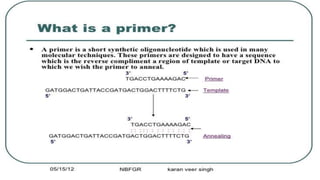
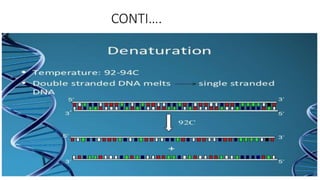
Habib U Rahman presents on PCR (polymerase chain reaction), a technique used to amplify a specific segment of DNA. PCR involves three main steps: 1) denaturation to separate DNA strands at high temperature (94C for 1 minute), 2) annealing to attach primers at lower temperature (55C for 45 seconds), and 3) extension where Taq polymerase synthesizes new strands at 72C for 1-2 minutes. PCR is useful for replicating small amounts of DNA for further testing and analysis in molecular biology applications.