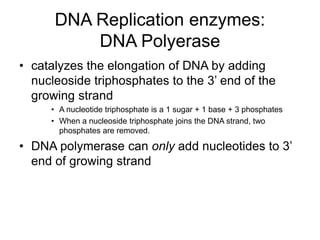
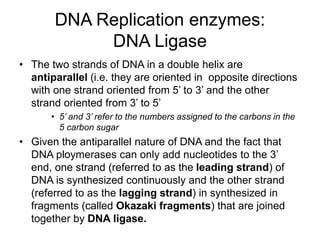
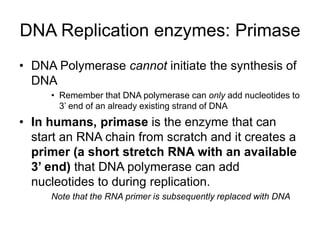
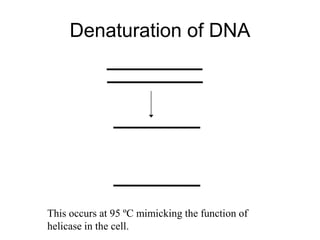
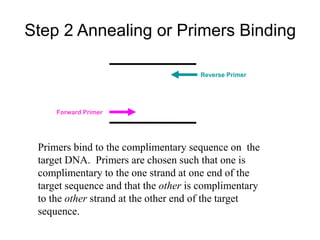
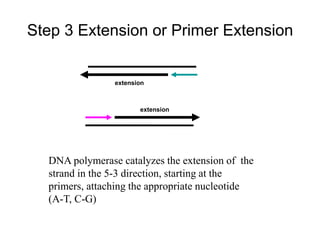
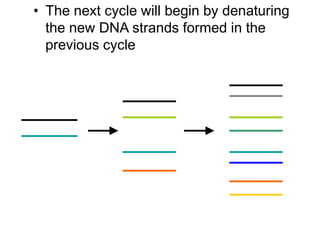
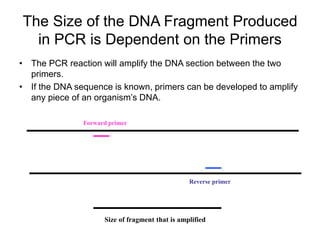
PCR is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA across multiple cycles. It involves separating the DNA strands through heating, followed by primers annealing to the complementary DNA sequences. The DNA polymerase then extends the strands to exponentially increase copies of the target DNA. PCR has many applications in molecular biology, forensics, disease diagnosis and more due to its ability to amplify very small amounts of DNA.