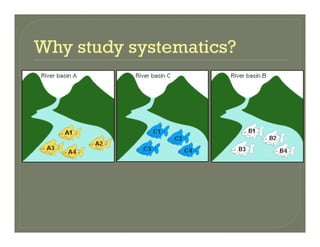
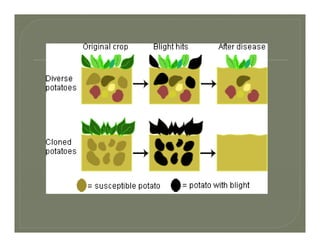
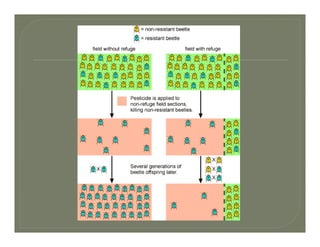
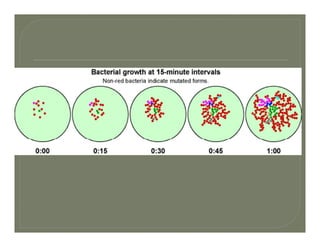
This document discusses the key concepts and components of systematics, which includes taxonomy and phylogeny. It covers topics such as:
- The goal of phylogenetic reconstruction and evolutionary history.
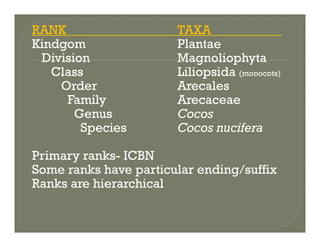
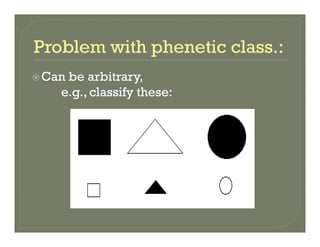
- The major parts of systematics including description, classification, nomenclature, and identification.
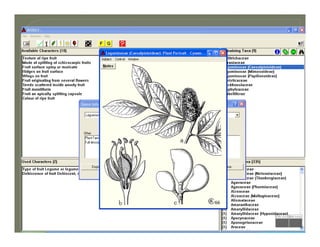
- Tools for communicating taxonomic information such as keys and scientific names.
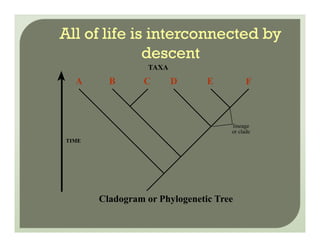
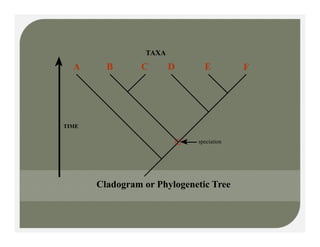
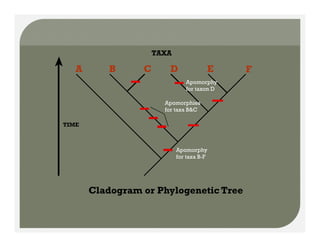
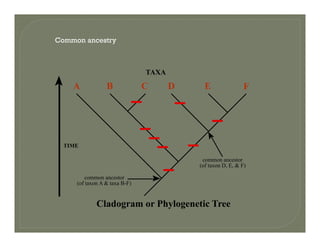
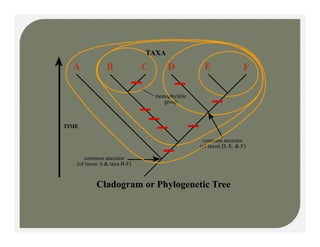
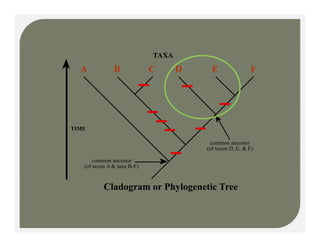
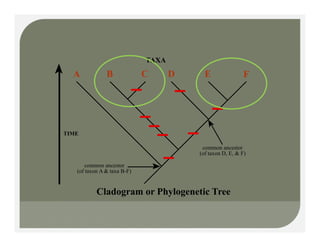
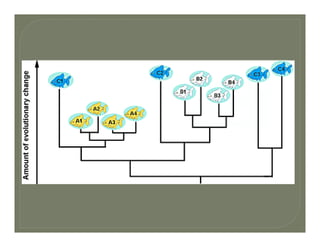
- Methods for determining evolutionary relationships including cladistics and cladograms.
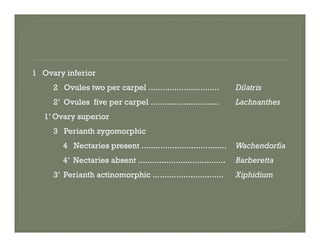
- Principles of formal taxonomic naming and types of specimens.
- Uses of keys to identify unknown taxa.