The document outlines the 10 key steps in the research process:
1. Selecting a research topic and defining the problem.
2. Specifying the research objectives.
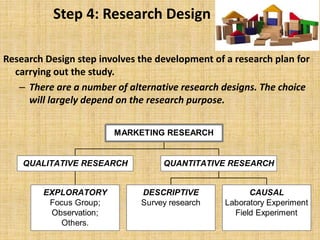
3. Developing a research design and determining what information is required.
4. Designing methods to collect primary and secondary data, such as through surveys.
5. Analyzing and interpreting the results to draw conclusions.
6. Preparing a final research report to communicate the findings to clients.