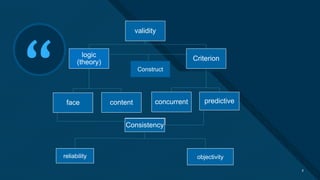
The document is a presentation on validity and its various types within the context of classroom assessment, presented by a student named Bibi Nadia. It discusses definitions of validity, including face validity, content validity, criterion validity (with subtypes of concurrent and predictive validity), as well as internal and external validity, highlighting the importance of measurement accuracy in education. The presentation is aimed at educating about the credibility and appropriateness of assessment tools in measuring intended outcomes.