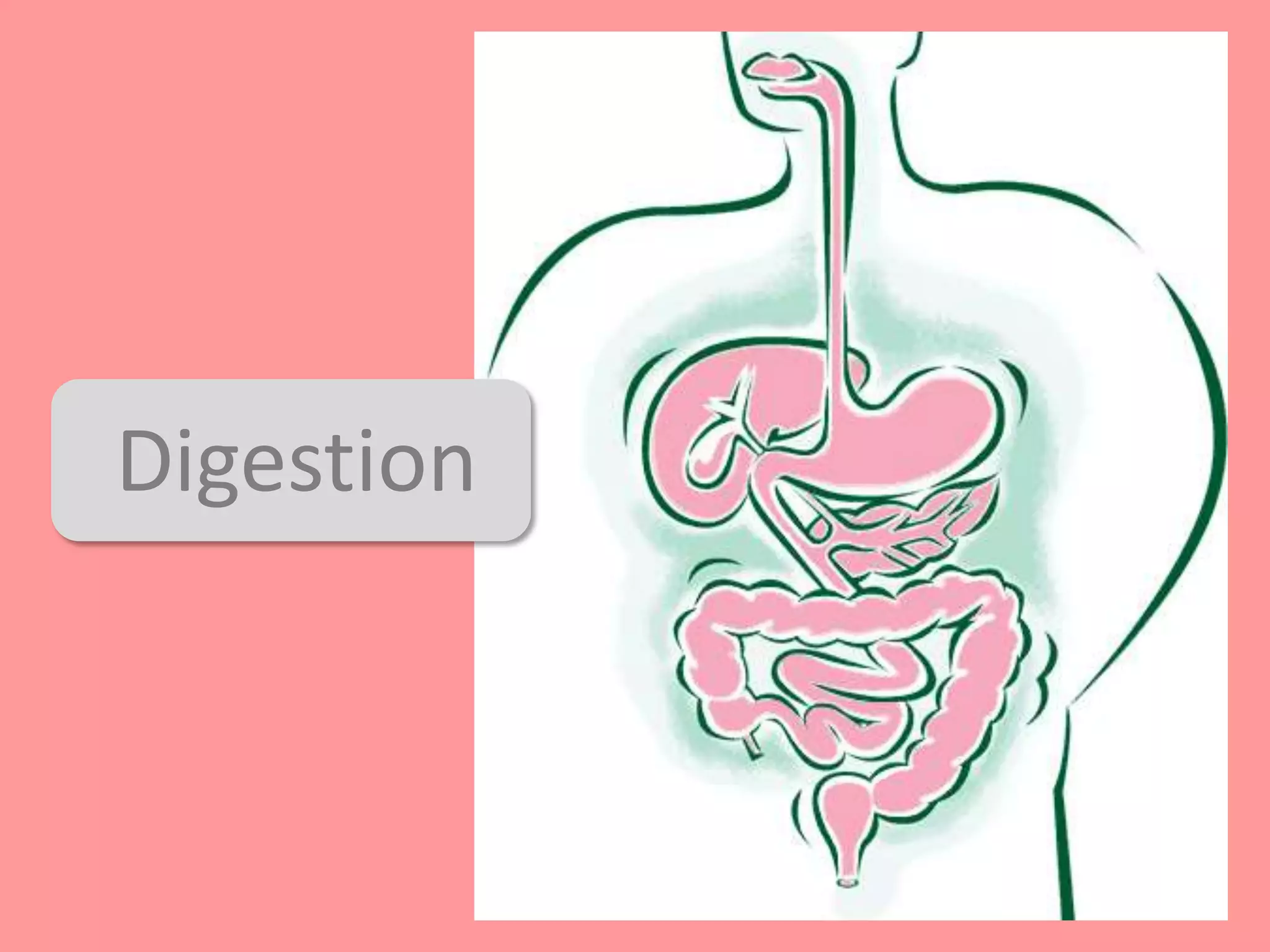
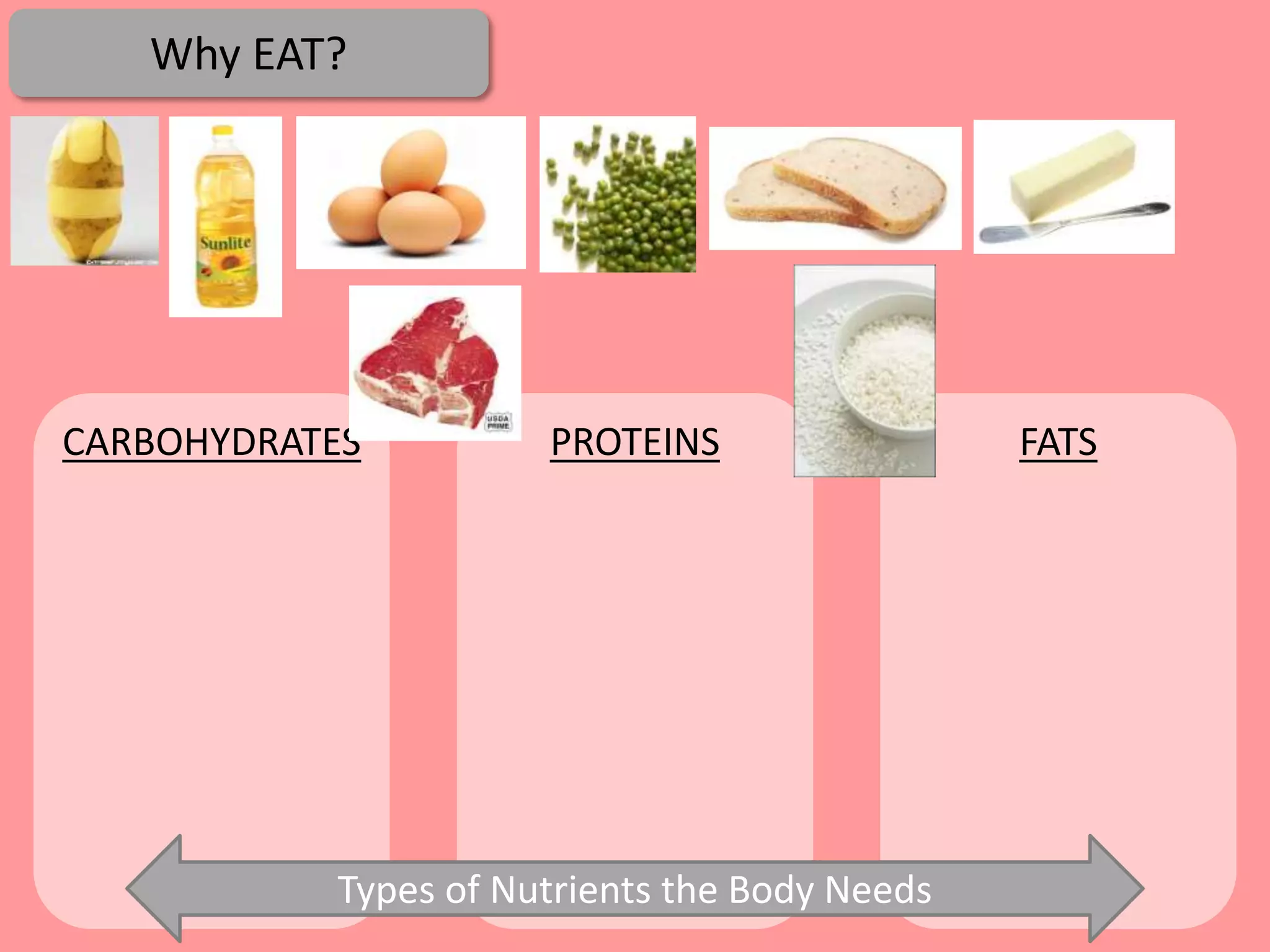
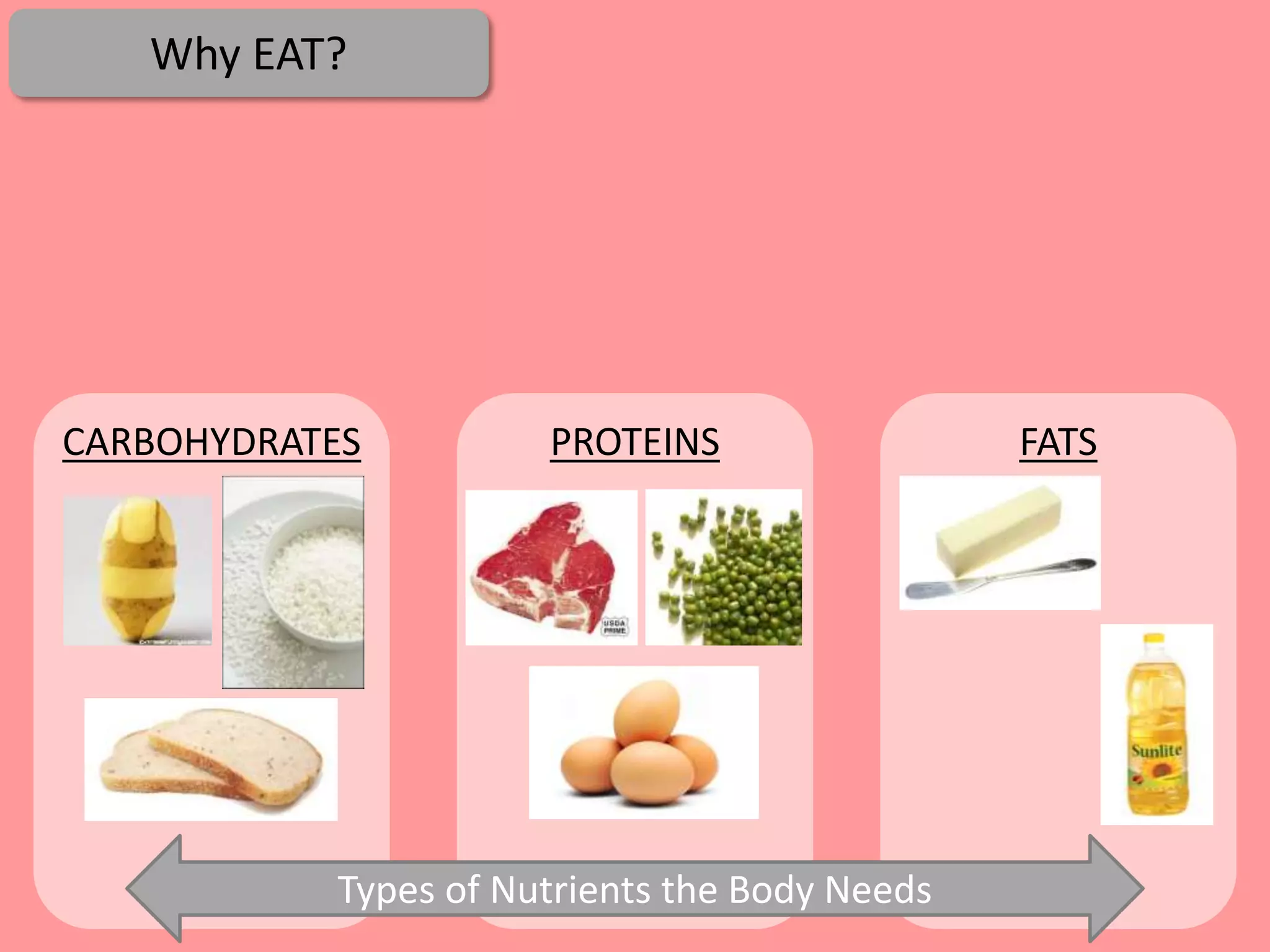
