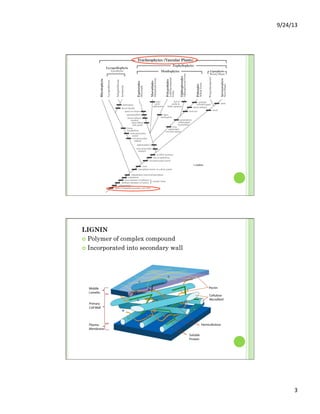
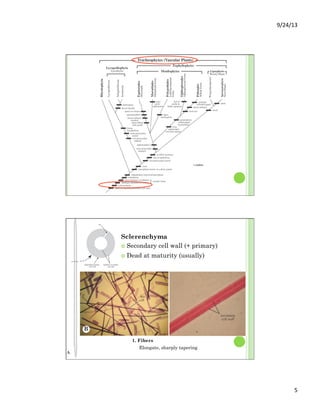
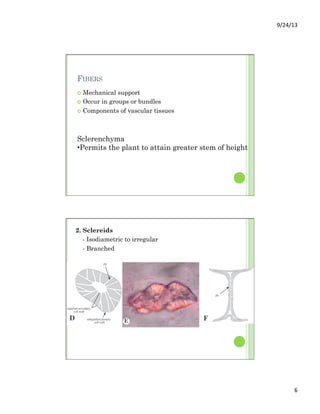
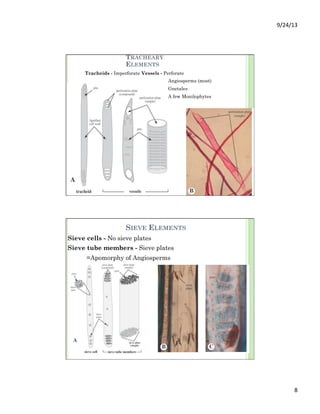
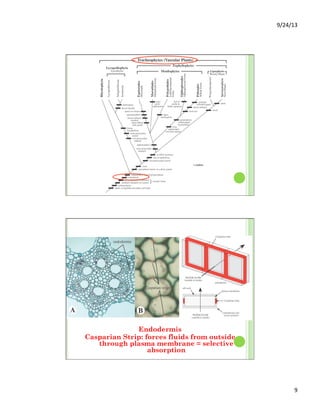
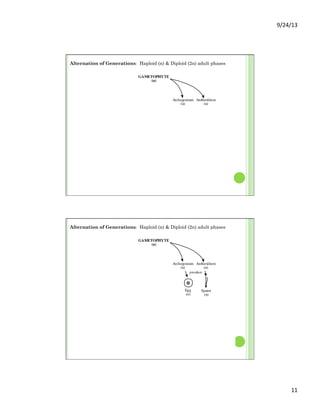
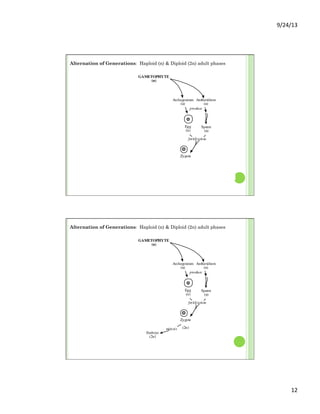
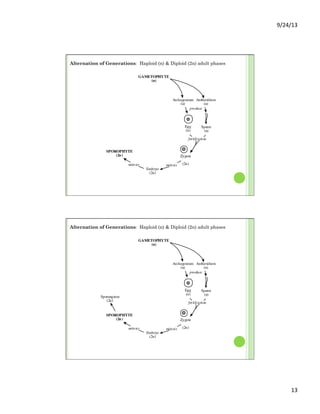
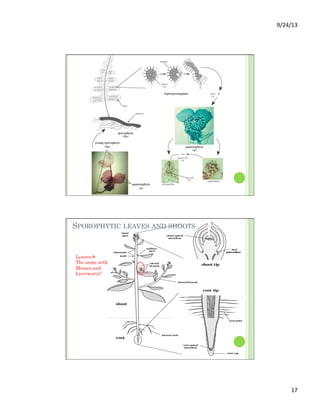
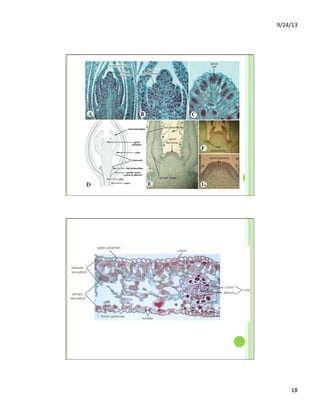
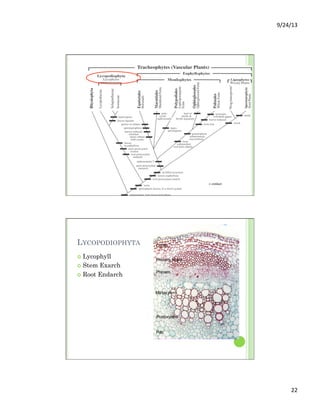
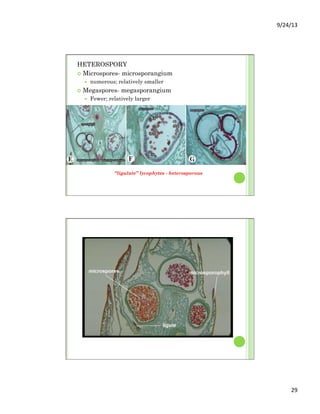
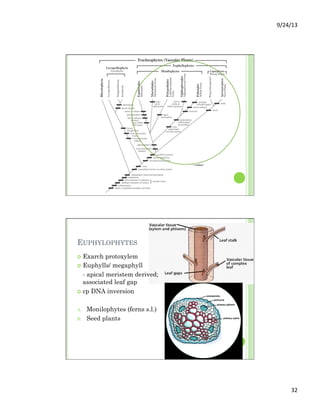
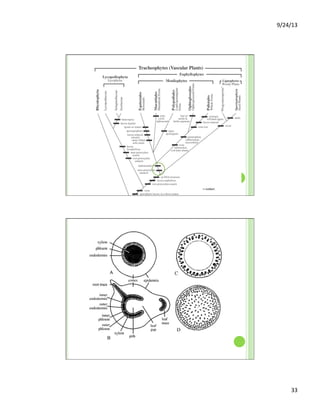
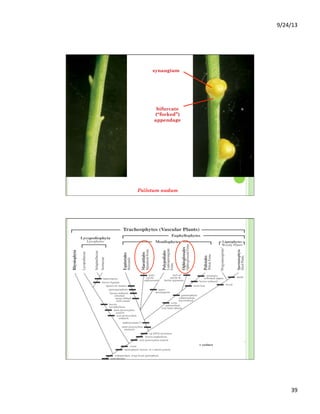
