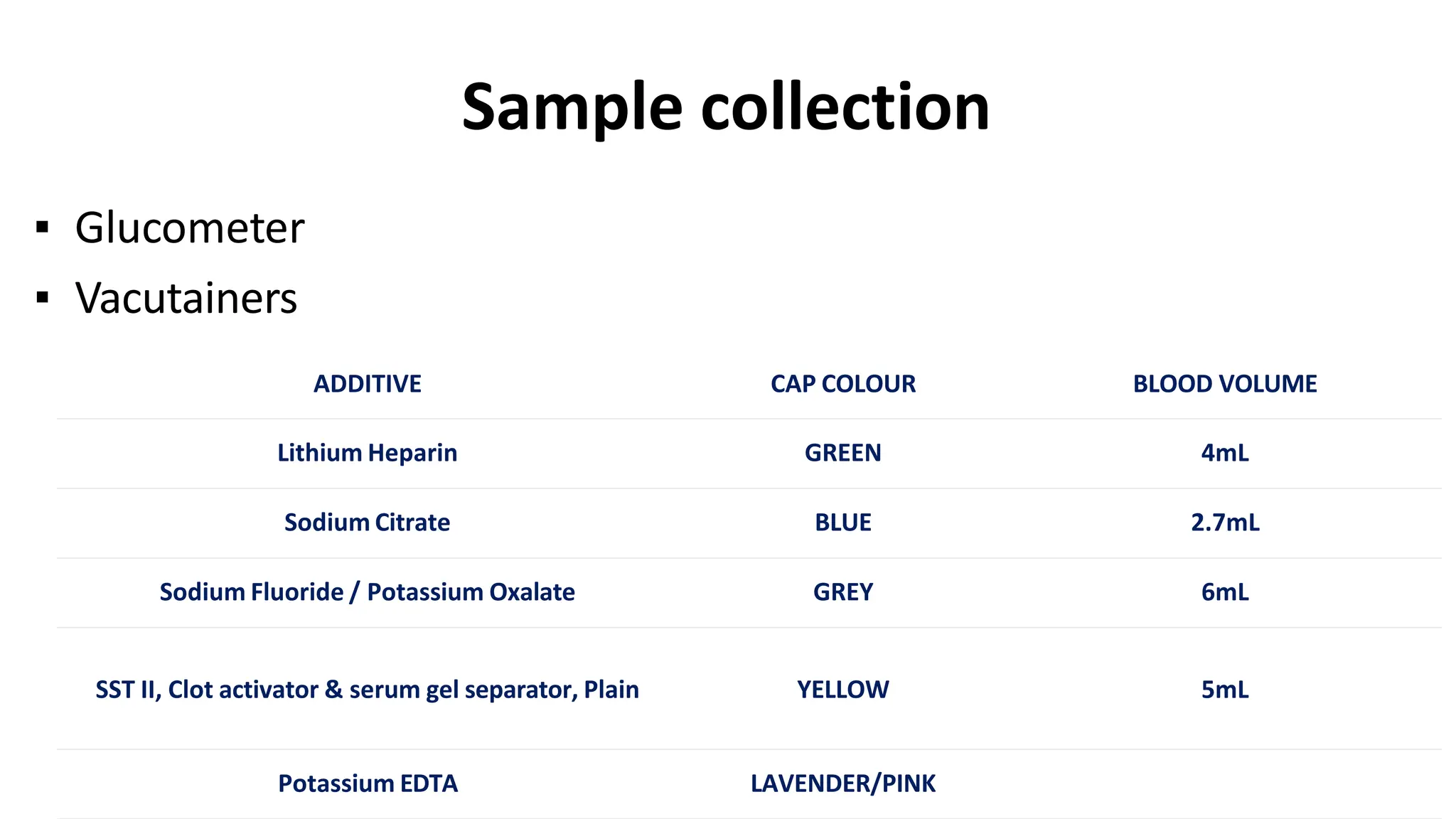
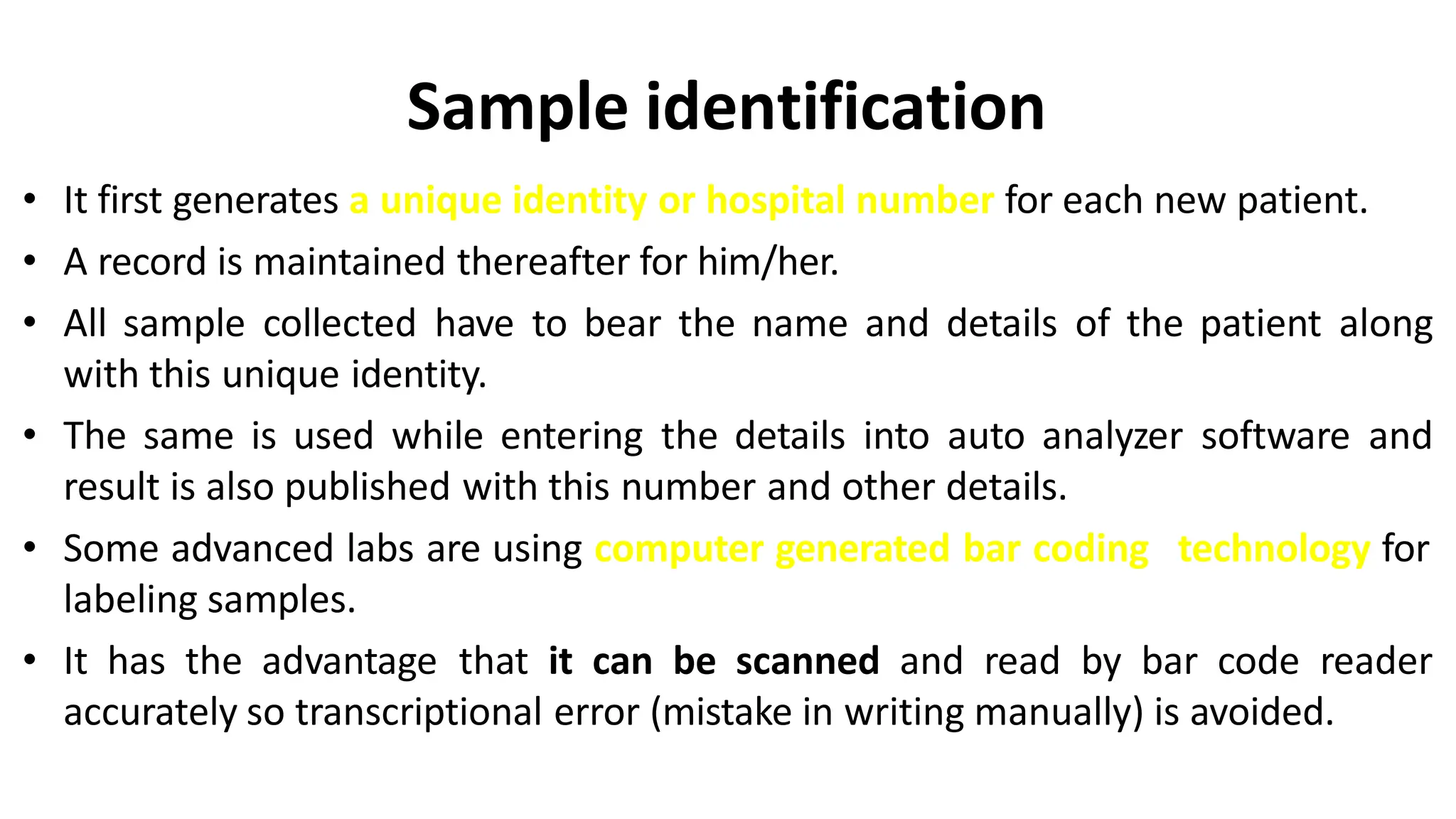
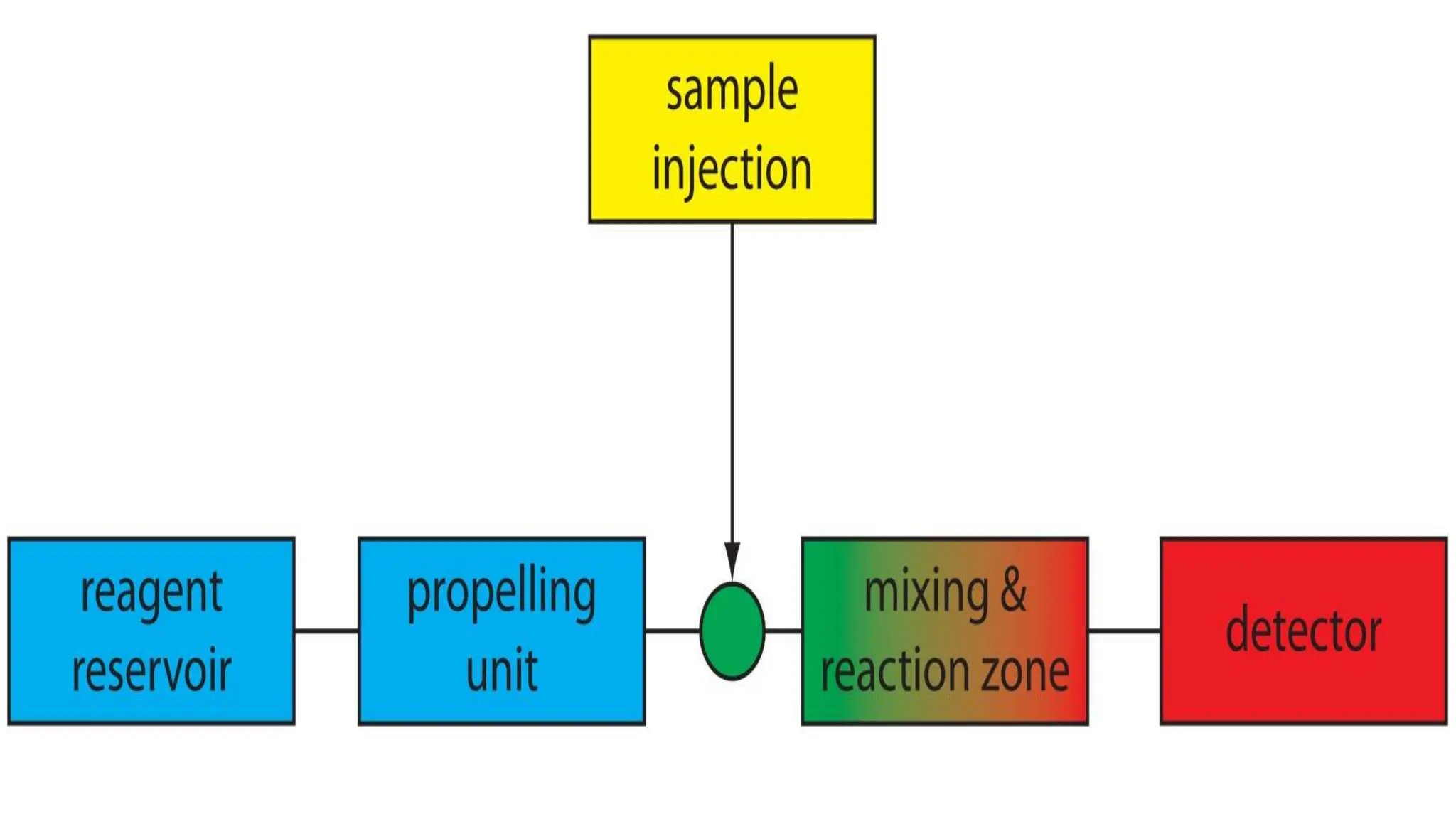