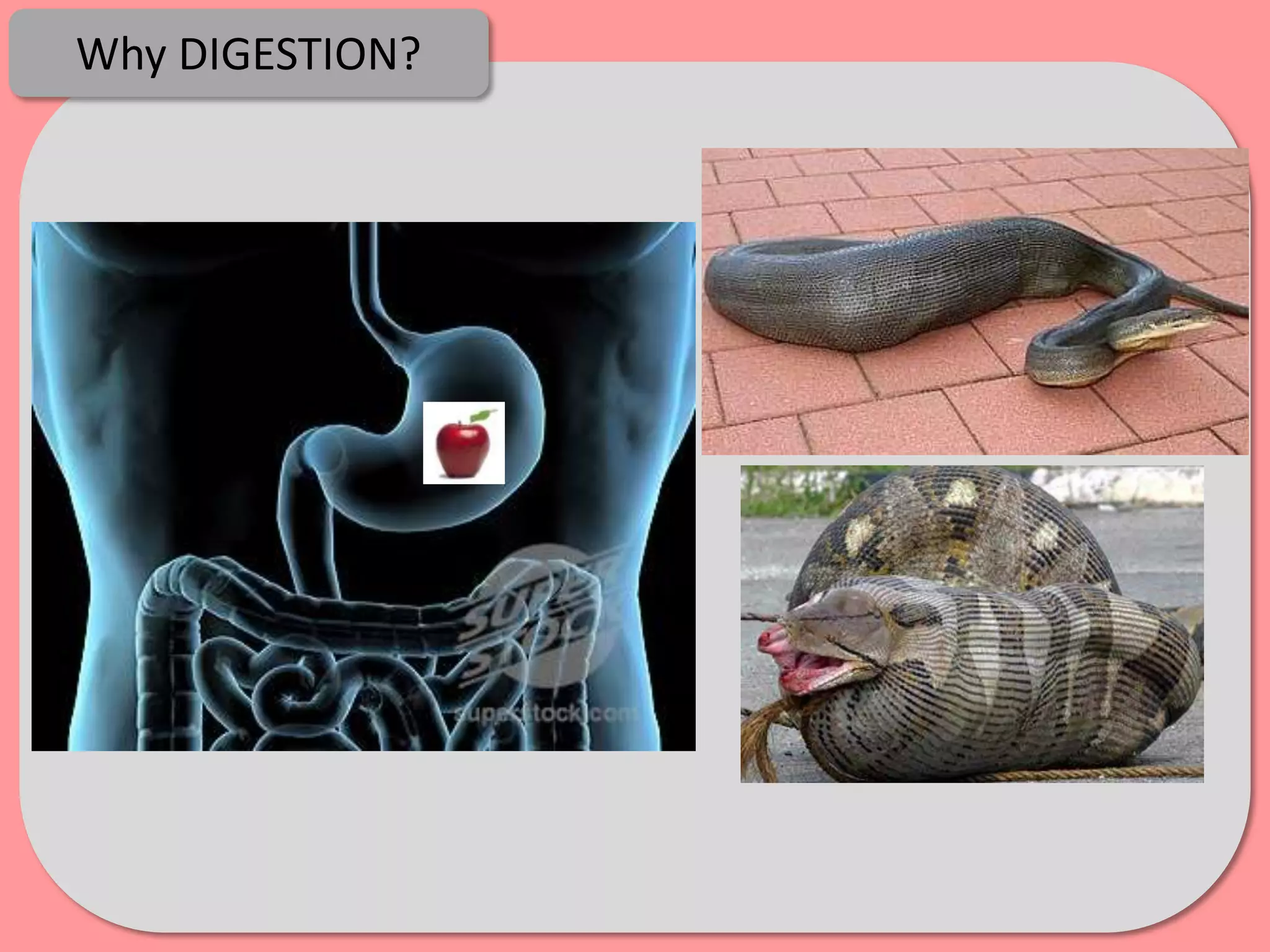
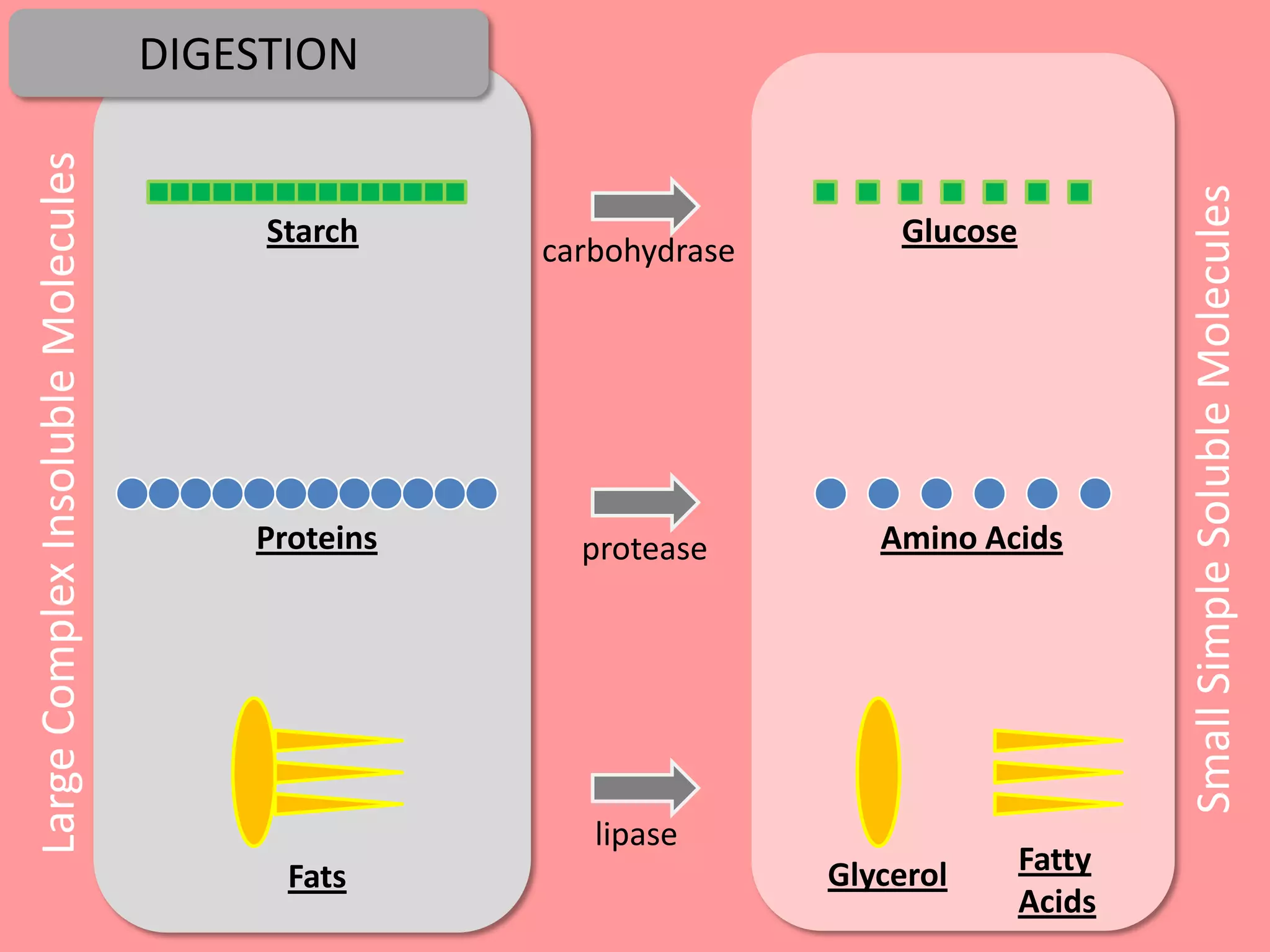
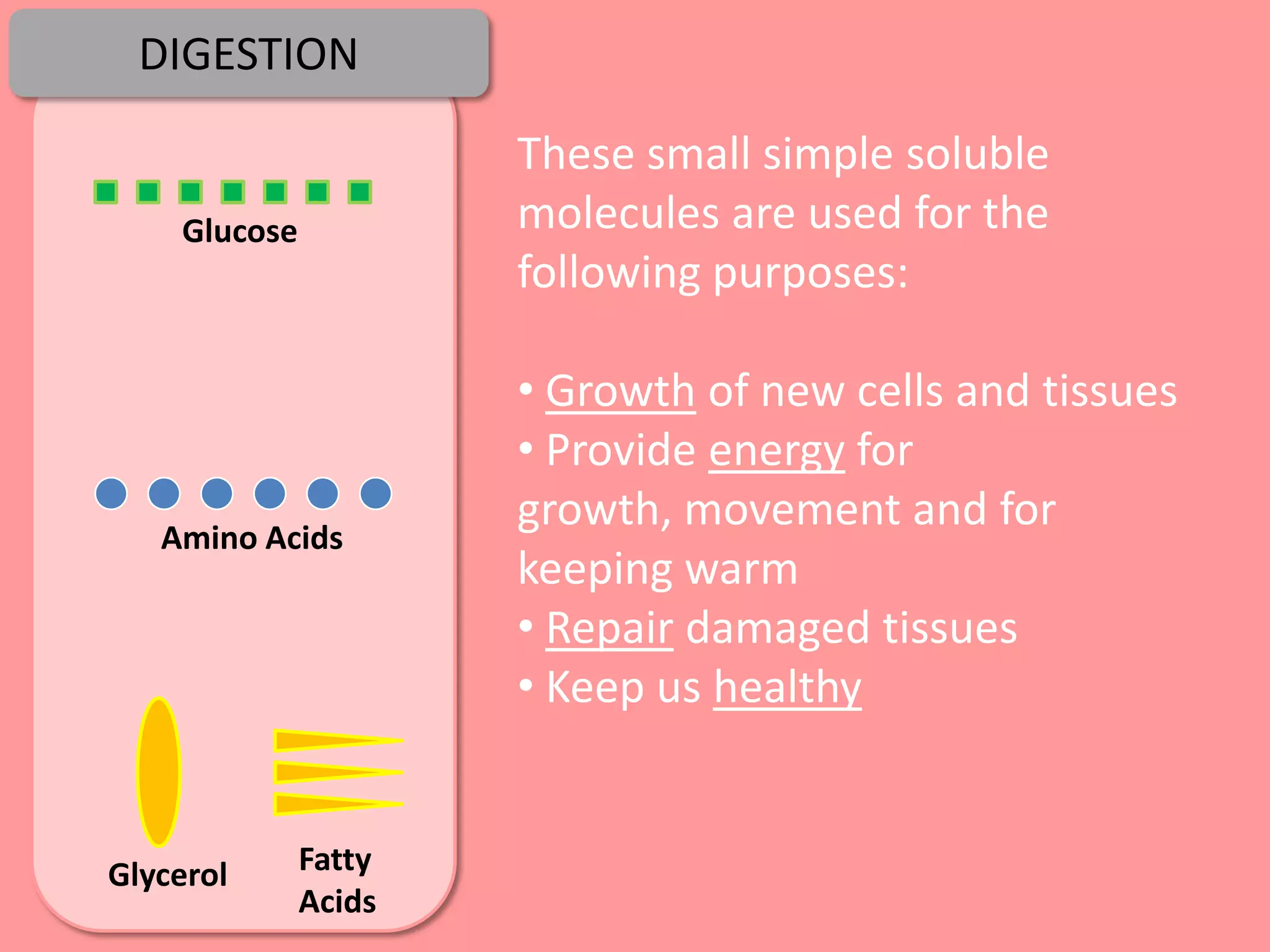
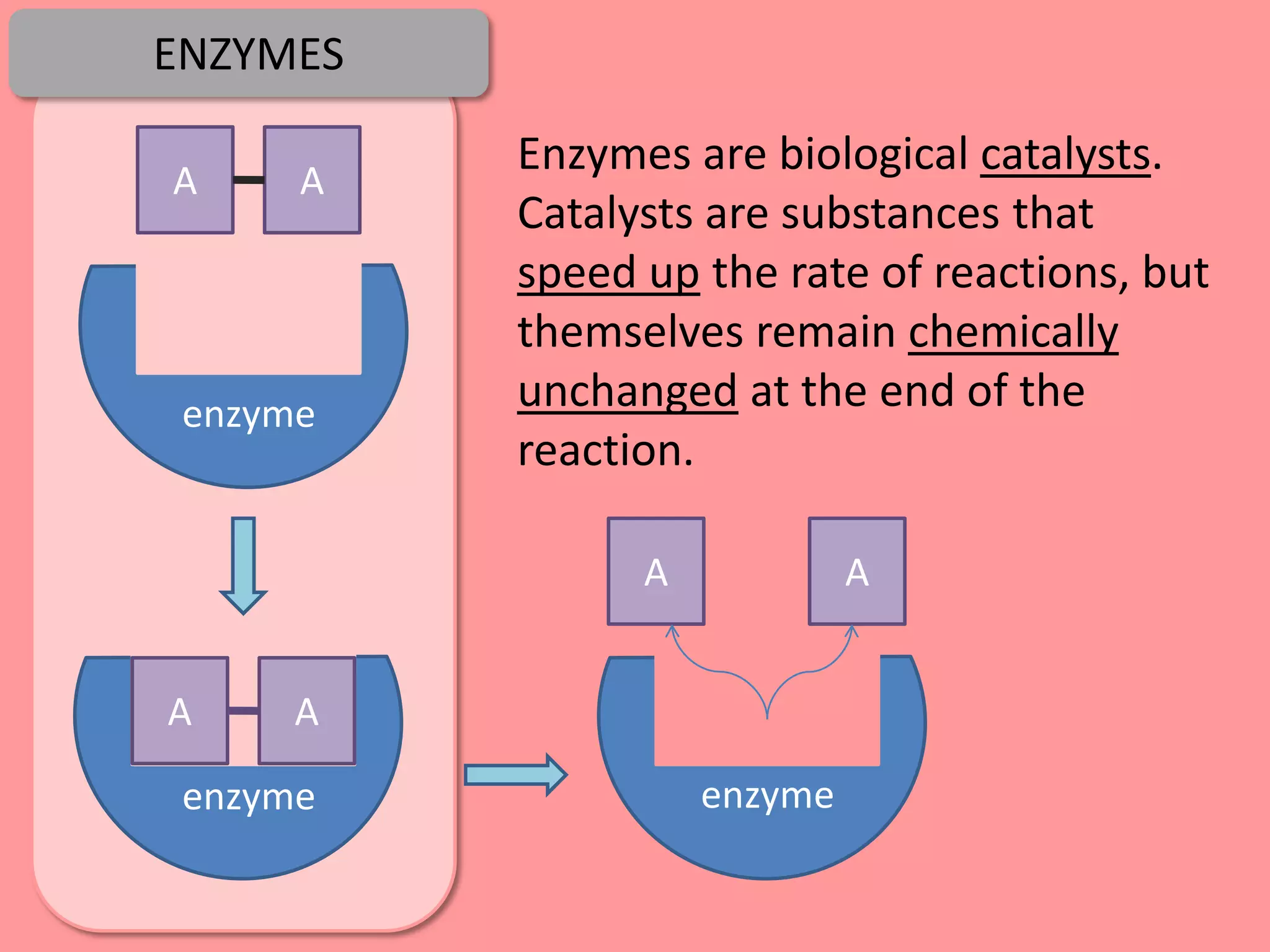