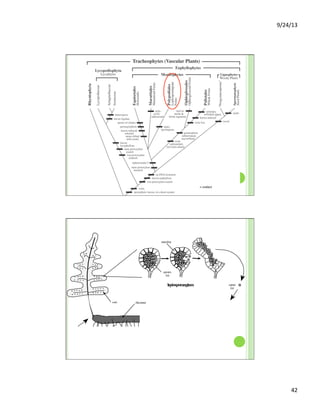
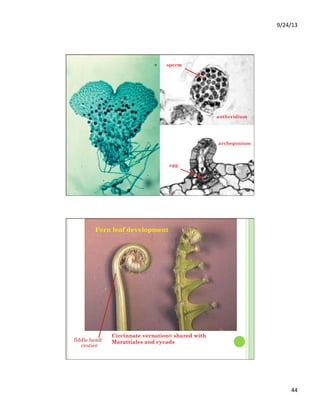
This document discusses the evolution and diversity of vascular plants. It defines key characteristics of tracheophytes, including vascular tissue, supportive tissue, roots and shoots. It describes lignin and secondary cell walls. It discusses the alternation of generations life cycle and key plant tissues/structures like xylem, phloem, sclerenchyma and fibers. The document outlines the major groups of vascular plants including rhyniophytes, lycopodiophytes, and euphyllophytes. It provides examples of extant lycophytes like club mosses, spike mosses and quillworts.