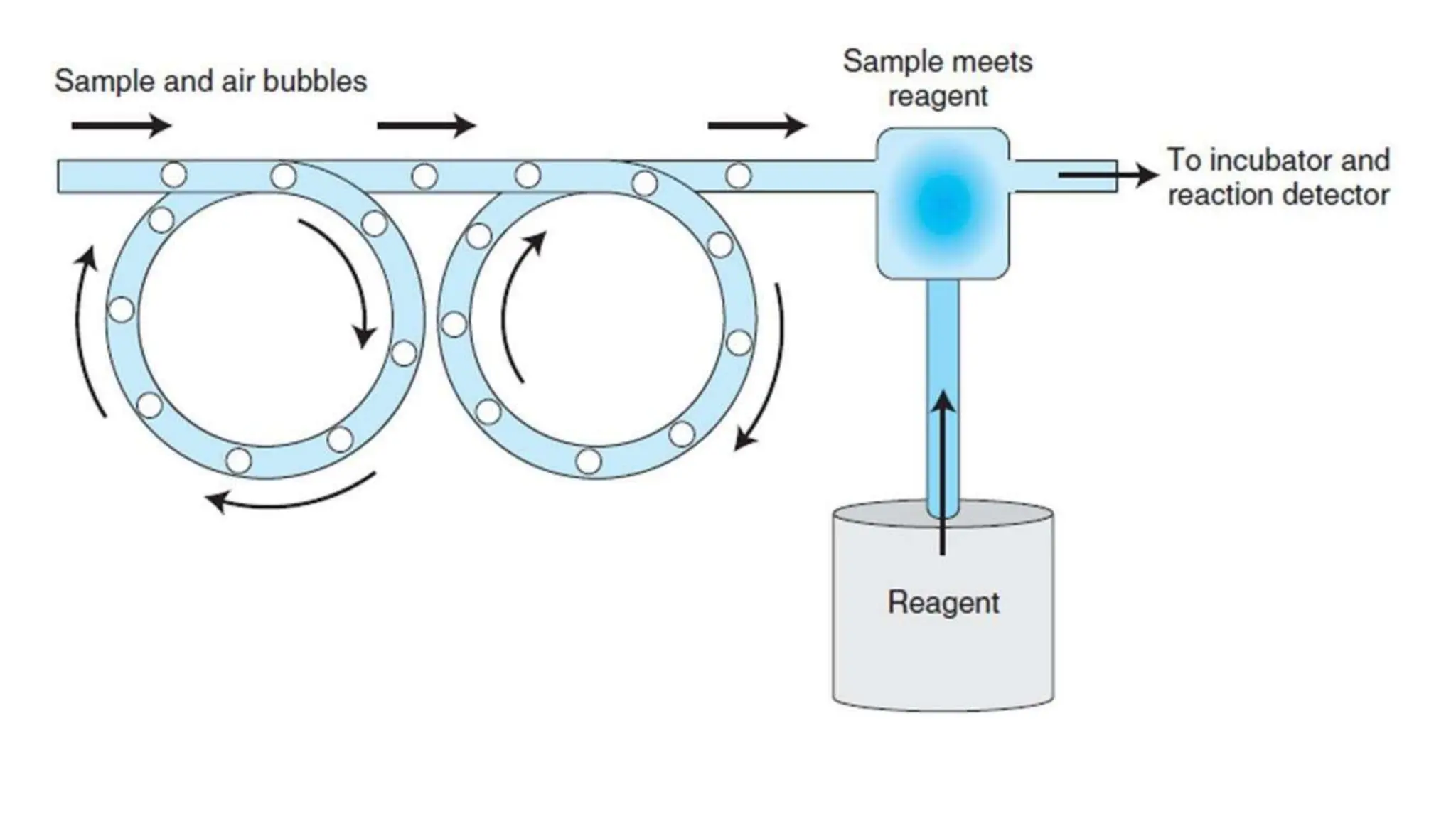
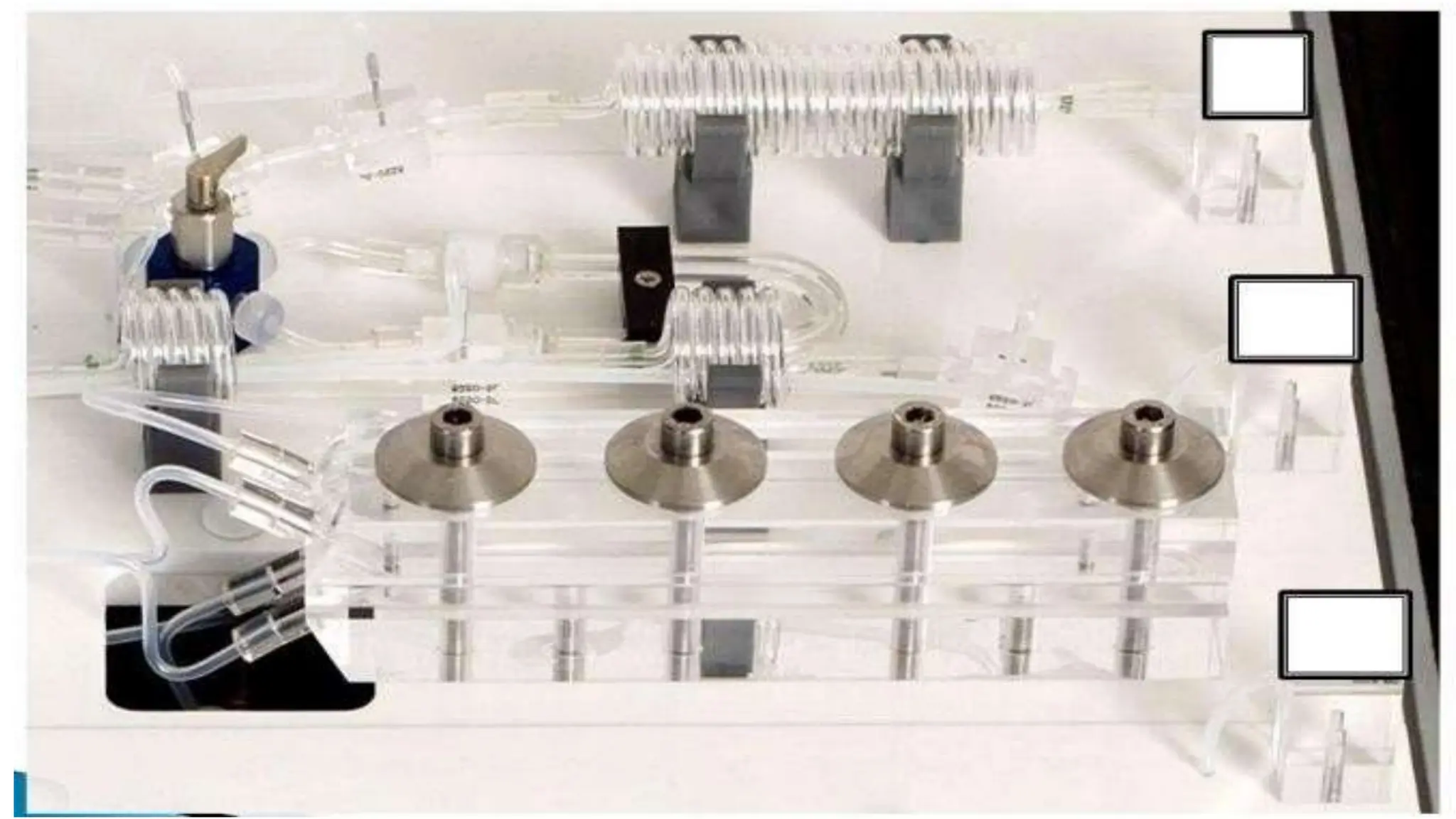
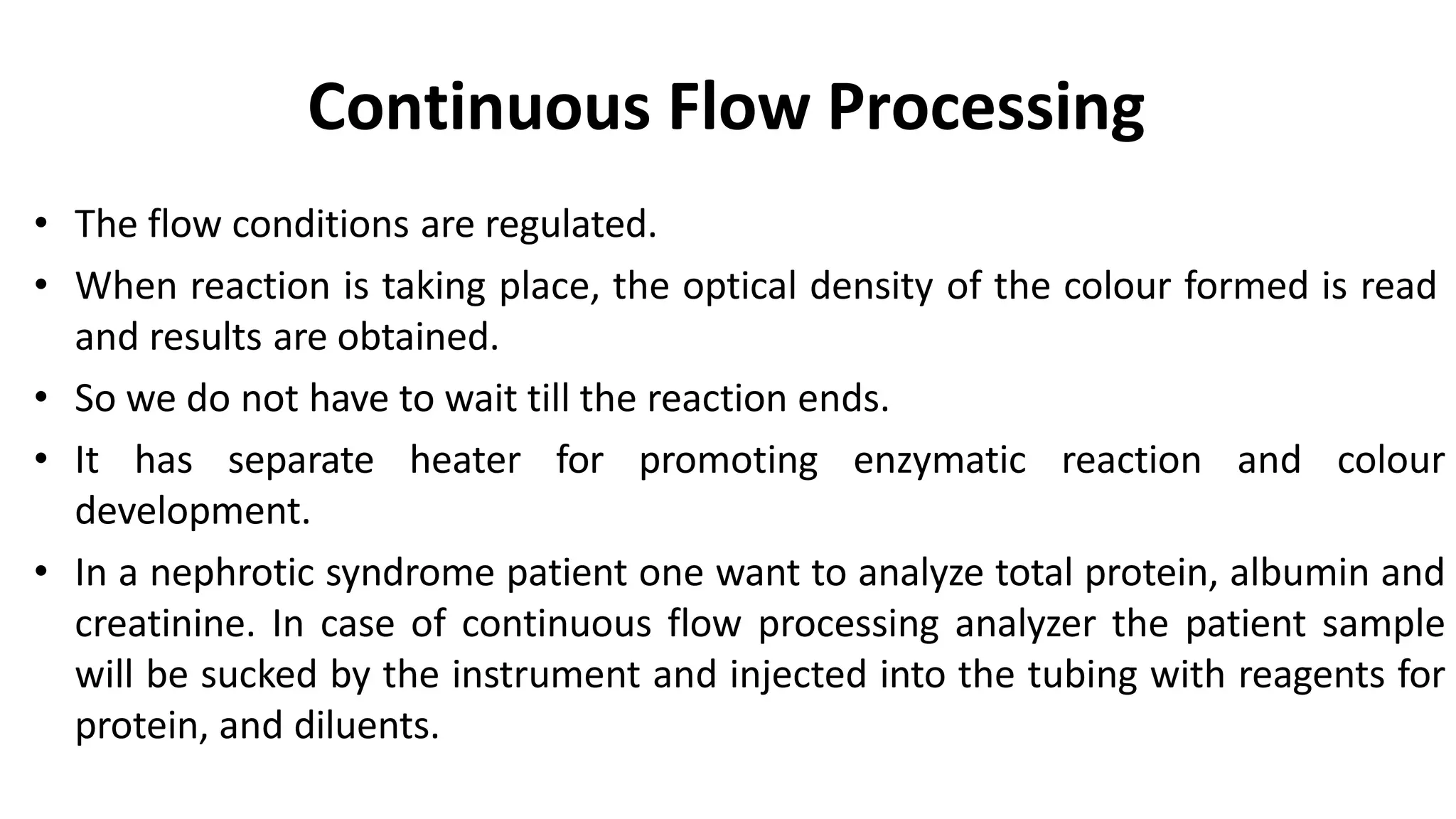
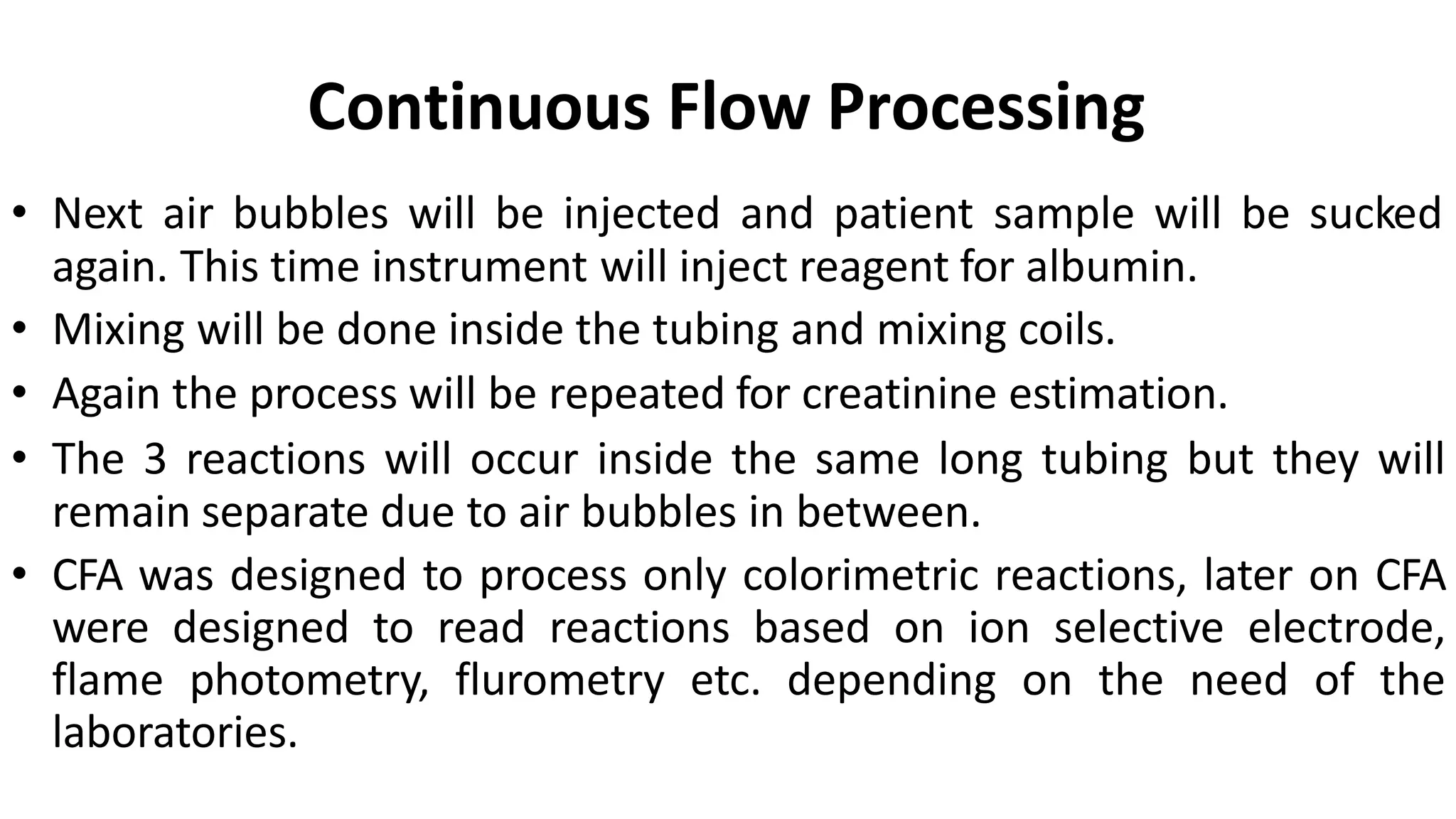