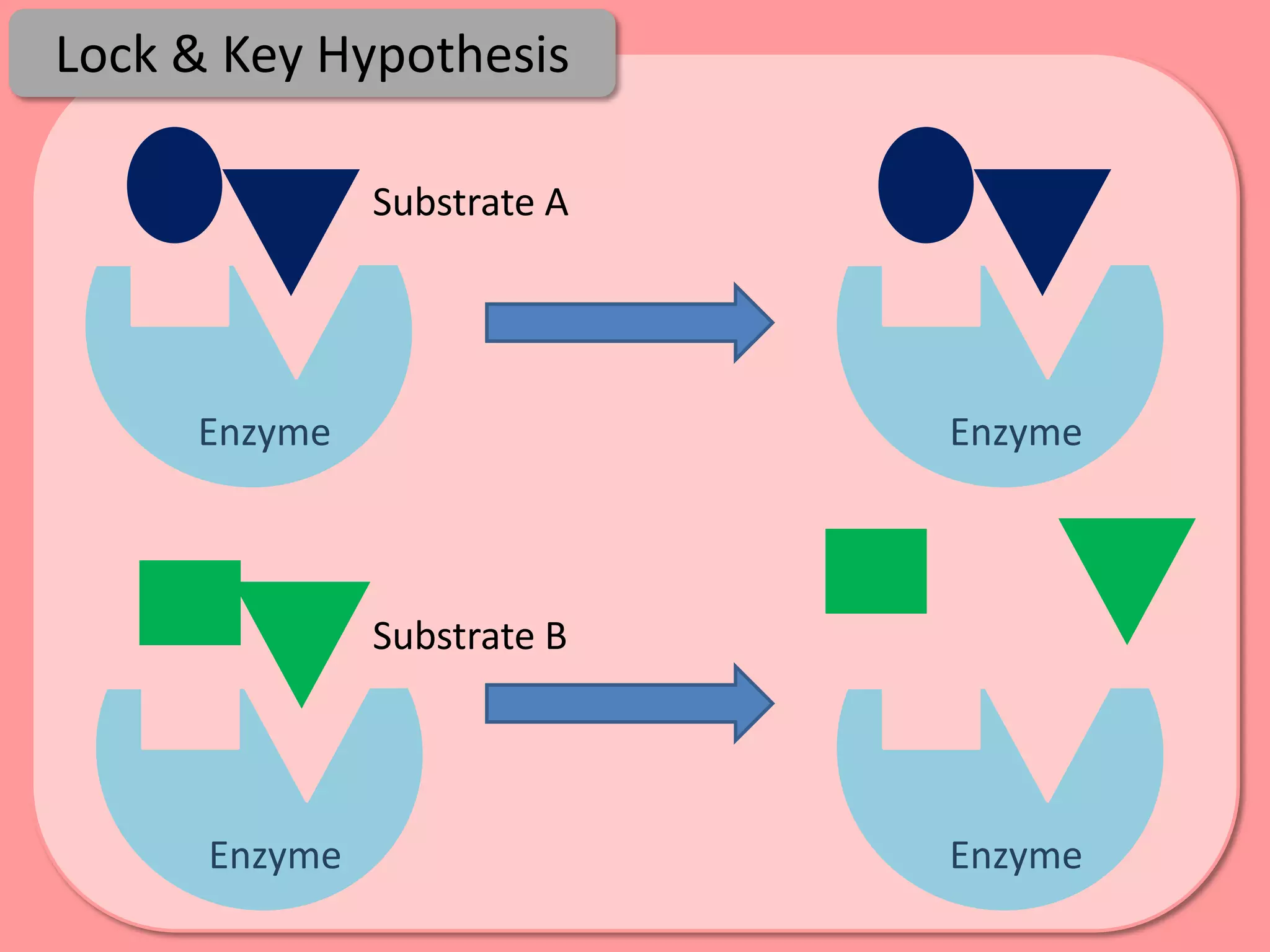
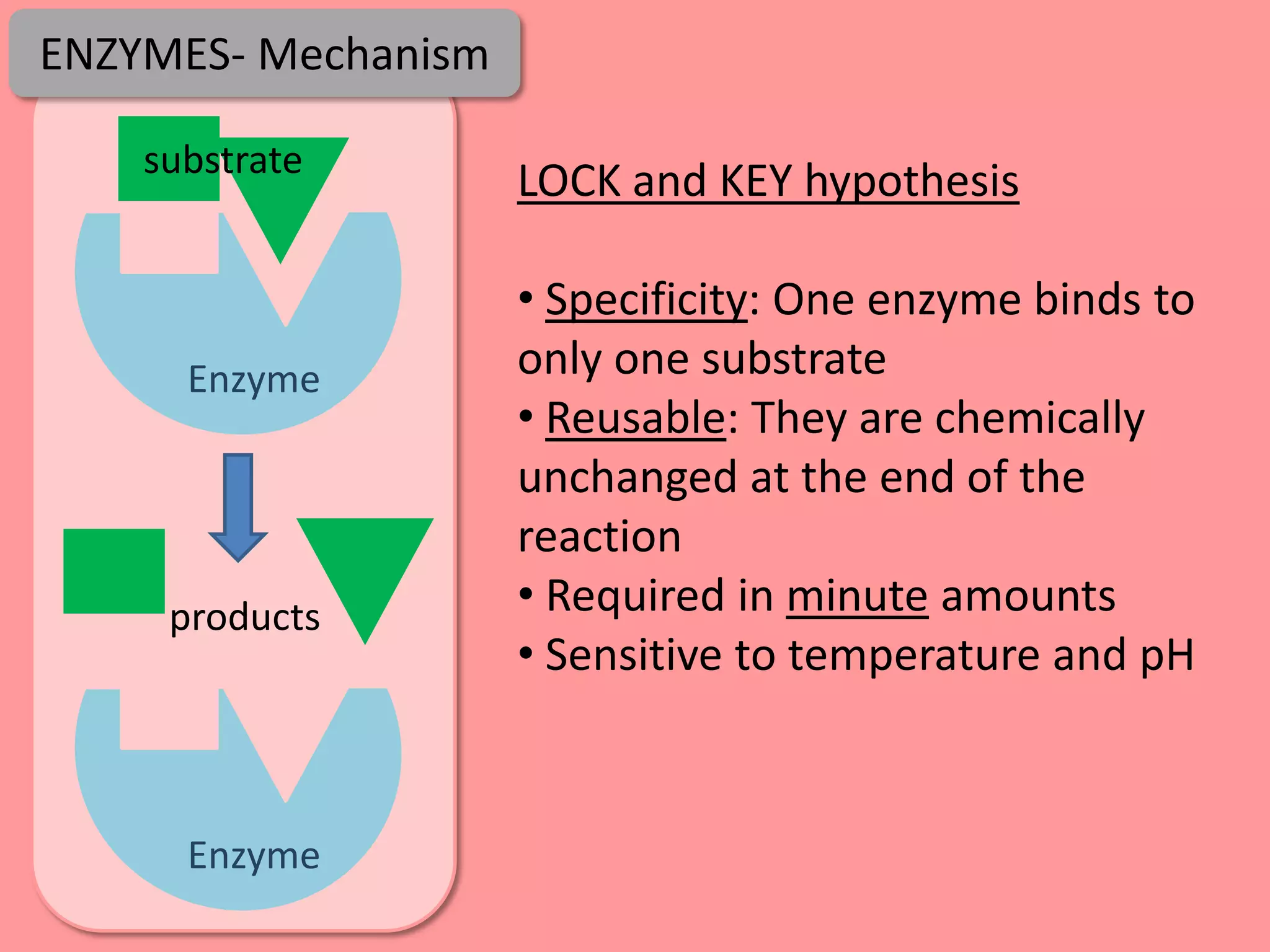
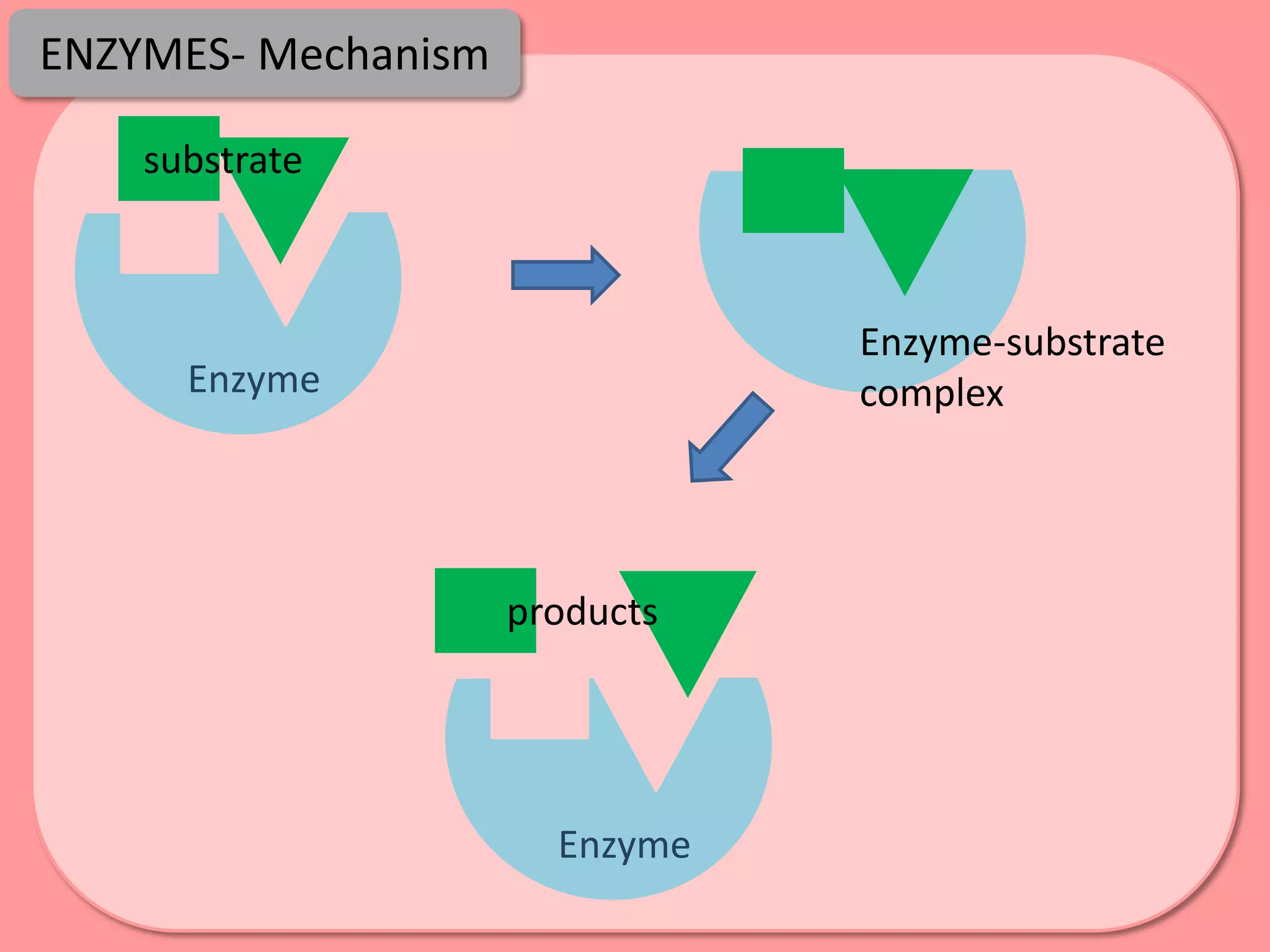
