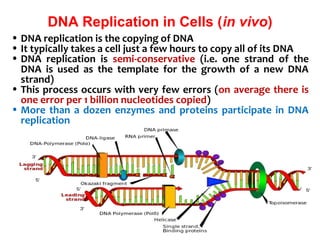
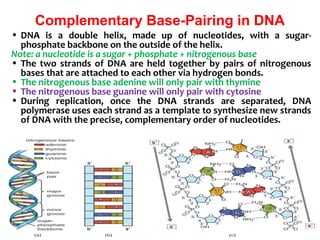
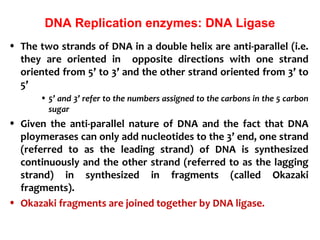
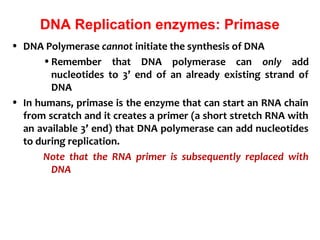
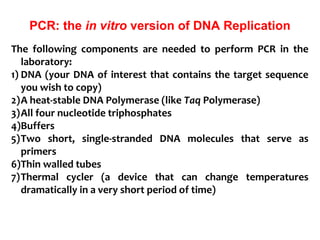
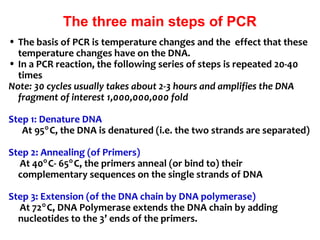
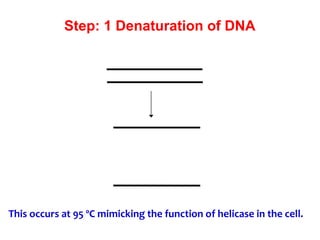
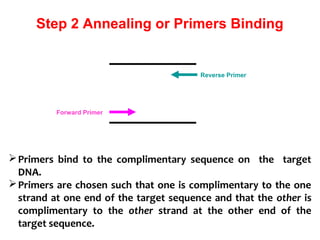
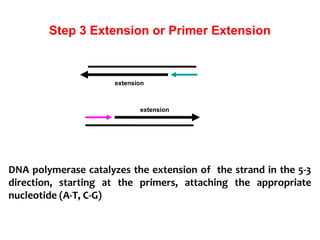
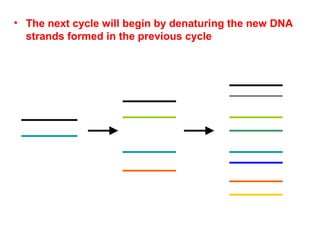
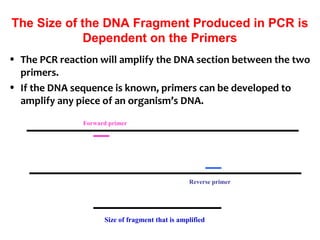
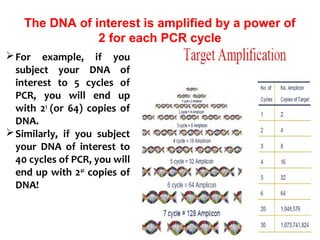
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA. It involves repeated cycles of heating and cooling of the DNA sample in the presence of DNA polymerase and primers to generate millions of copies of the target sequence. PCR has many applications in molecular biology, biotechnology, and forensic science. It can be used to detect genetic diseases, identify pathogens, and generate unique DNA profiles for individual identification.