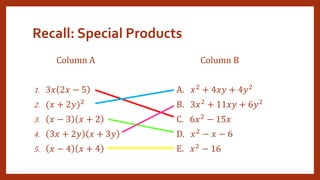
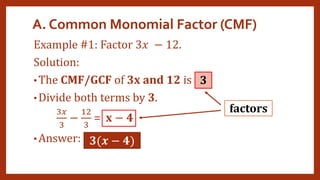
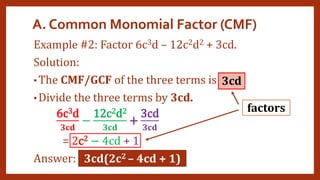
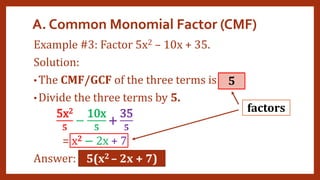
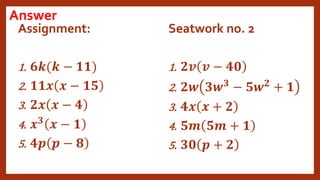
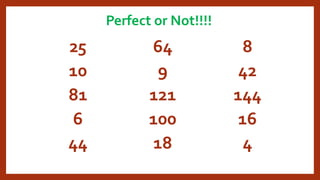
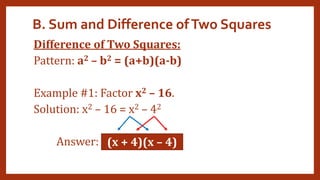
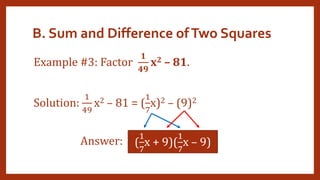
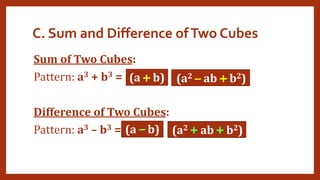
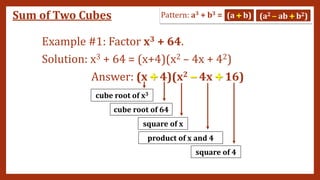
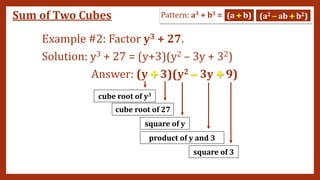
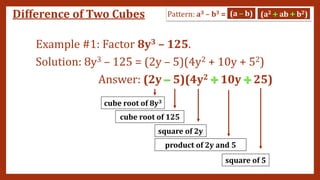
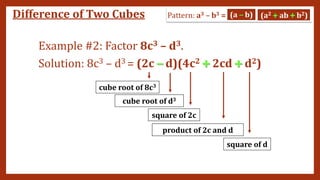
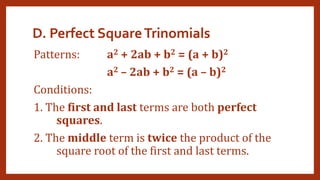
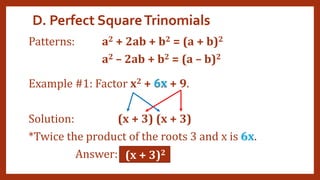
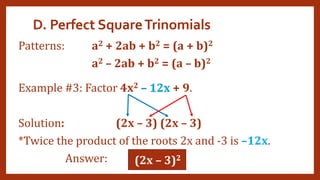
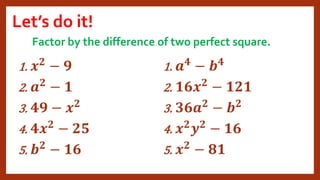This document provides instruction on factoring polynomials. It covers several factoring methods including common monomial factoring, difference of squares, sum and difference of cubes, perfect square trinomials, and general trinomials. Examples are provided for each method. The objectives are to determine appropriate factoring methods, factor polynomials completely using various techniques, and solve problems involving polynomial factors.