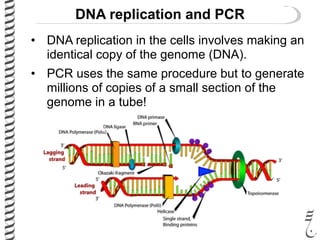
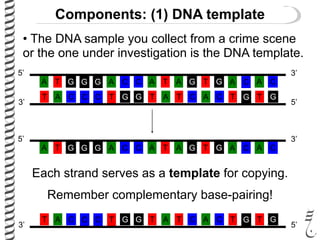
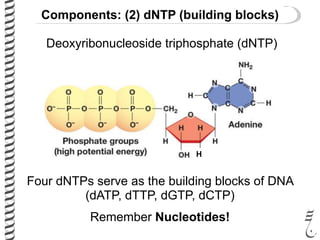
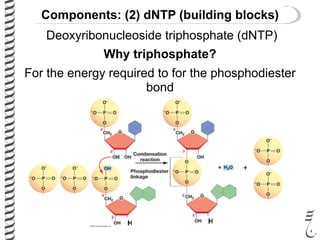
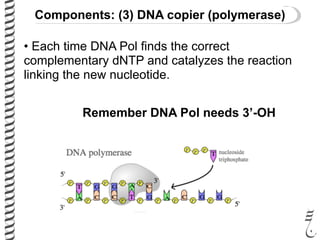
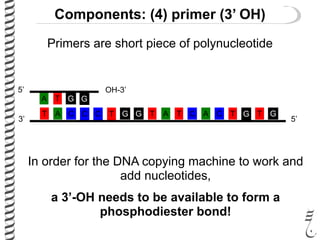
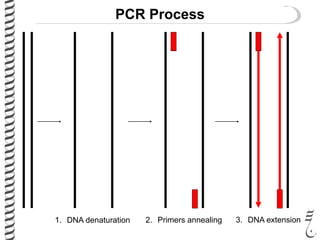
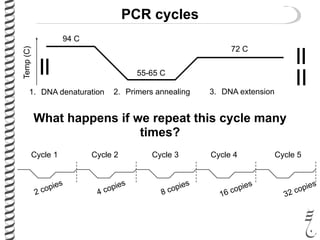
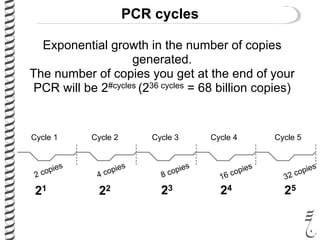
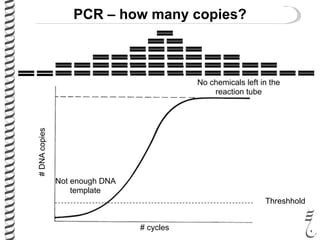
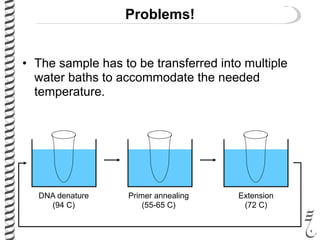
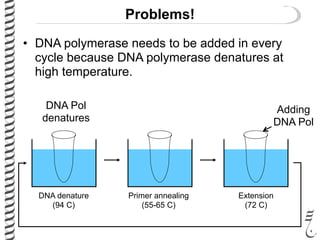
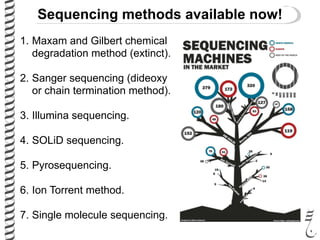
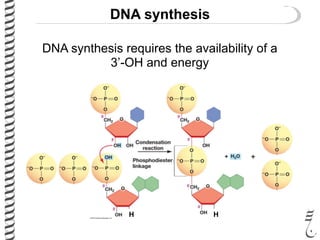
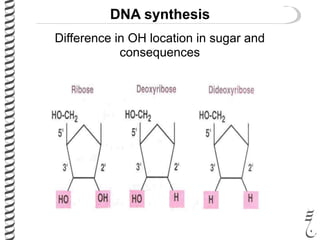
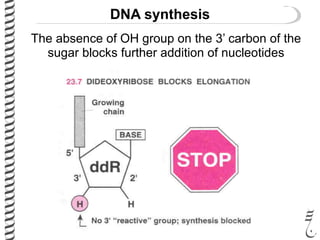
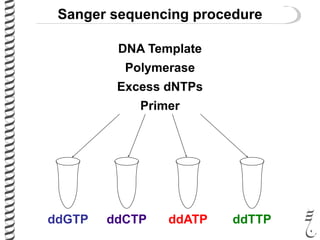
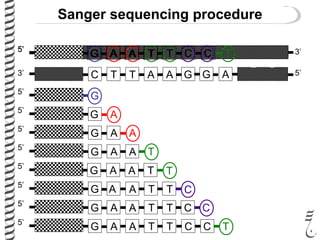
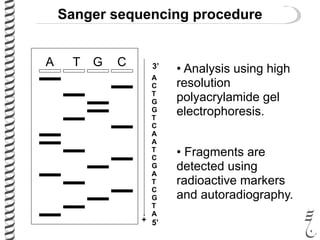
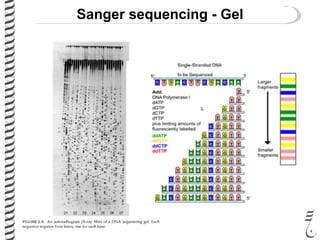
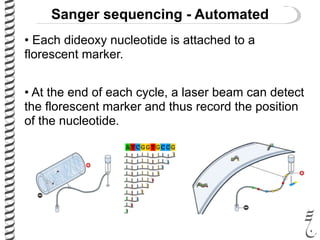
PCR allows for the amplification of small amounts of DNA, generating millions of copies. It involves three steps - denaturation of the DNA template, annealing of primers, and extension of the primers by DNA polymerase. Repeating this process results in exponential growth in the number of DNA copies. DNA sequencing, such as the Sanger method, is used to determine the exact order of nucleotides in a DNA fragment and can be used to map genomes and detect genetic variations.