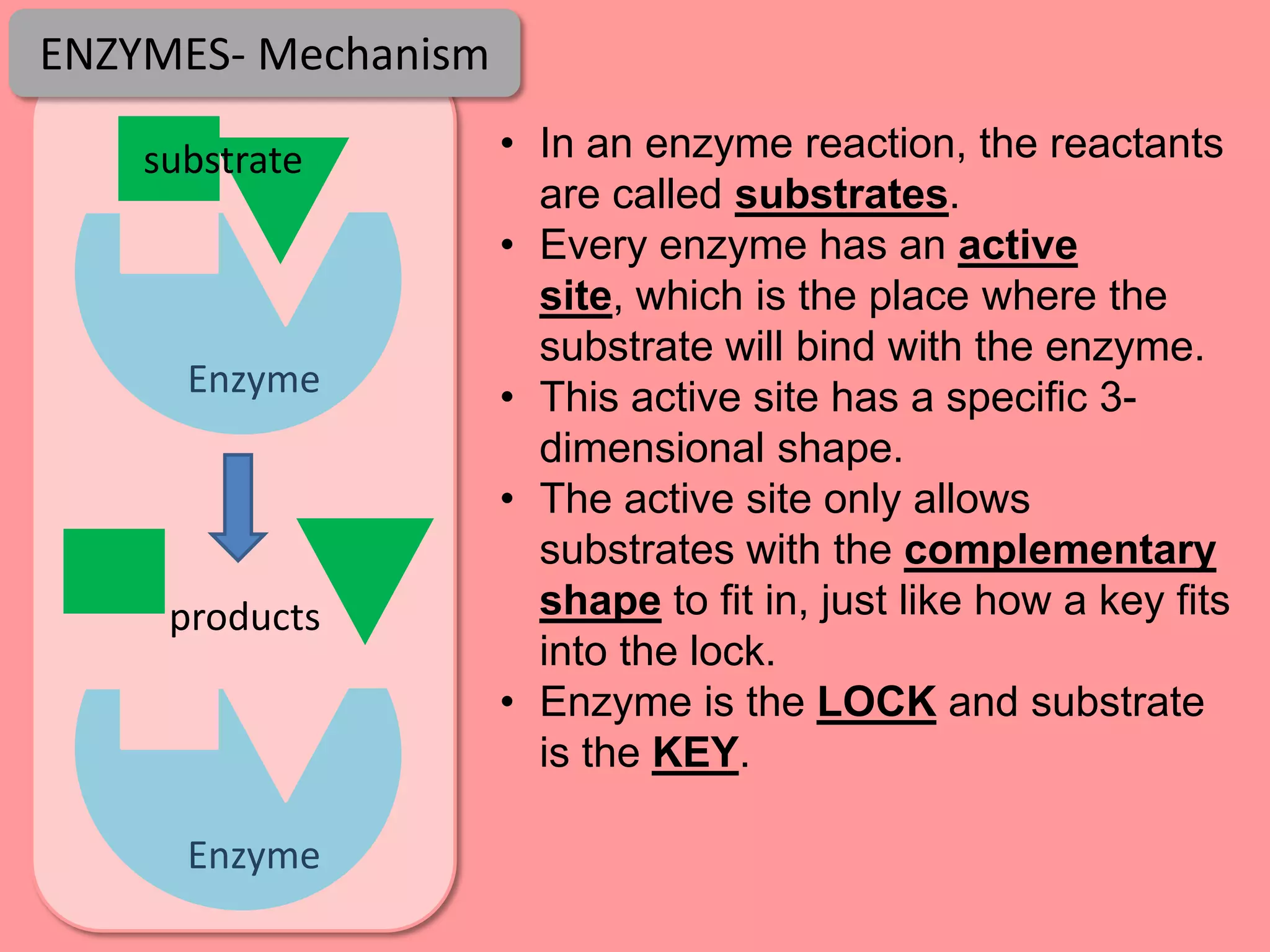
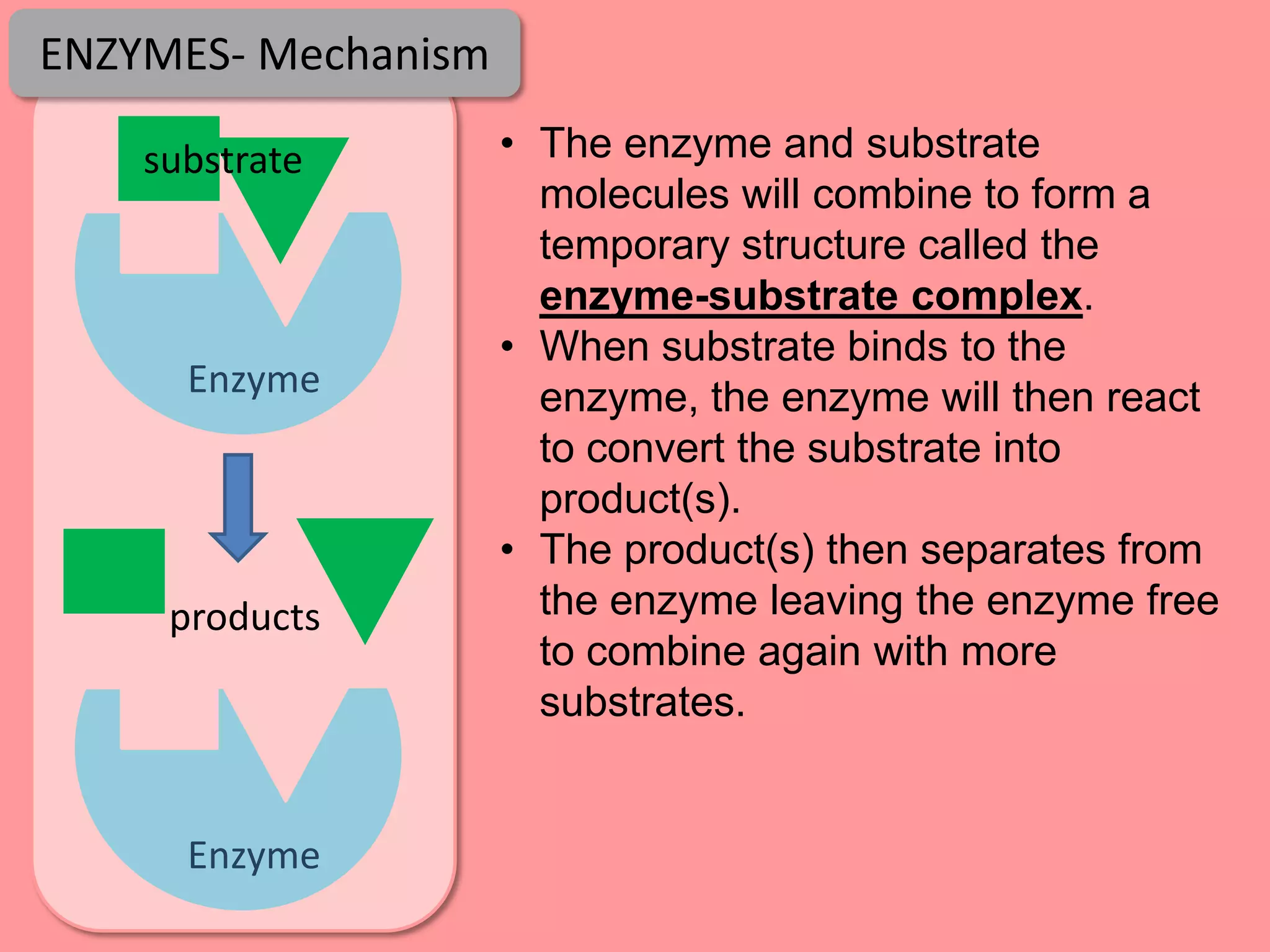
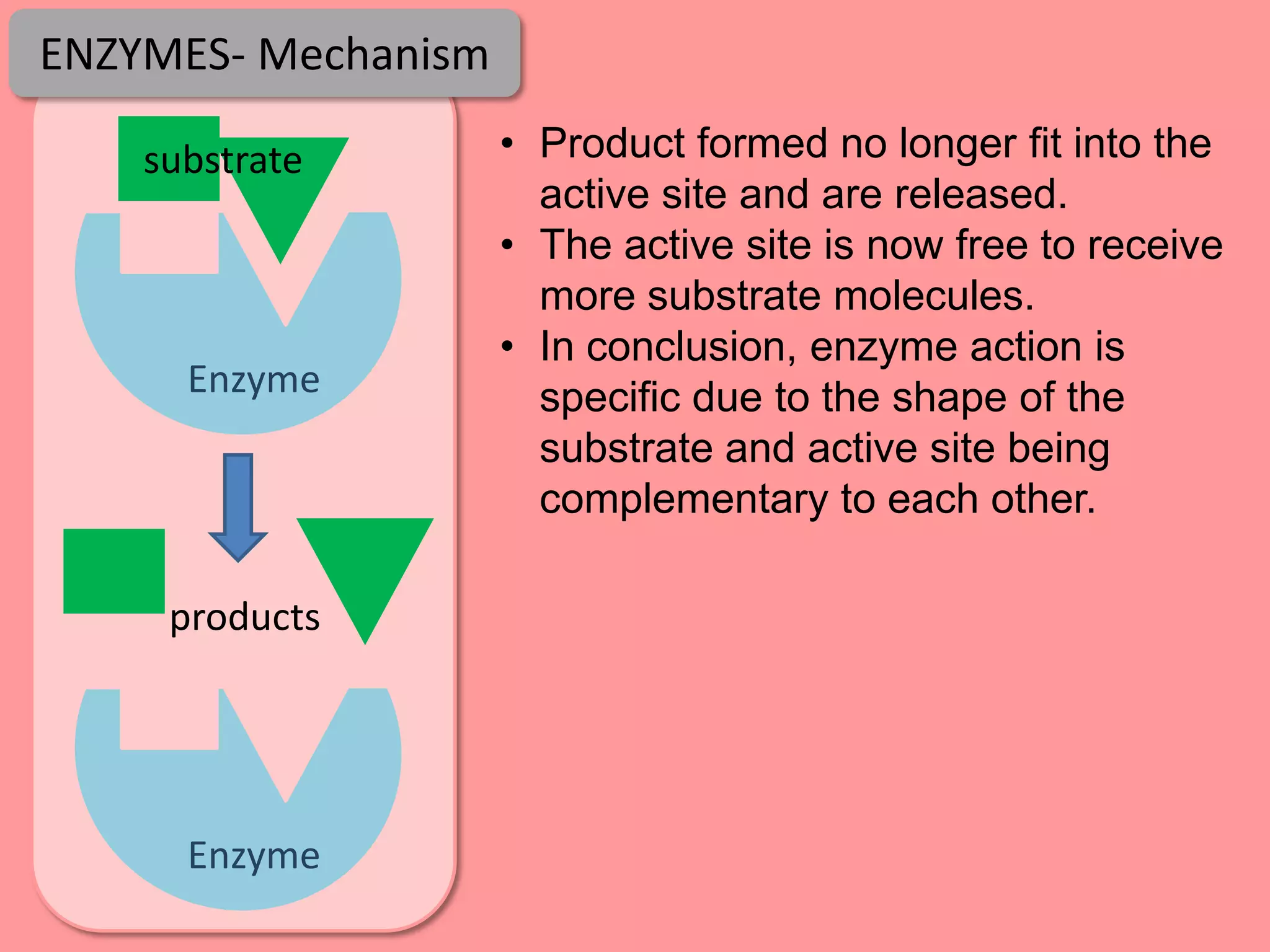
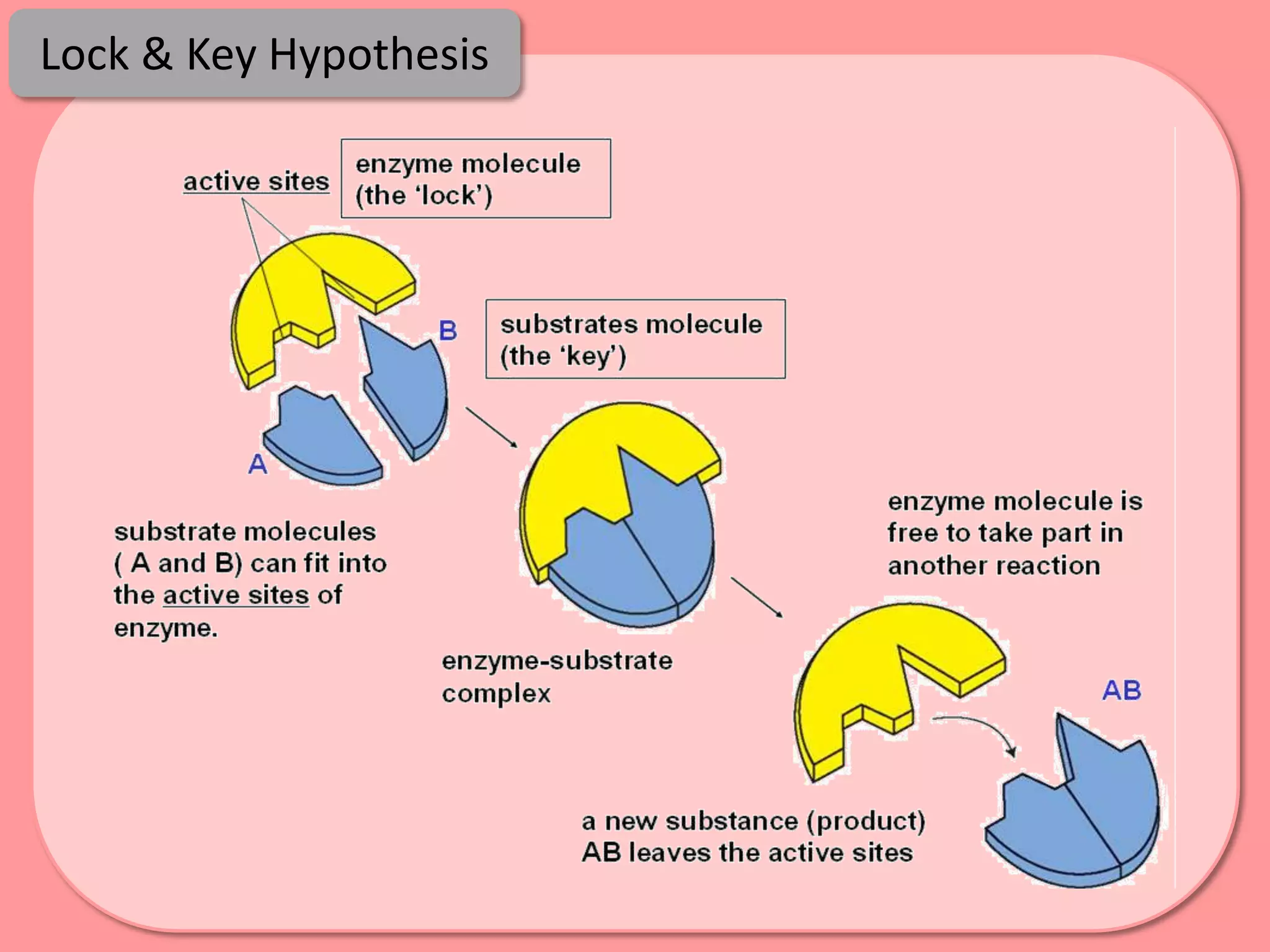
