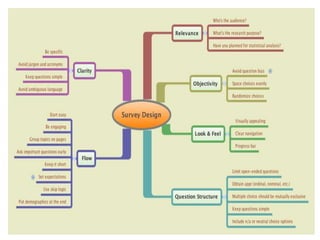
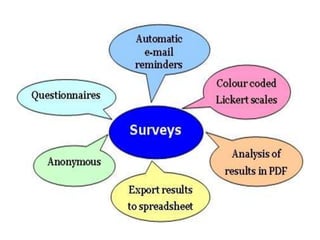
This document discusses survey research design. It defines survey research as collecting information from subjects within a population using questionnaires or interviews. Surveys can study either a sample of the population or the entire population. The document outlines different types of surveys, including descriptive surveys that describe phenomena, exploratory surveys of unknown factors, correlational surveys that study relationships between variables, and comparative surveys that compare groups. It also discusses methods of survey data collection, such as written questionnaires, oral interviews, and electronic methods like email or mobile messages.