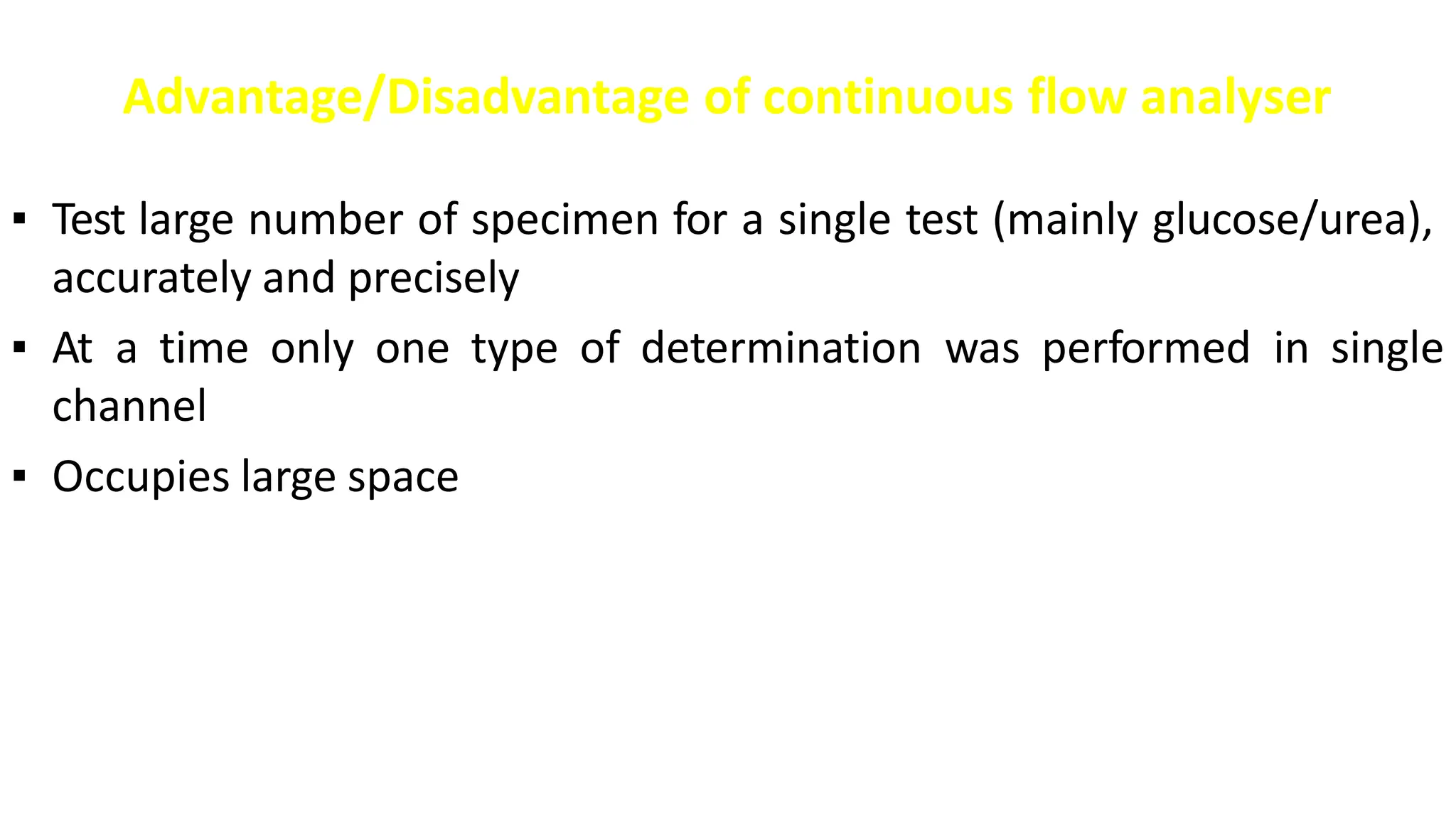
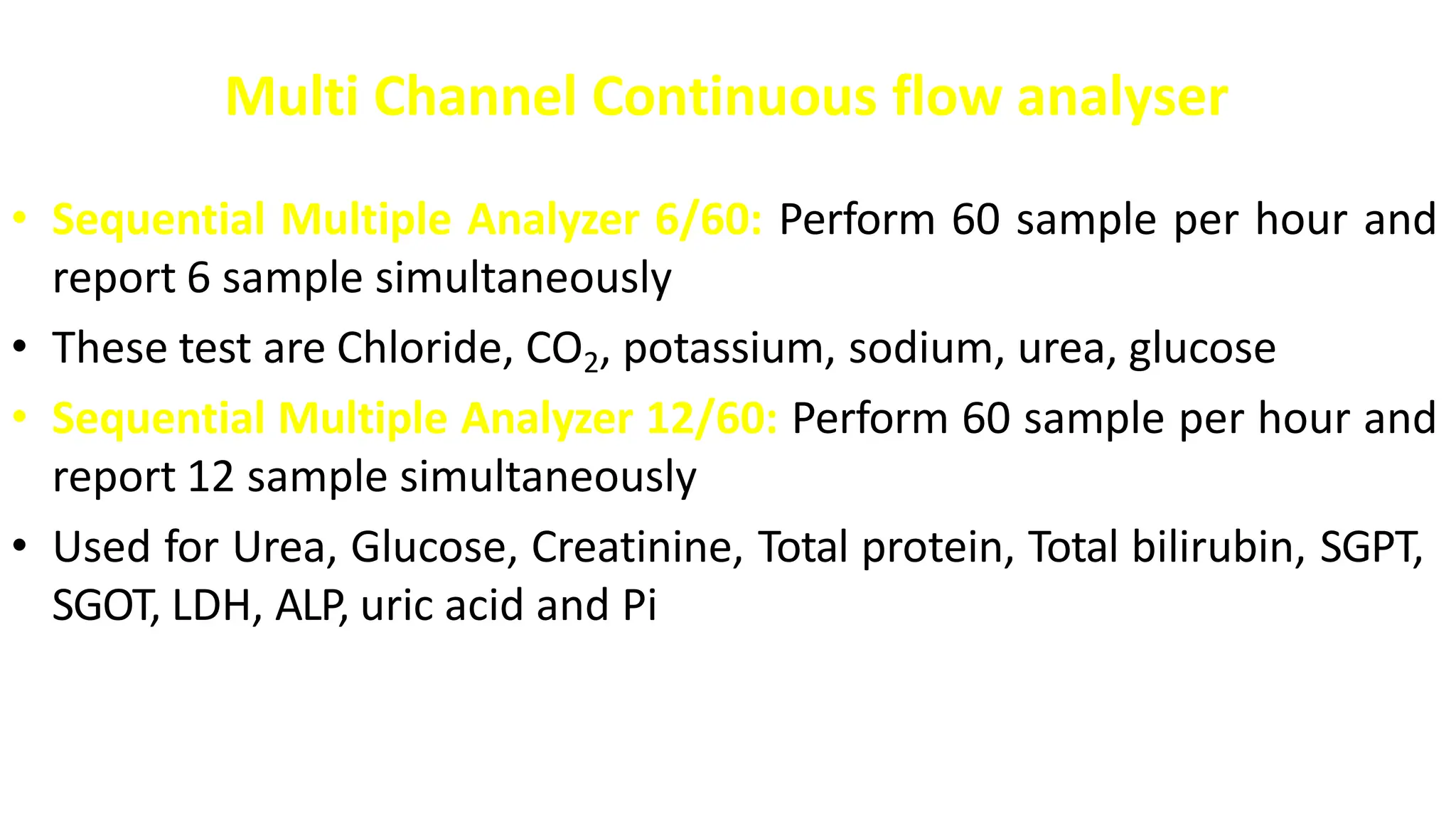
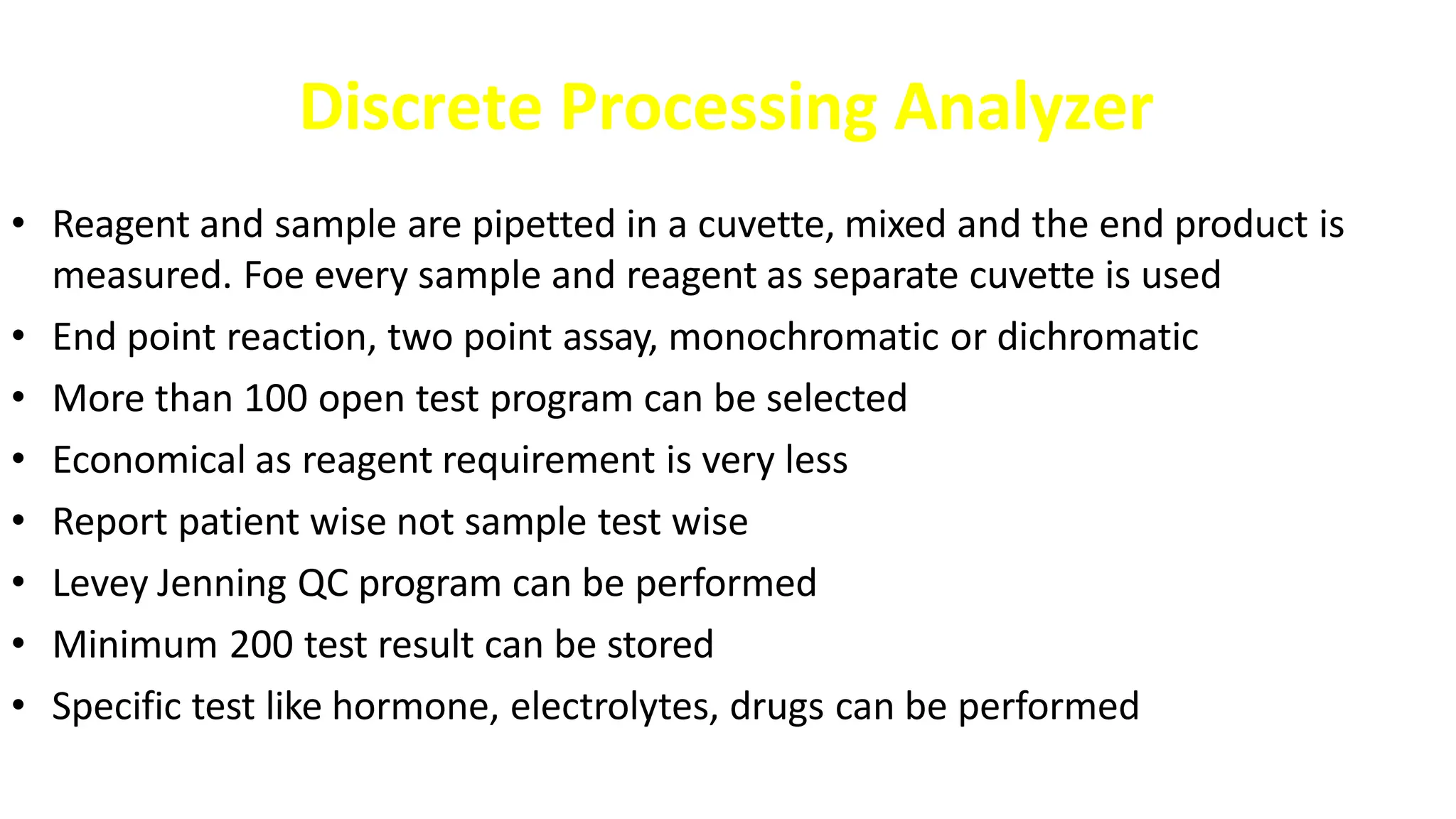