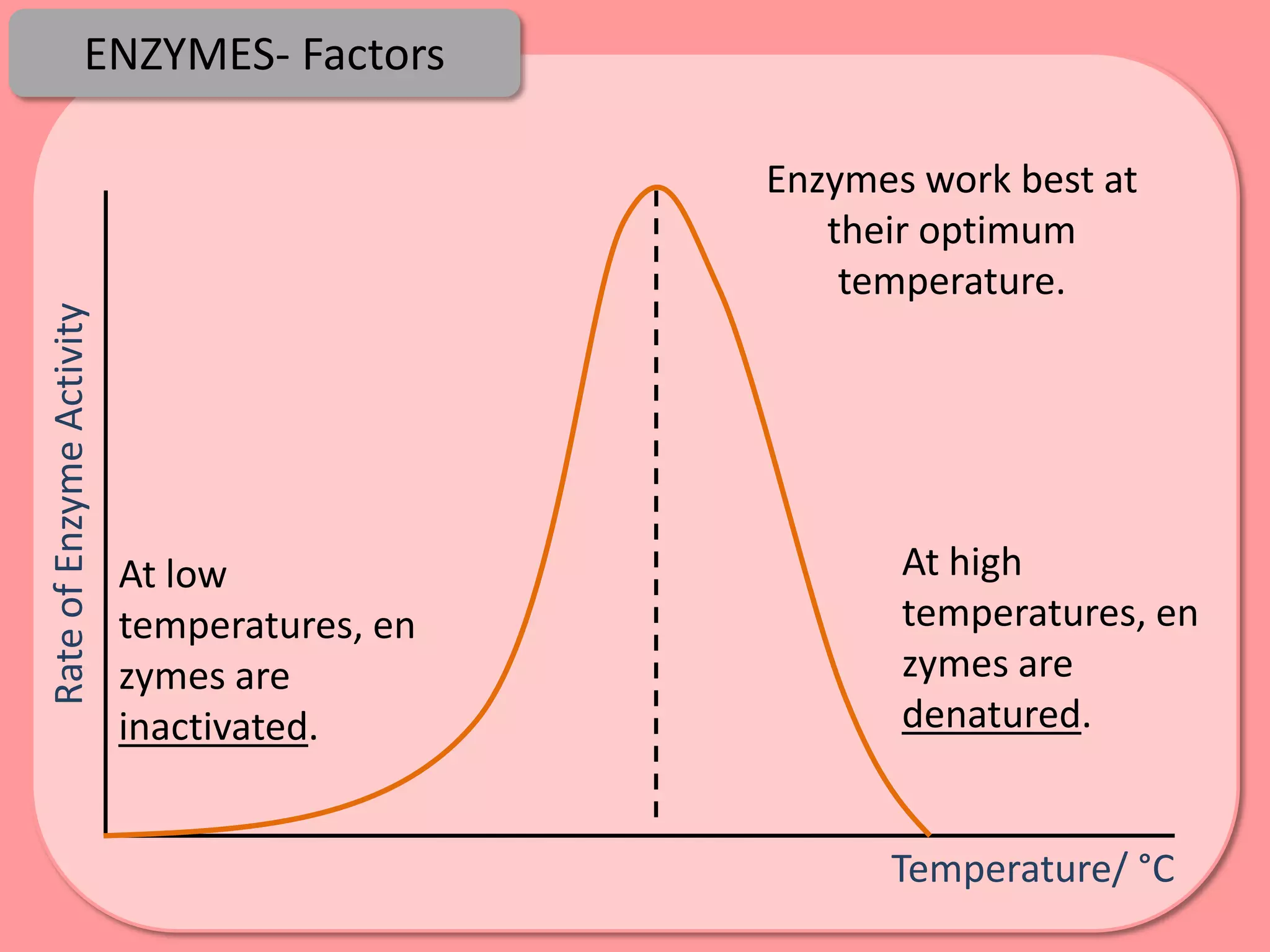
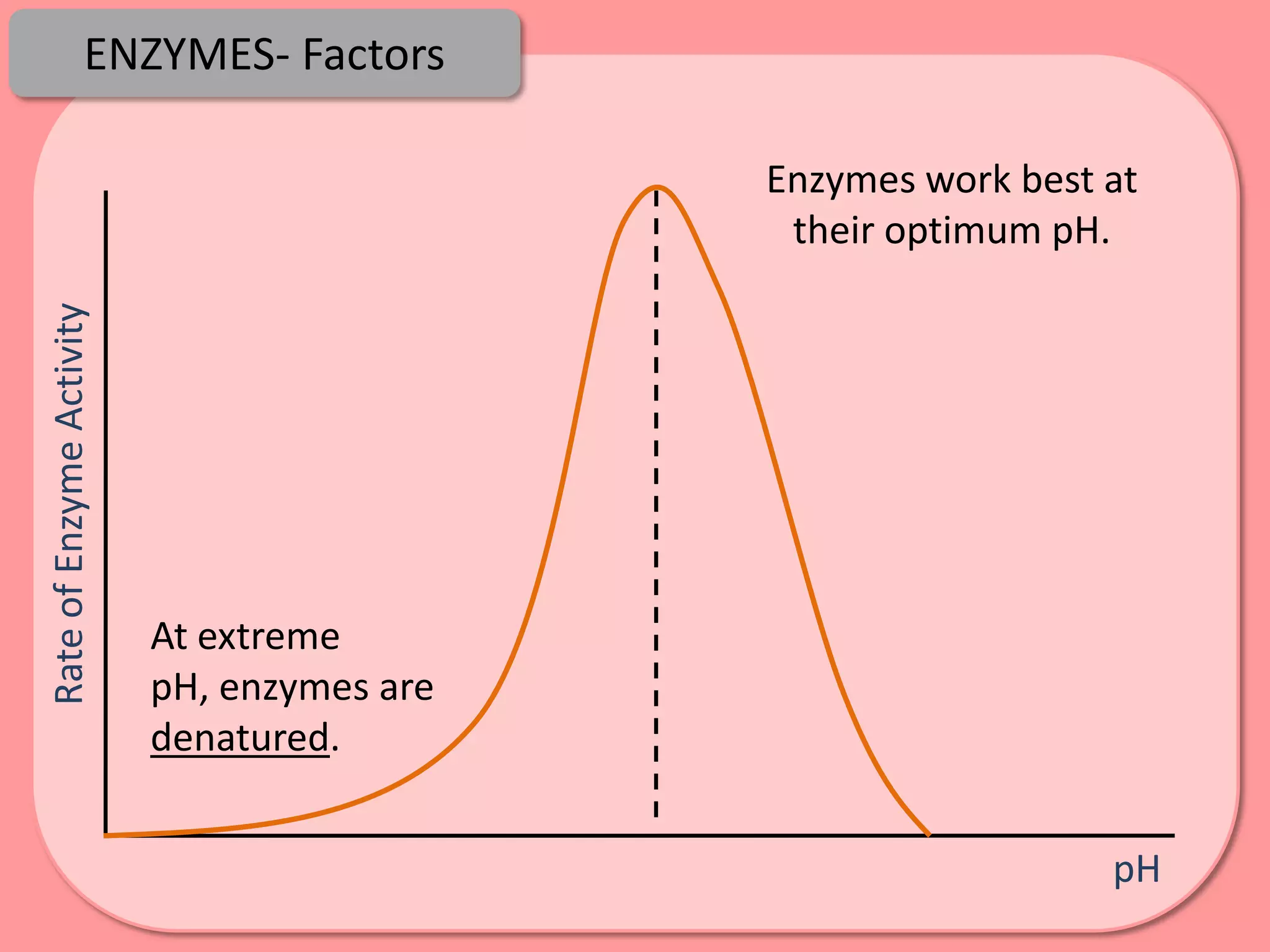
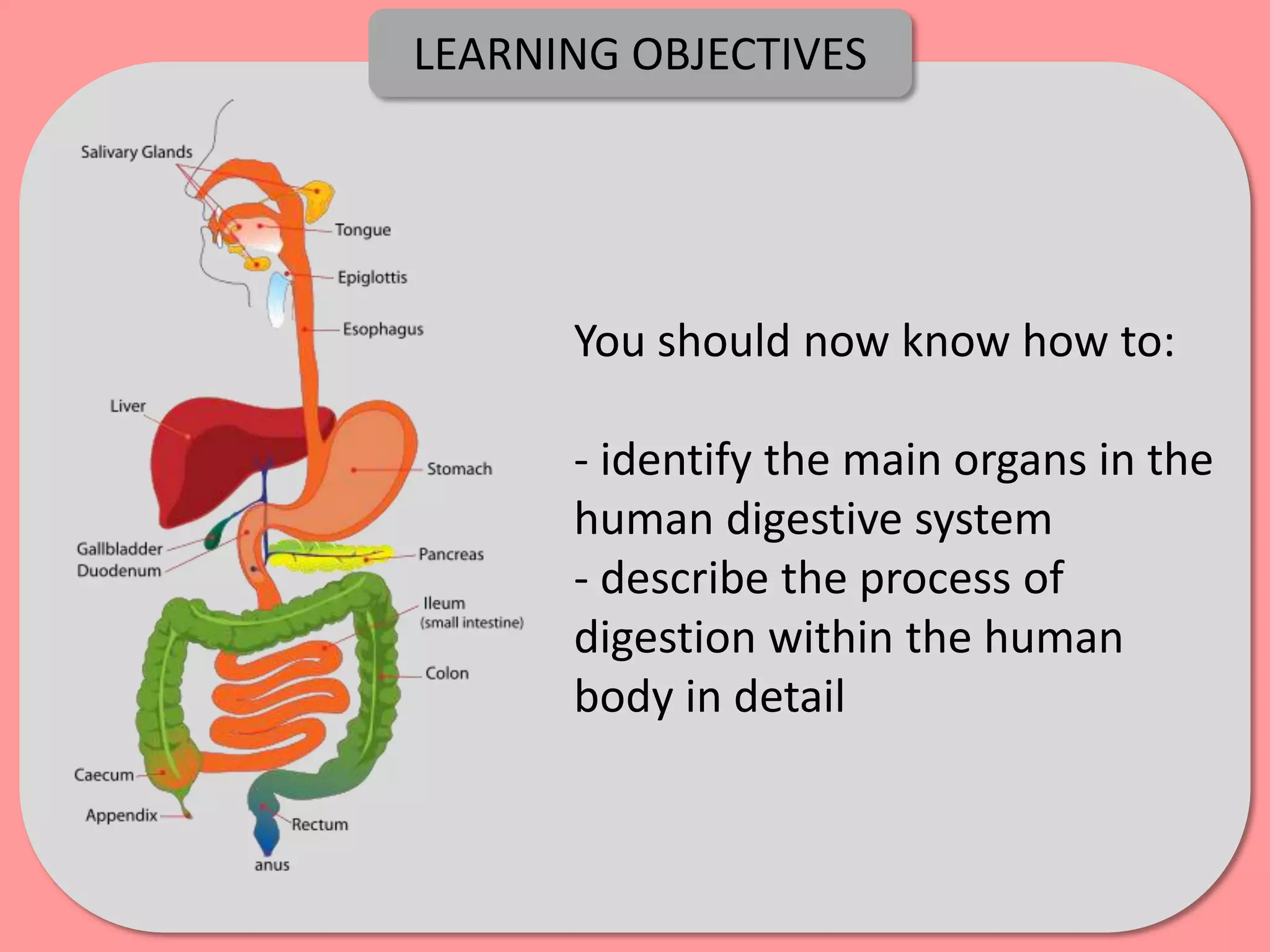
