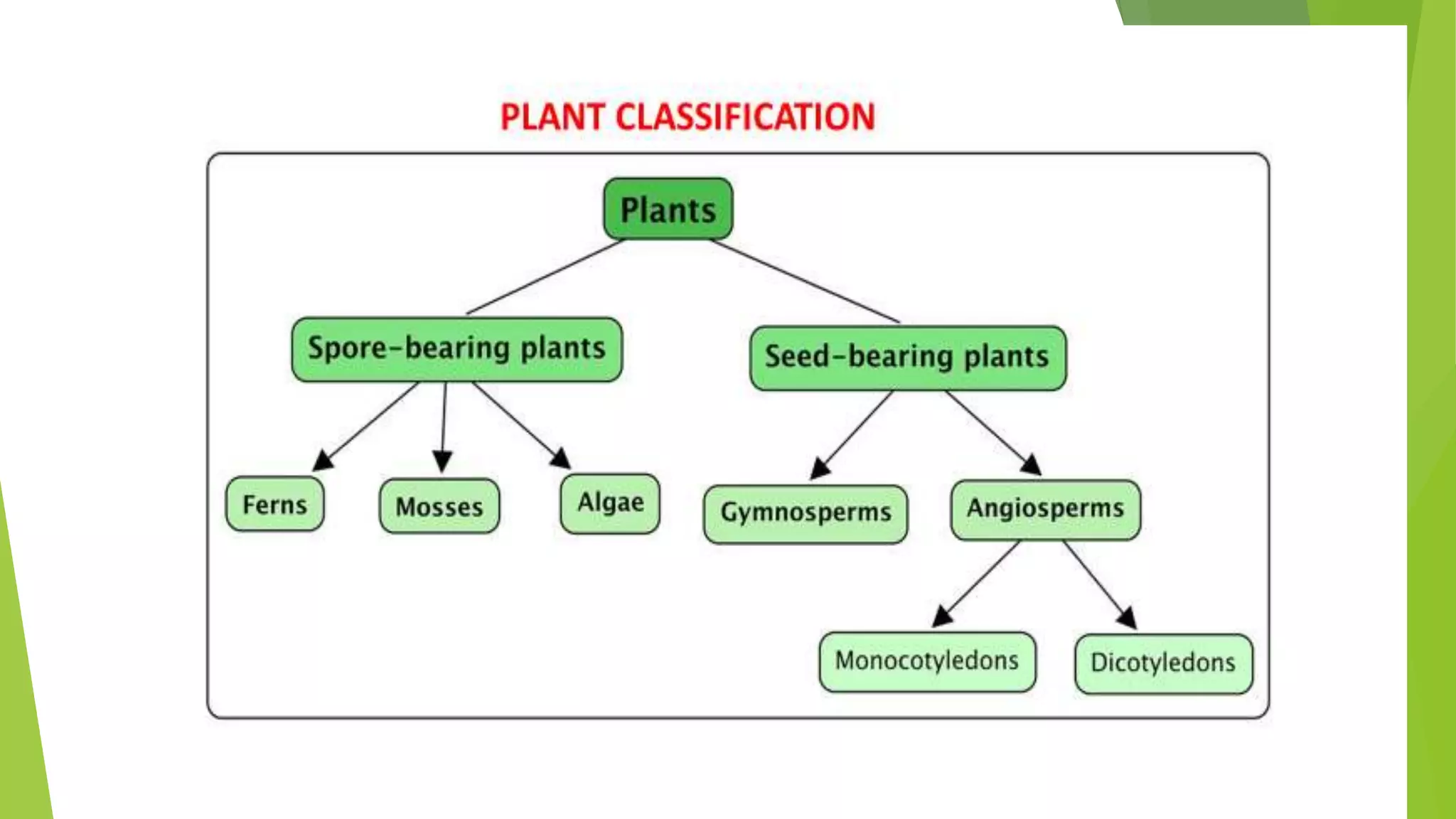
This document discusses the taxonomic hierarchy used for classifying organisms, specifically angiosperms. It explains that taxonomic hierarchy arranges organisms into successive levels from kingdom down to species. The main levels are kingdom, division, class, order, family, genus, and species. Major categories include division, class, and order, while minor categories are genus and species. The hierarchy allows grouping of organisms based on their diversity and helps classify plants into appropriate groups.