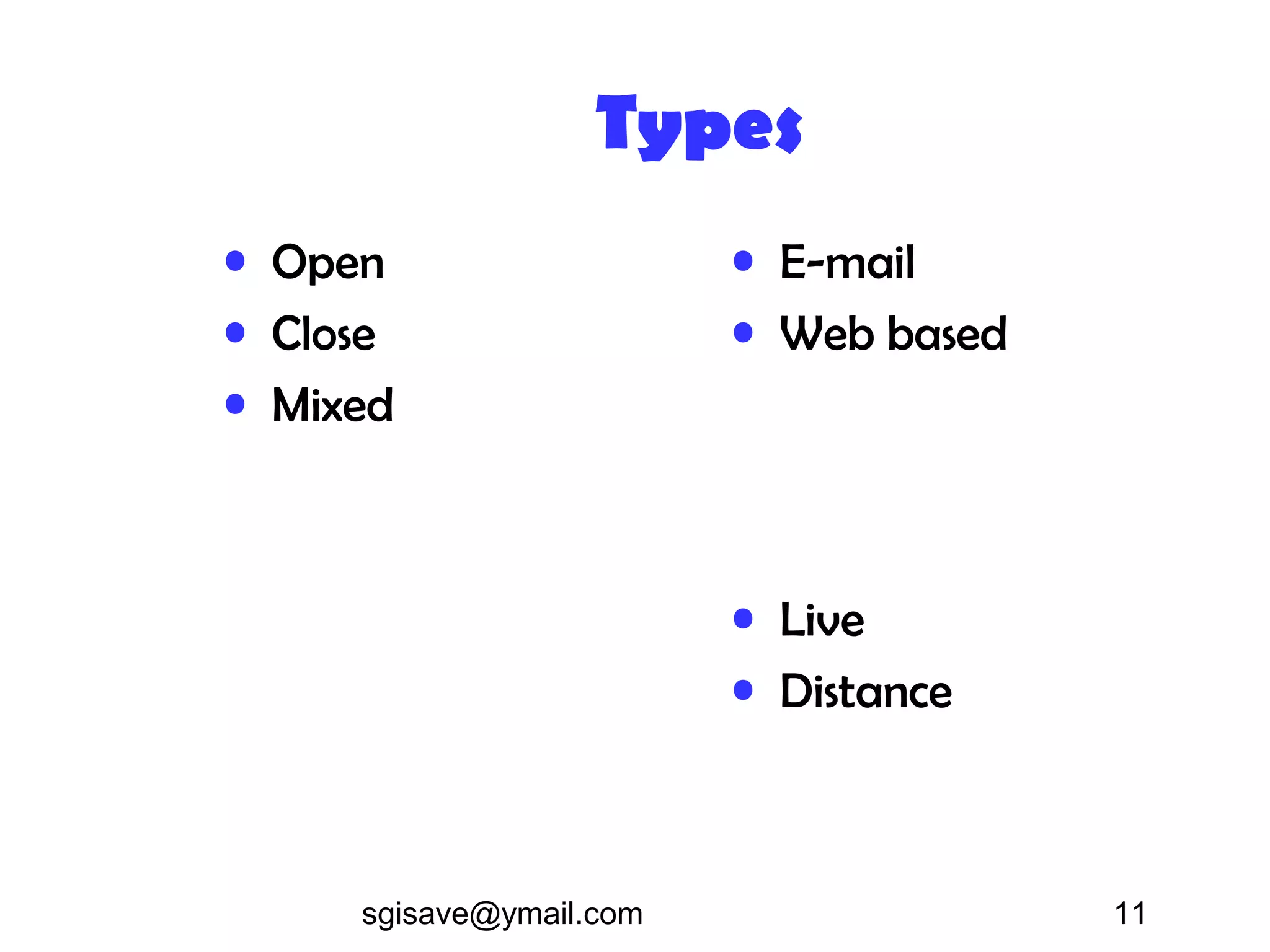
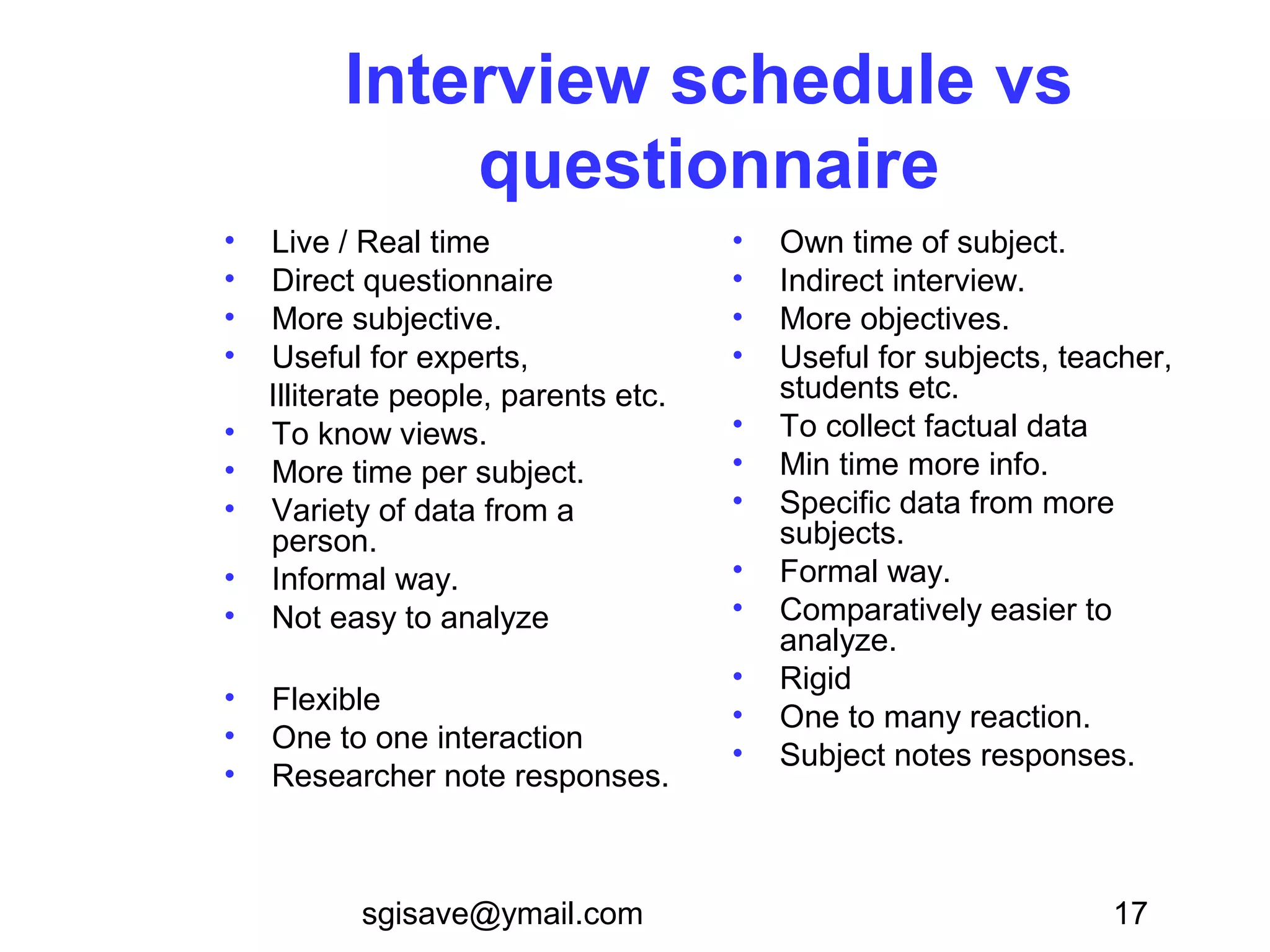
The document discusses various tools for data collection, including interview schedules and questionnaires, highlighting their definitions, types, advantages, and limitations. It also compares these methods, emphasizing their different applications and the contexts in which they are most effective. Additionally, it provides guidance on interview conduct and questionnaire development while touching on observational research methods.