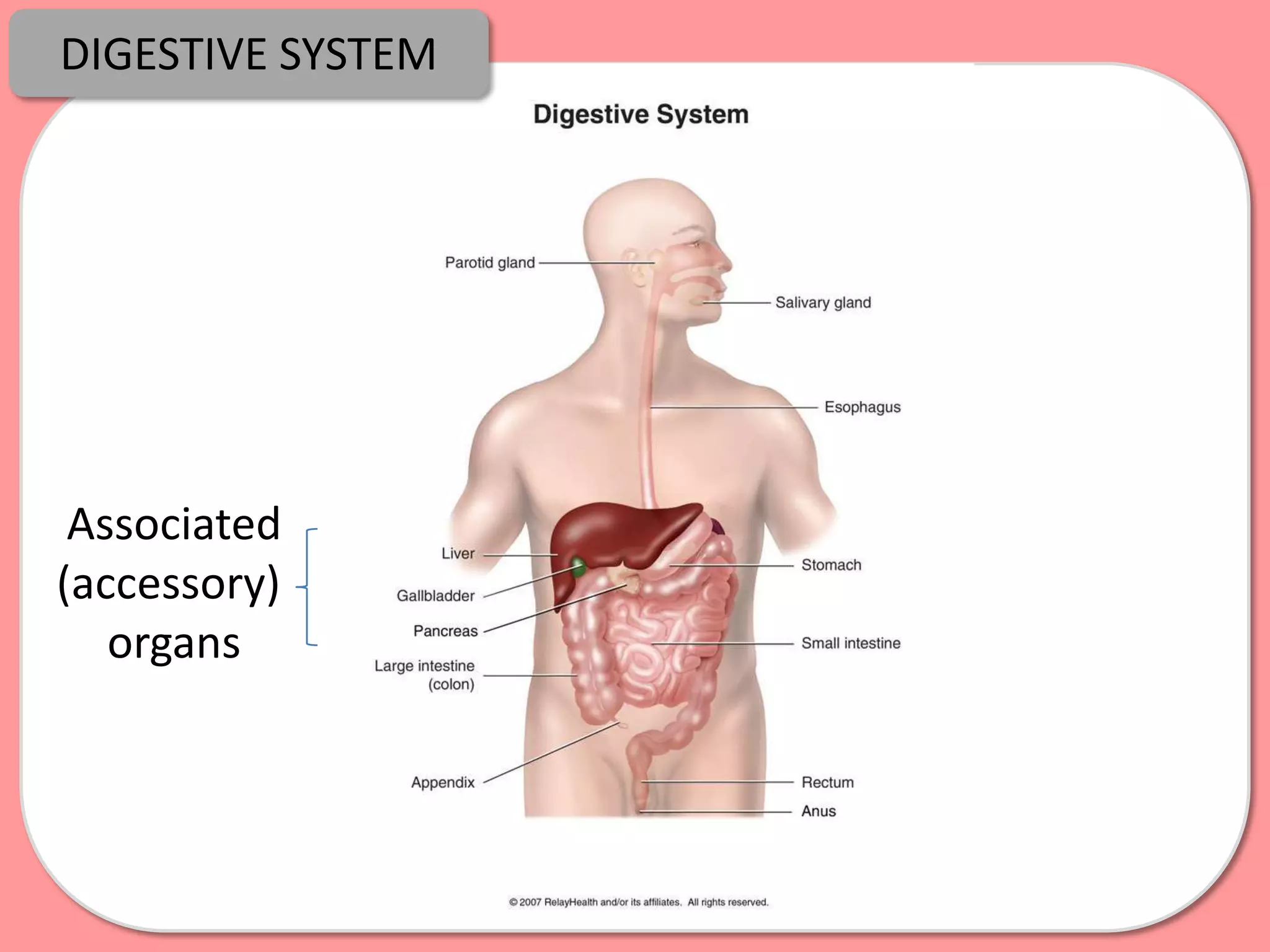
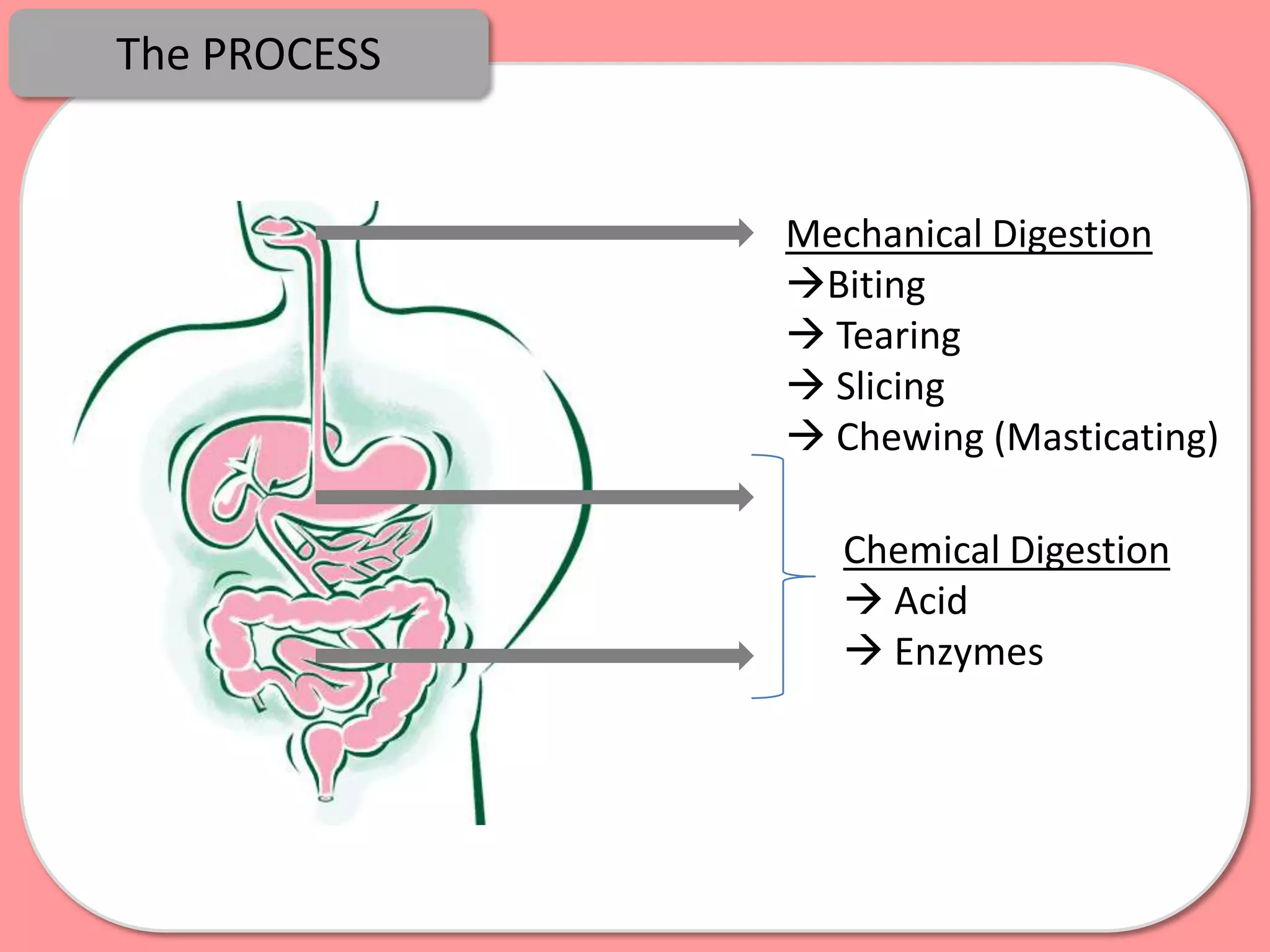
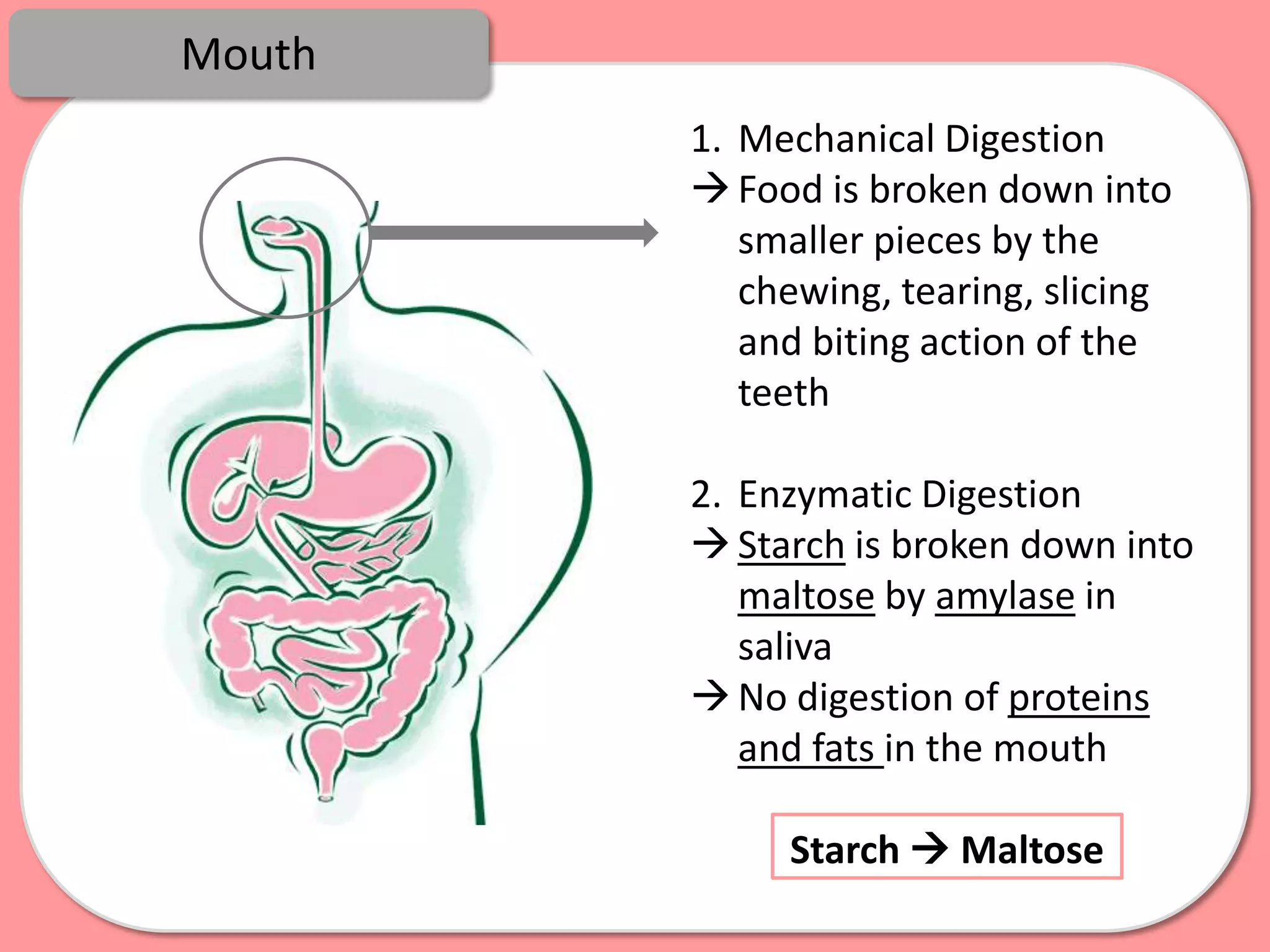
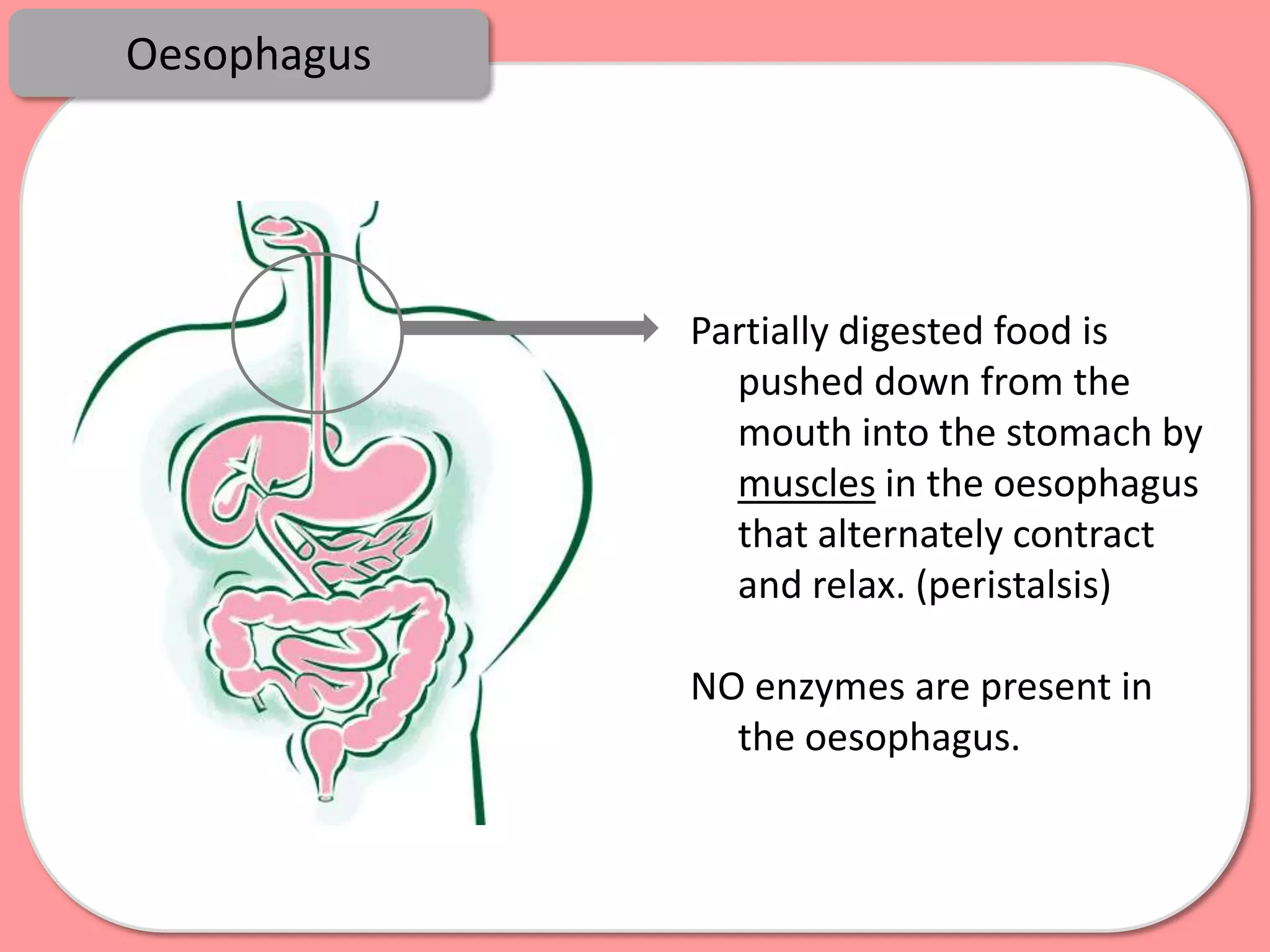