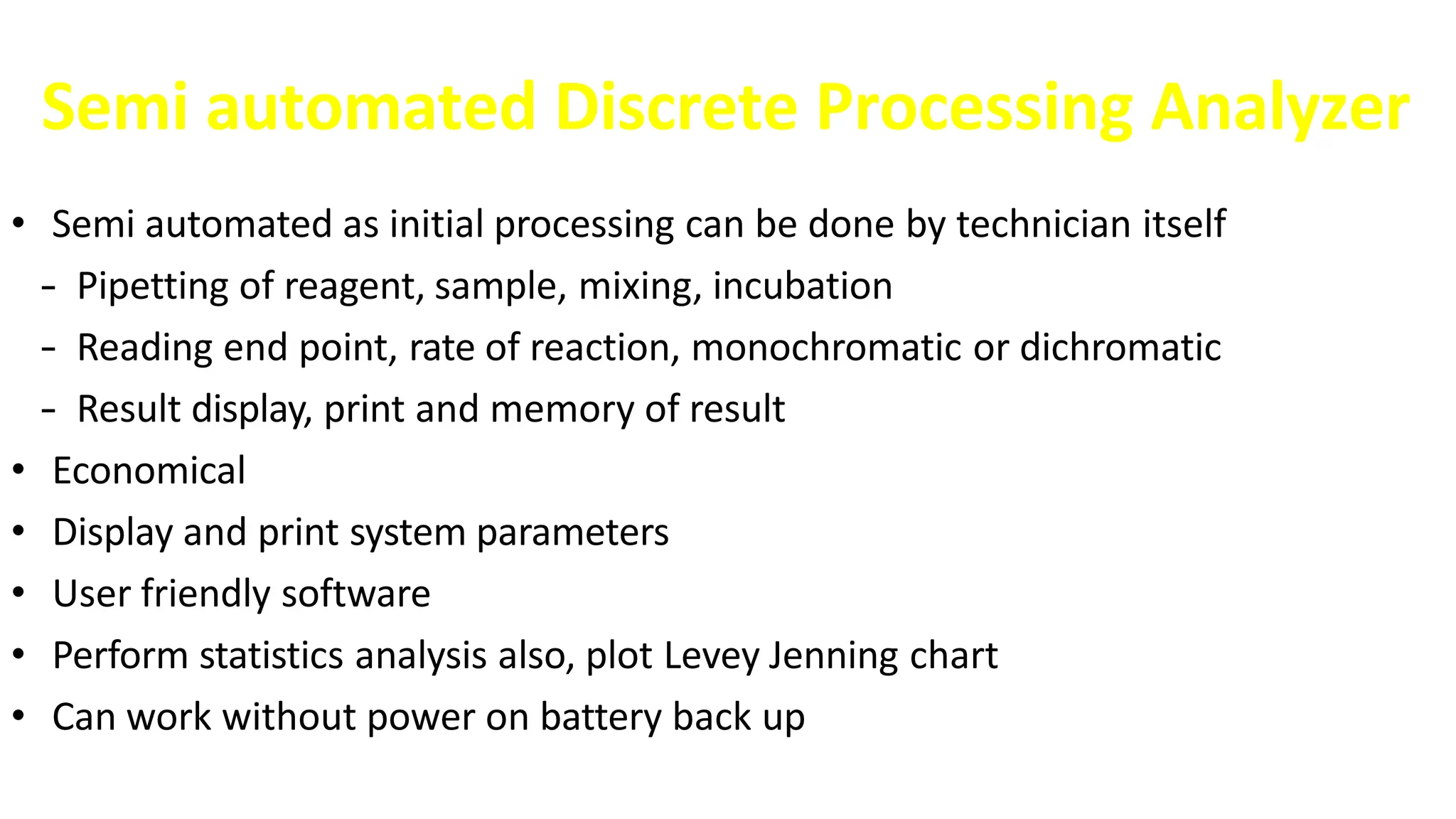
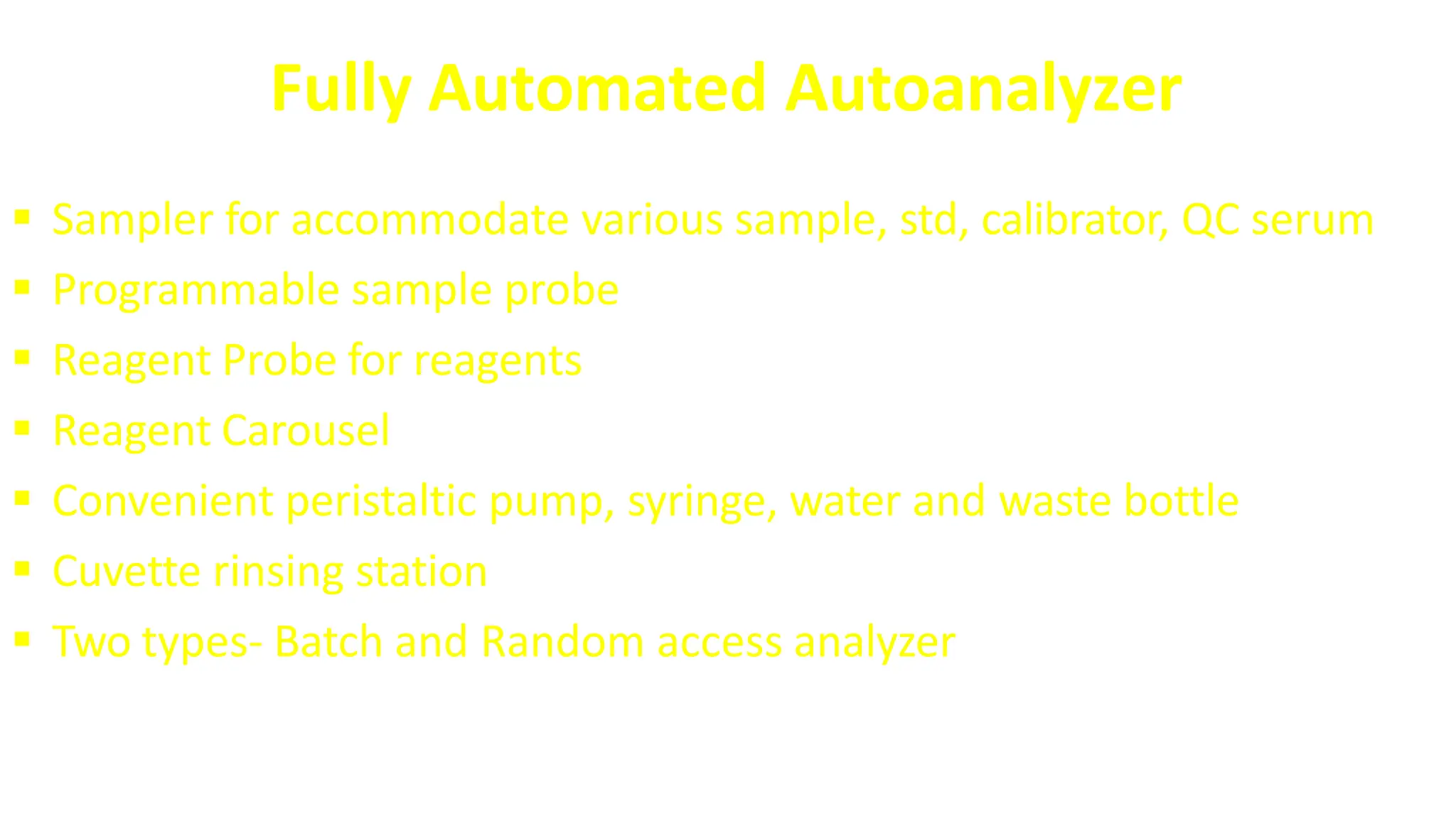
Automation in clinical biochemistry provides several benefits such as reducing workload, increasing throughput, improving accuracy, and eliminating human error. There are various steps in automated analysis including sample collection, identification, delivery, preparation, and analysis. Automation uses laboratory instruments and equipment to perform assays with minimal human involvement. Common types of automated analyzers are continuous flow analyzers, discrete analyzers, batch analyzers, and random access analyzers. Automation allows for processing of larger sample volumes and multiple tests per sample.