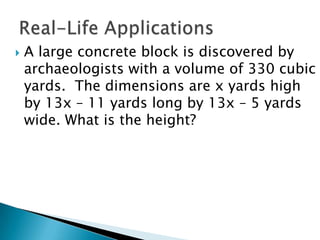
The document provides examples and instructions for factoring polynomials of various types, including:
- Trinomials like x^2 - 5x - 12
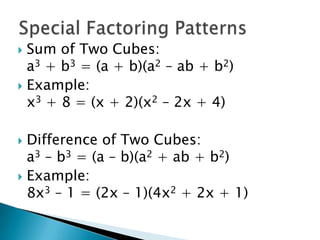
- Sum and difference of cubes like x^3 + 8 and 8x^3 - 1
- Polynomials with a common monomial factor like 6x^2 + 15x
- Quadratics in the form of au^2 + bu + c
It also discusses using the zero product property to solve polynomial equations by factoring and setting each factor equal to zero.