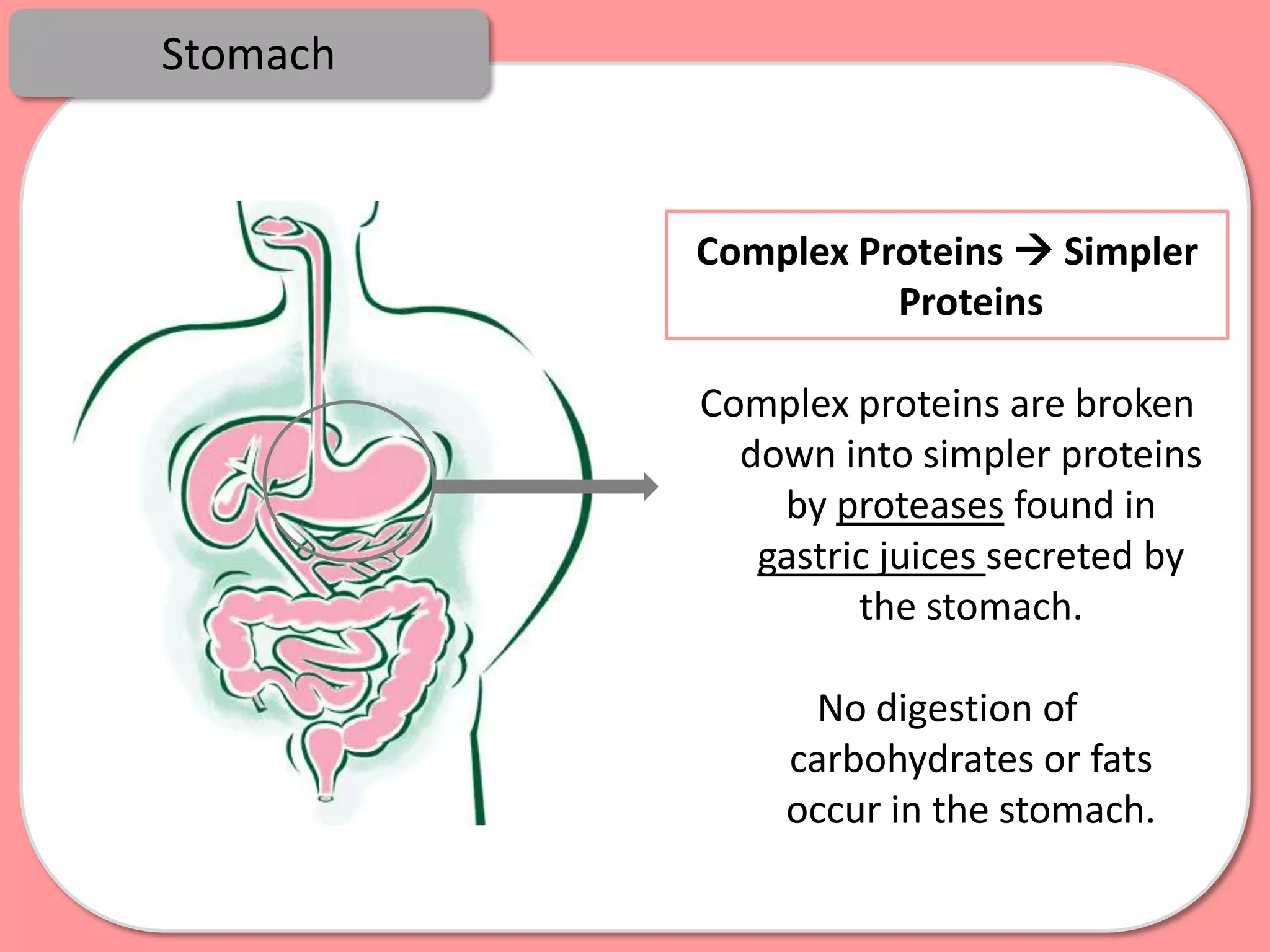
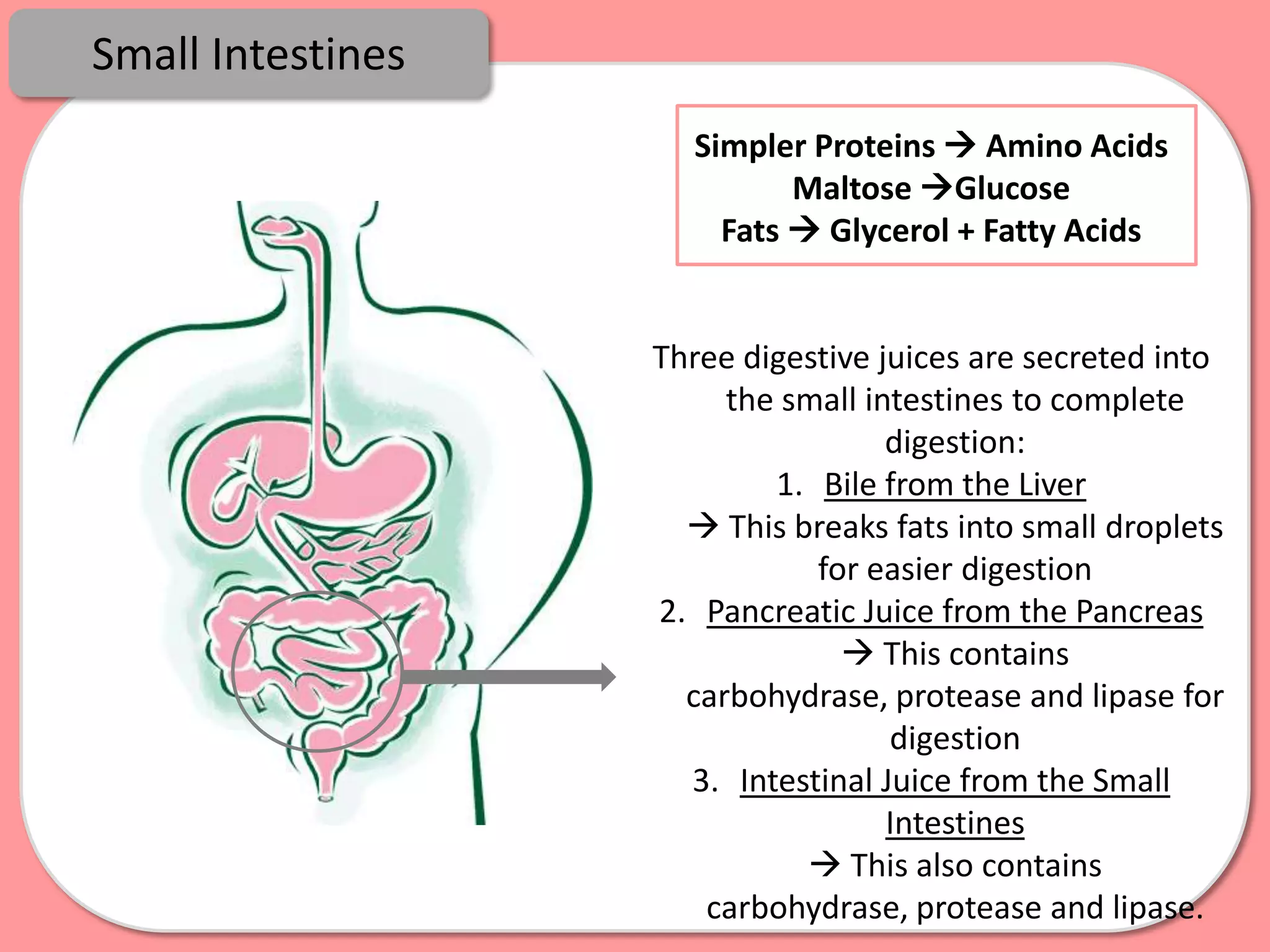
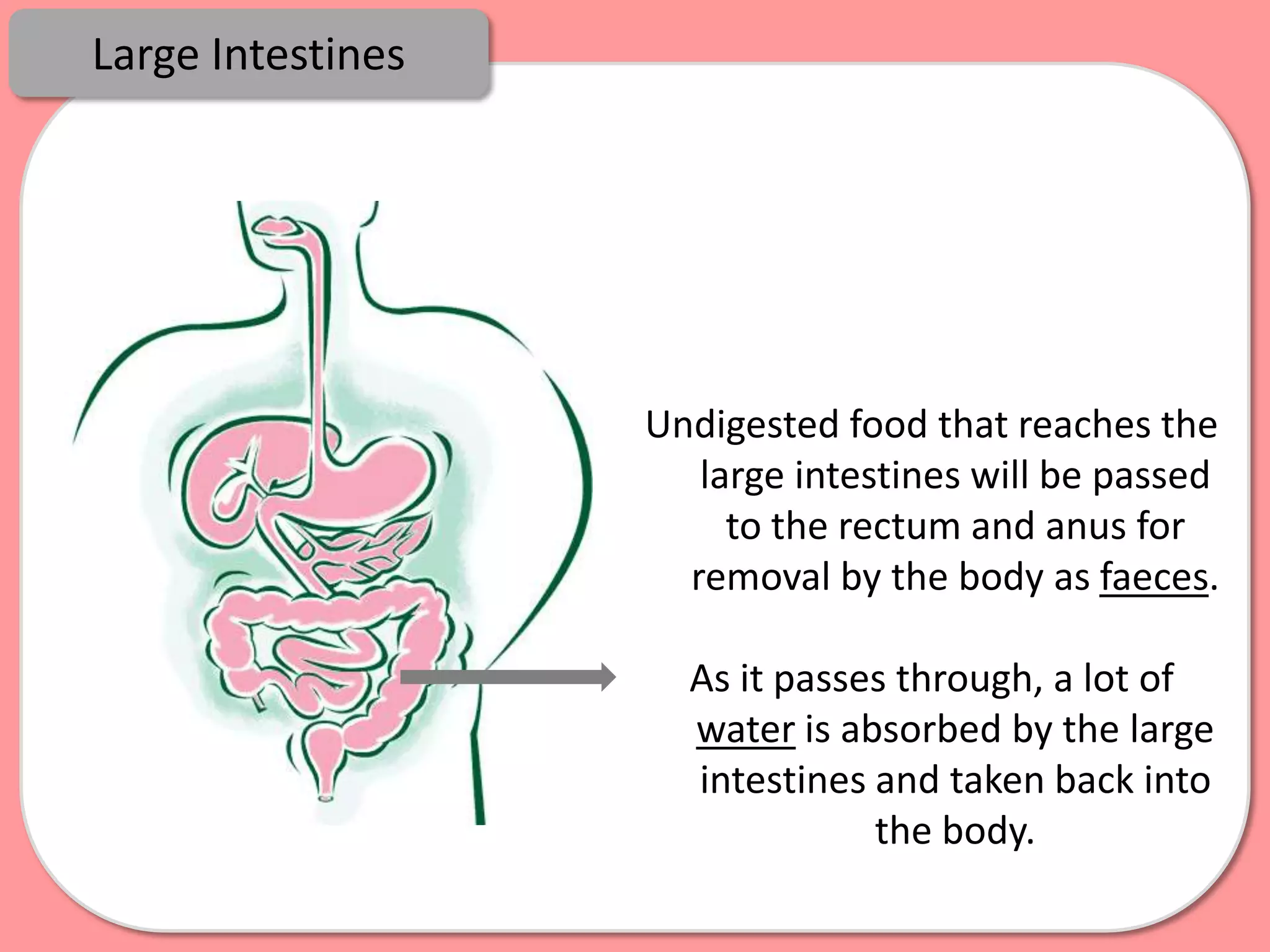
