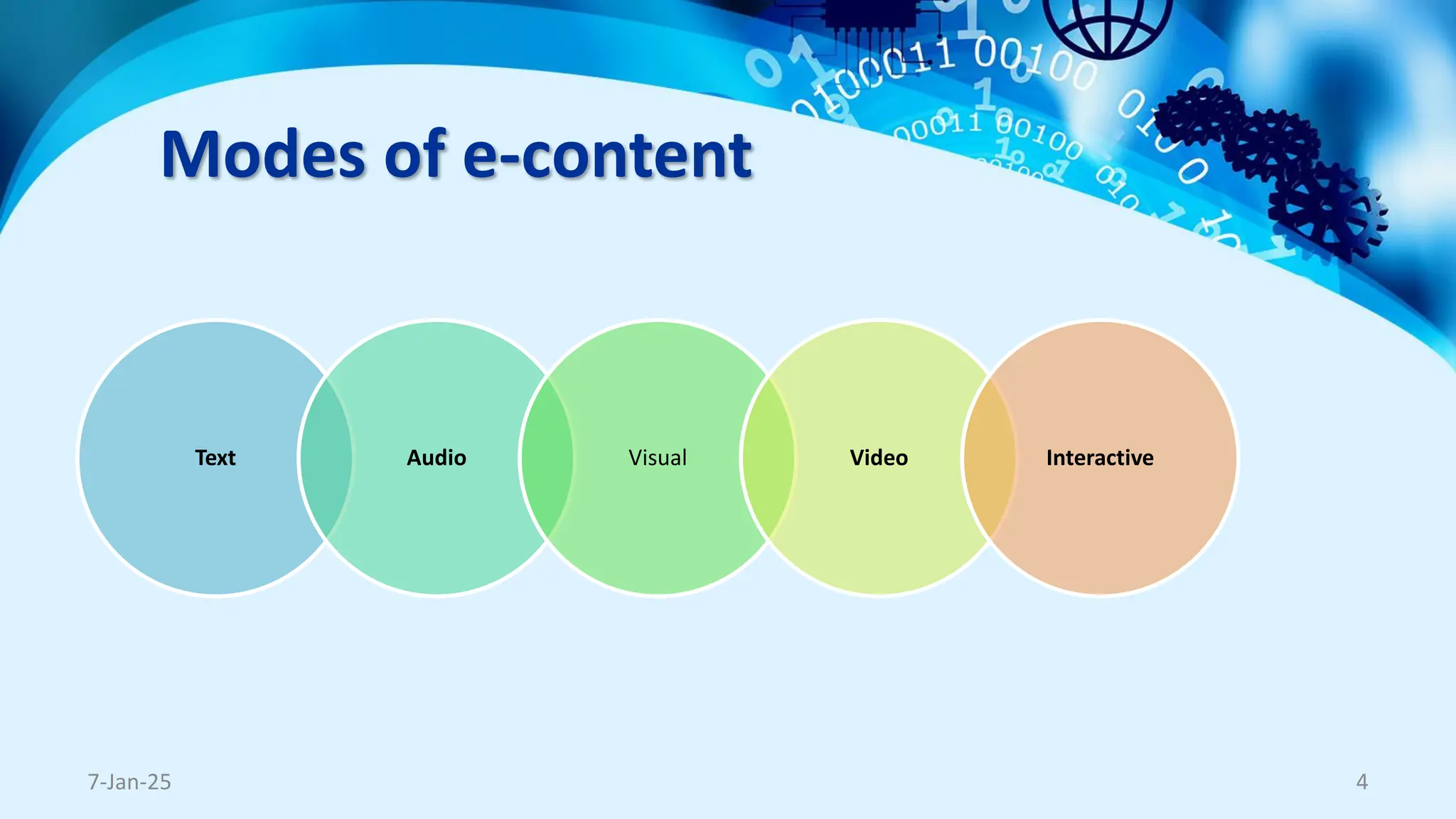
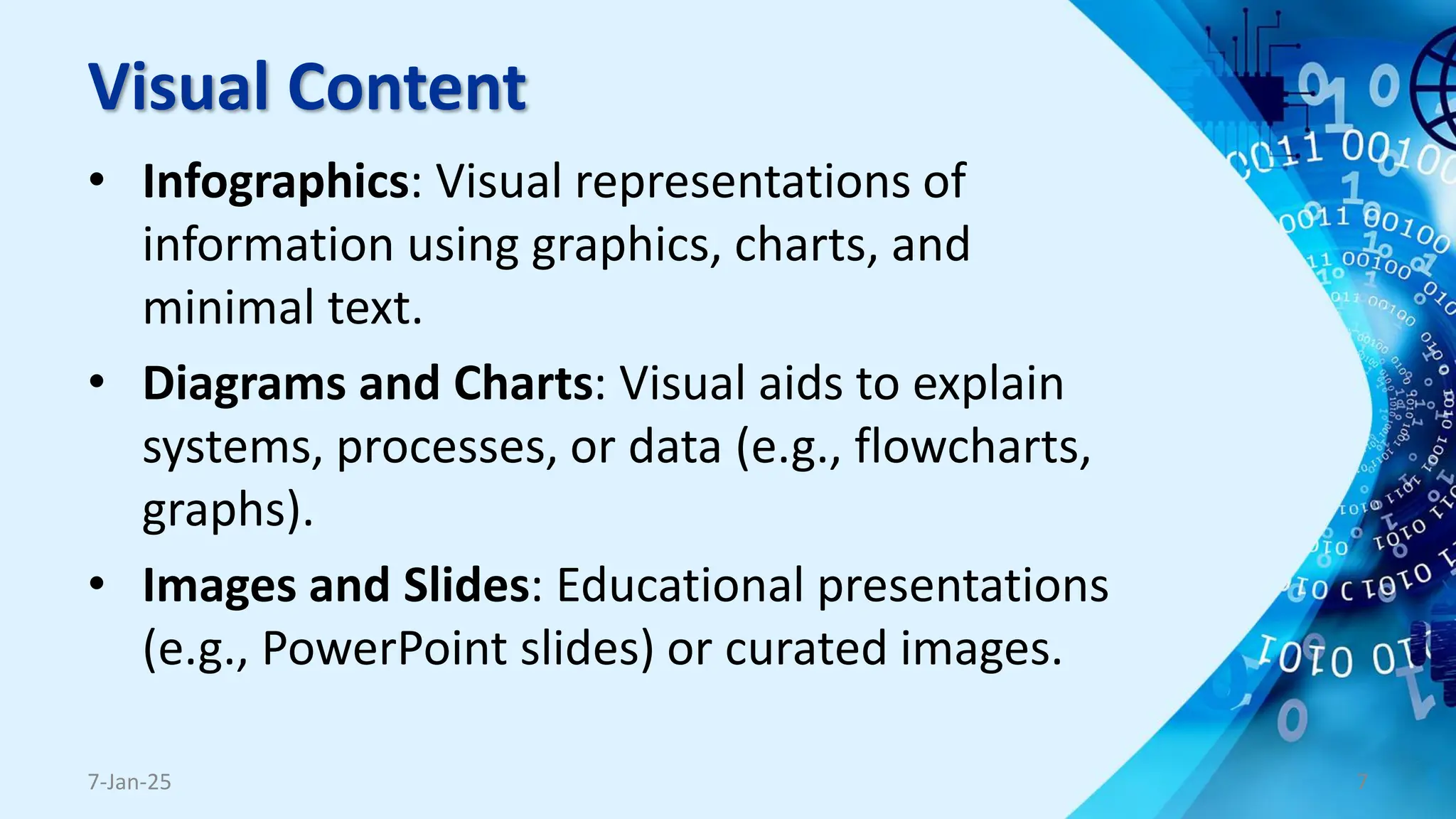
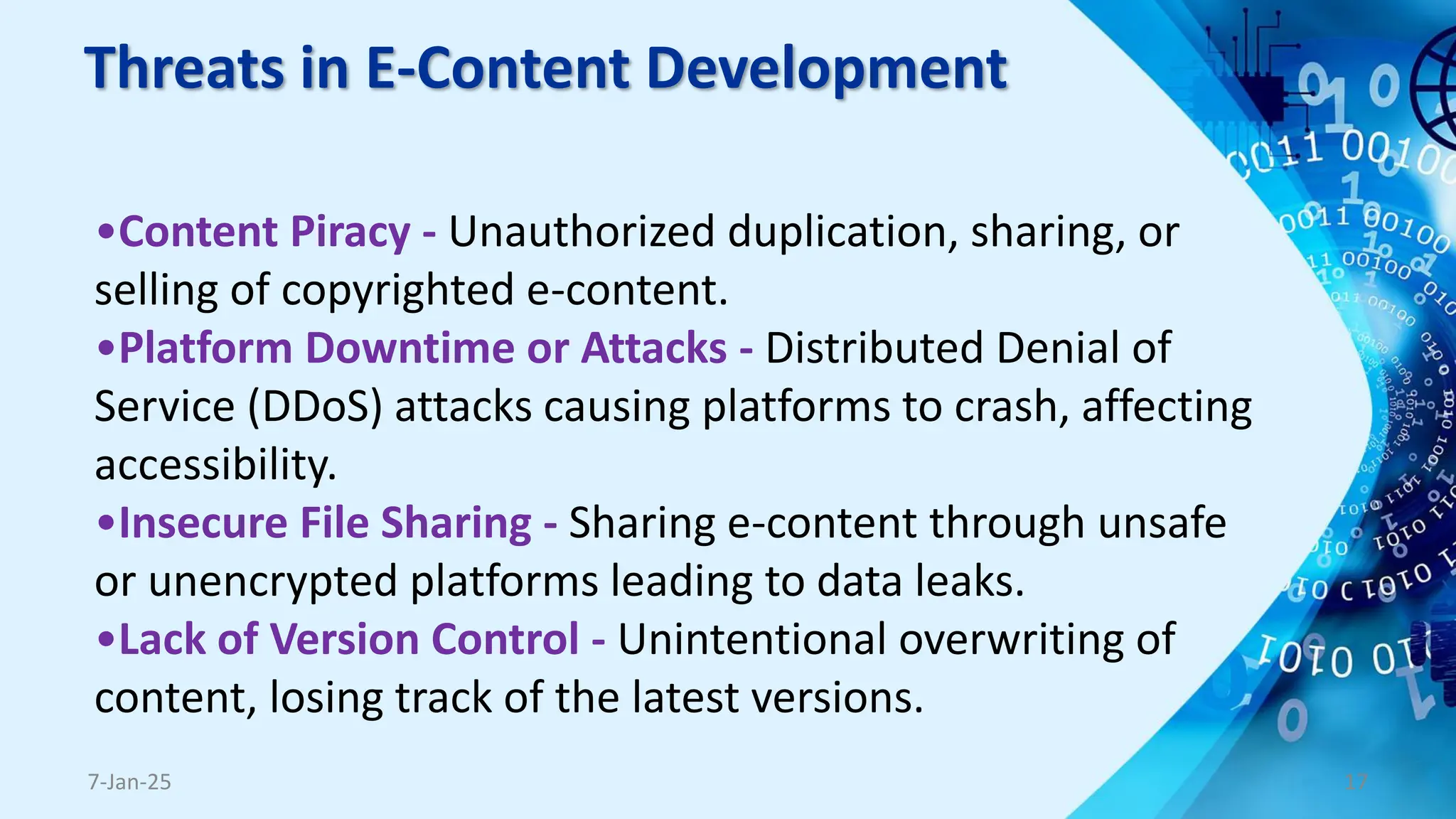
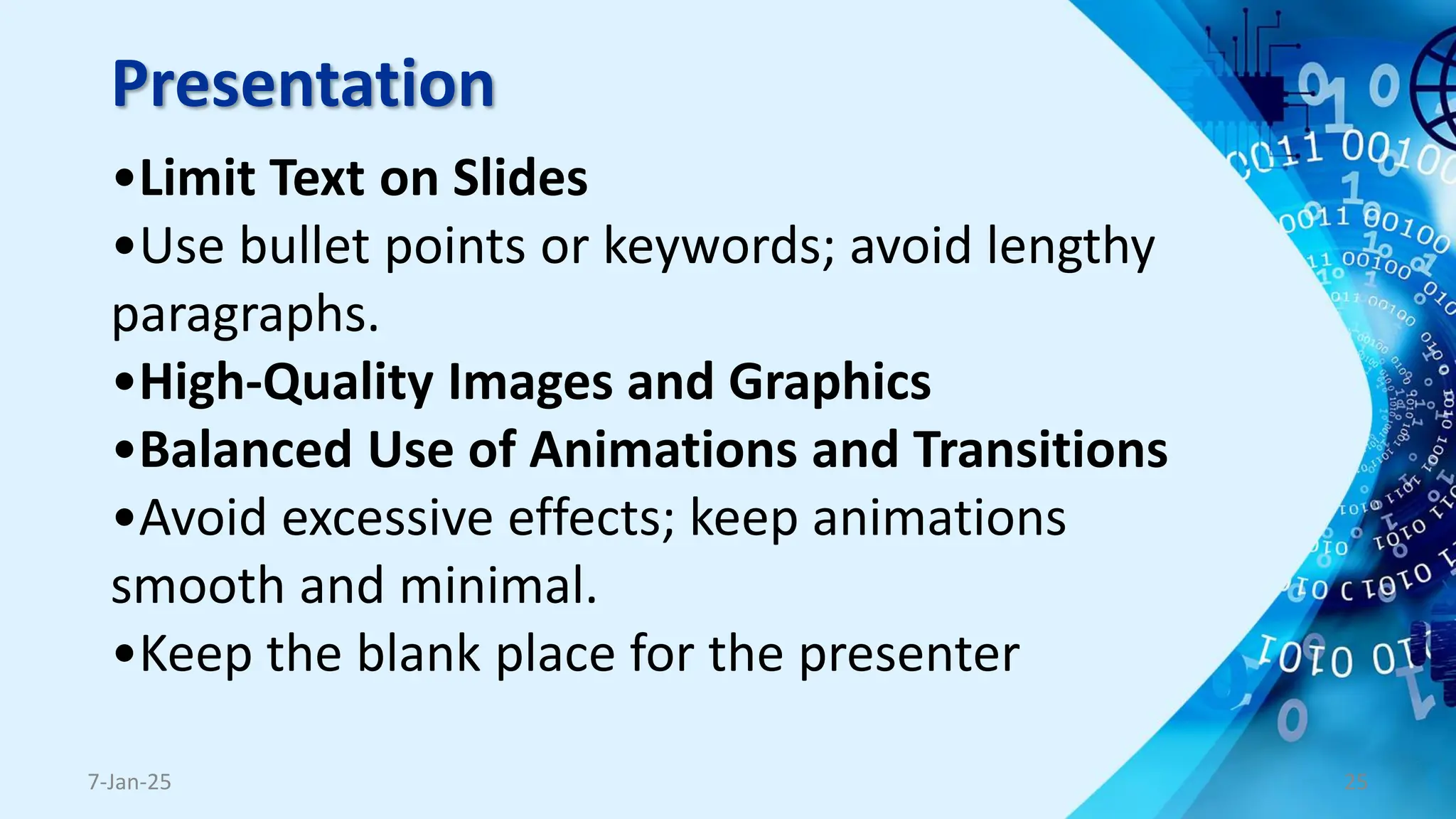
The document outlines the concept and necessity of e-content development, emphasizing various formats such as text, audio, visual, video, and interactive content. It discusses platforms for e-content delivery, threats to cybersecurity in e-content development, copyright precautions, and the importance of adhering to pedagogical and andragogical principles. The document also includes tips for presentation and tips for presenters to ensure effective communication and engagement.