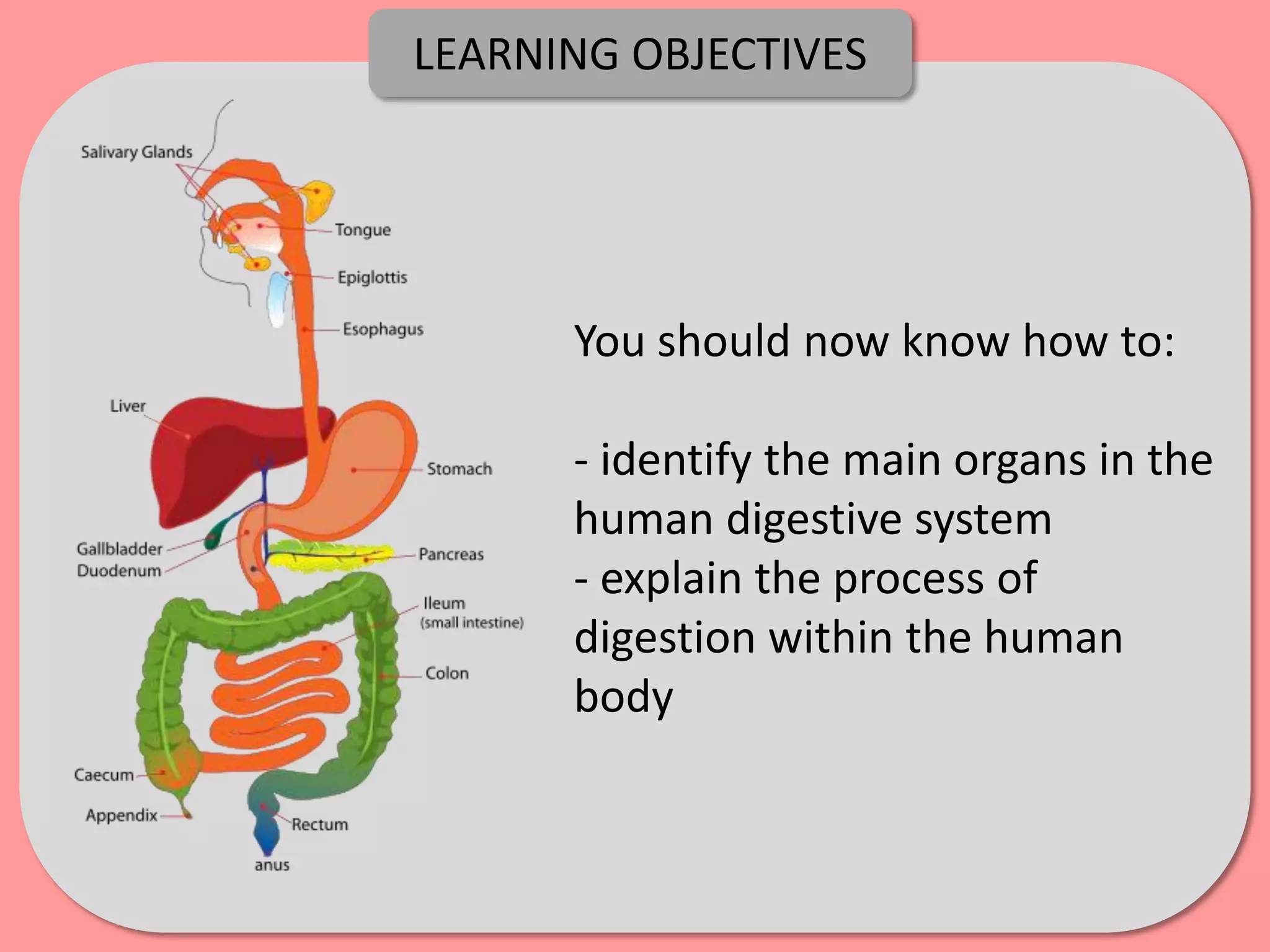
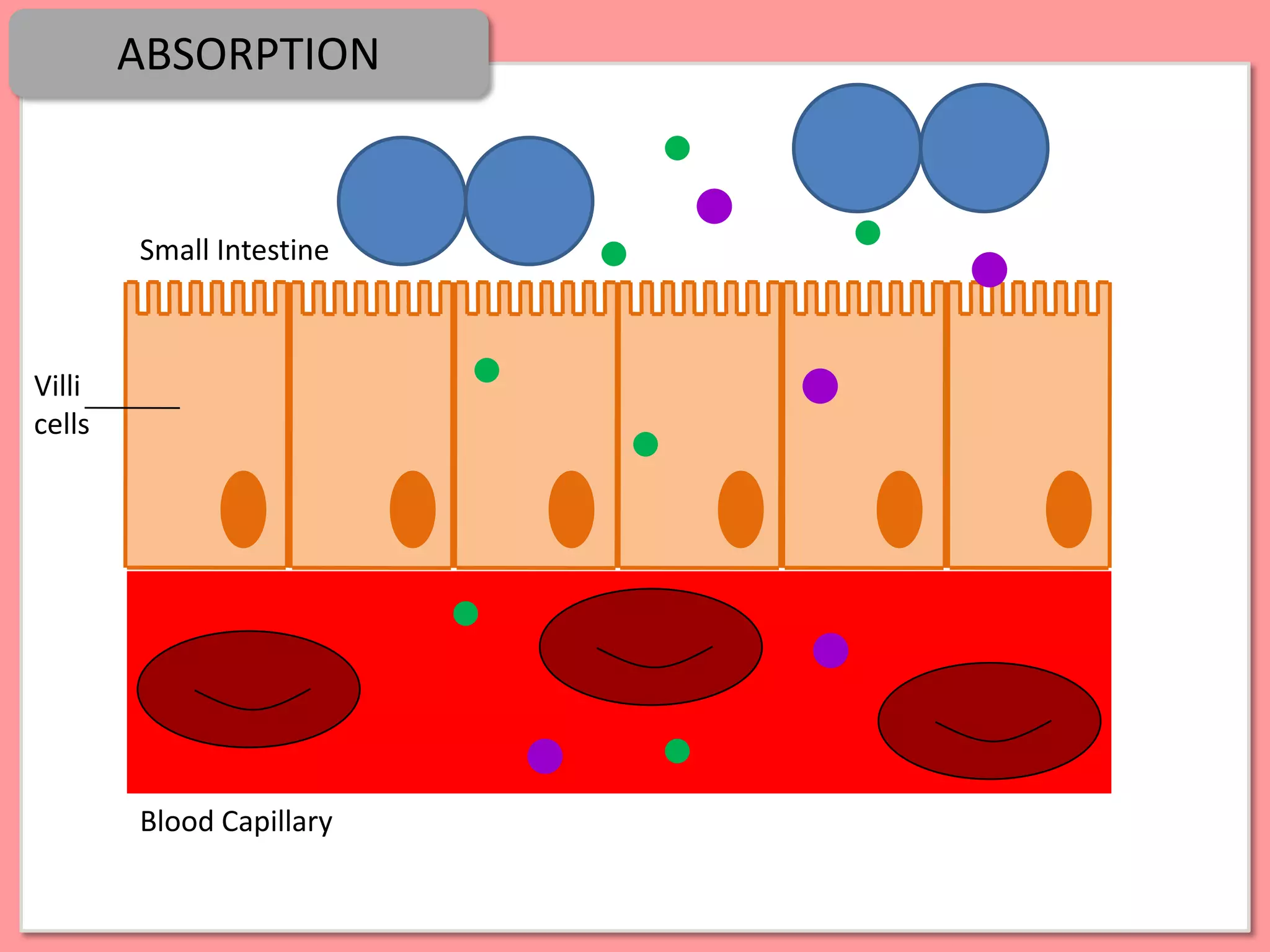
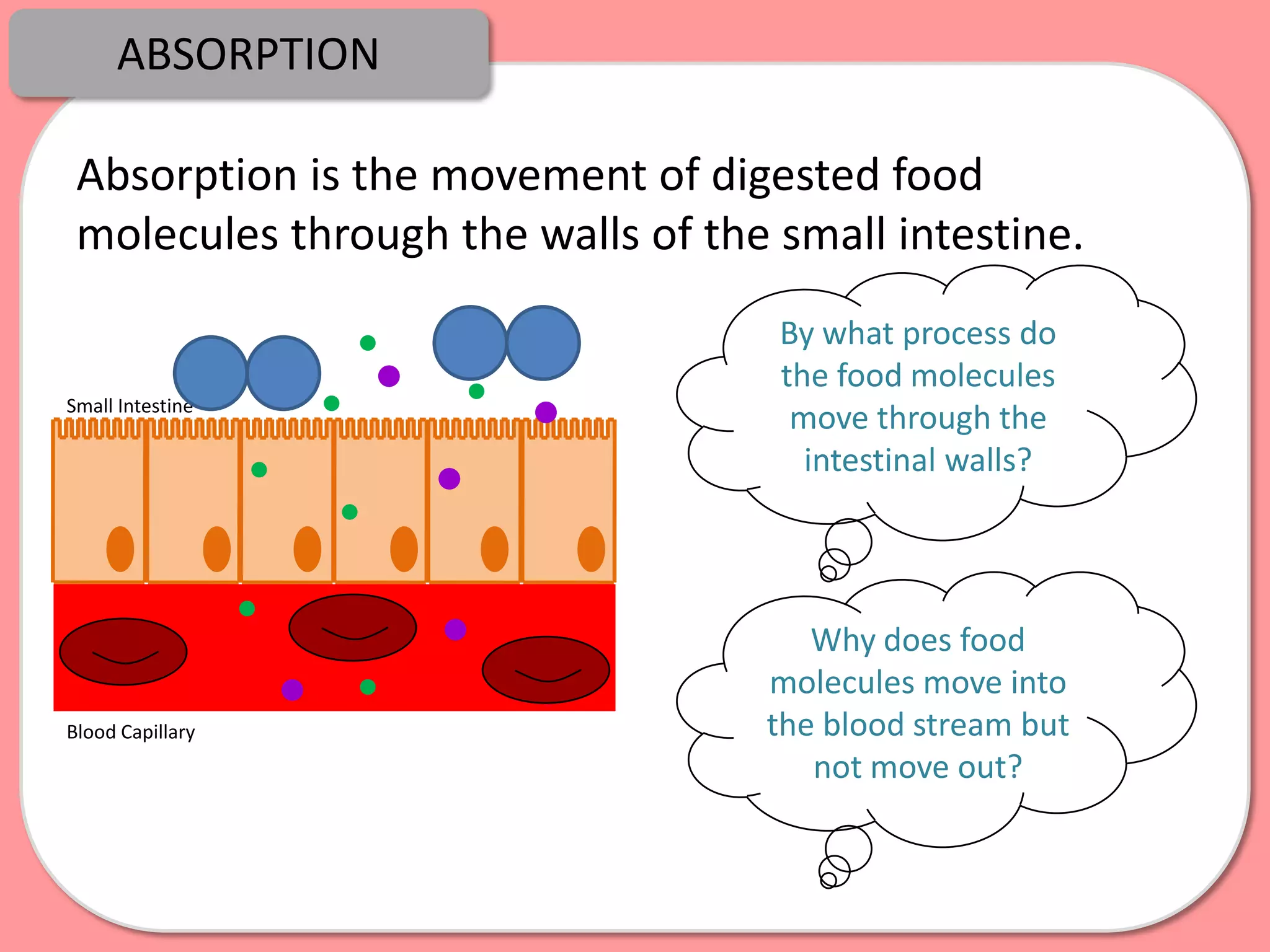
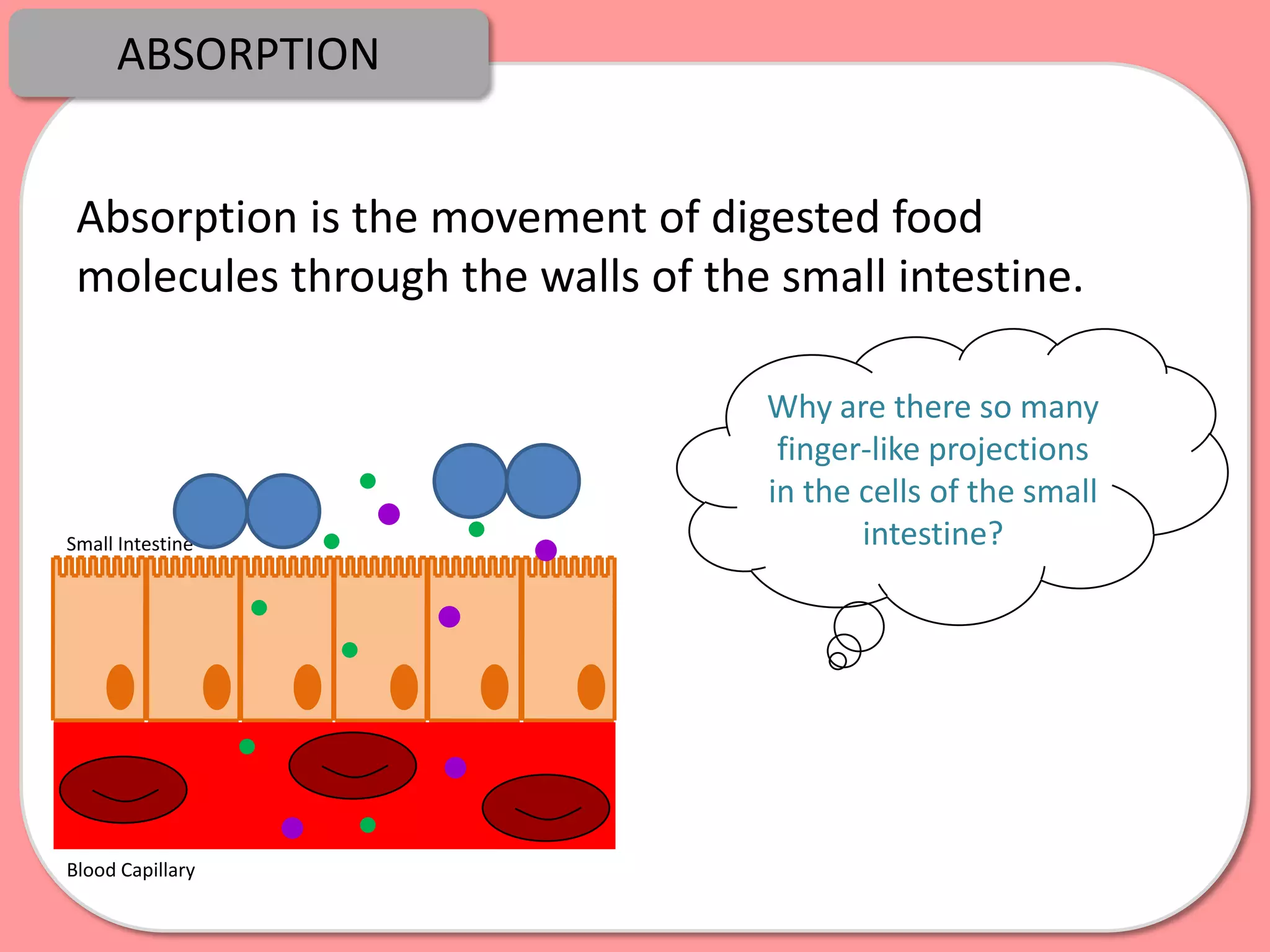
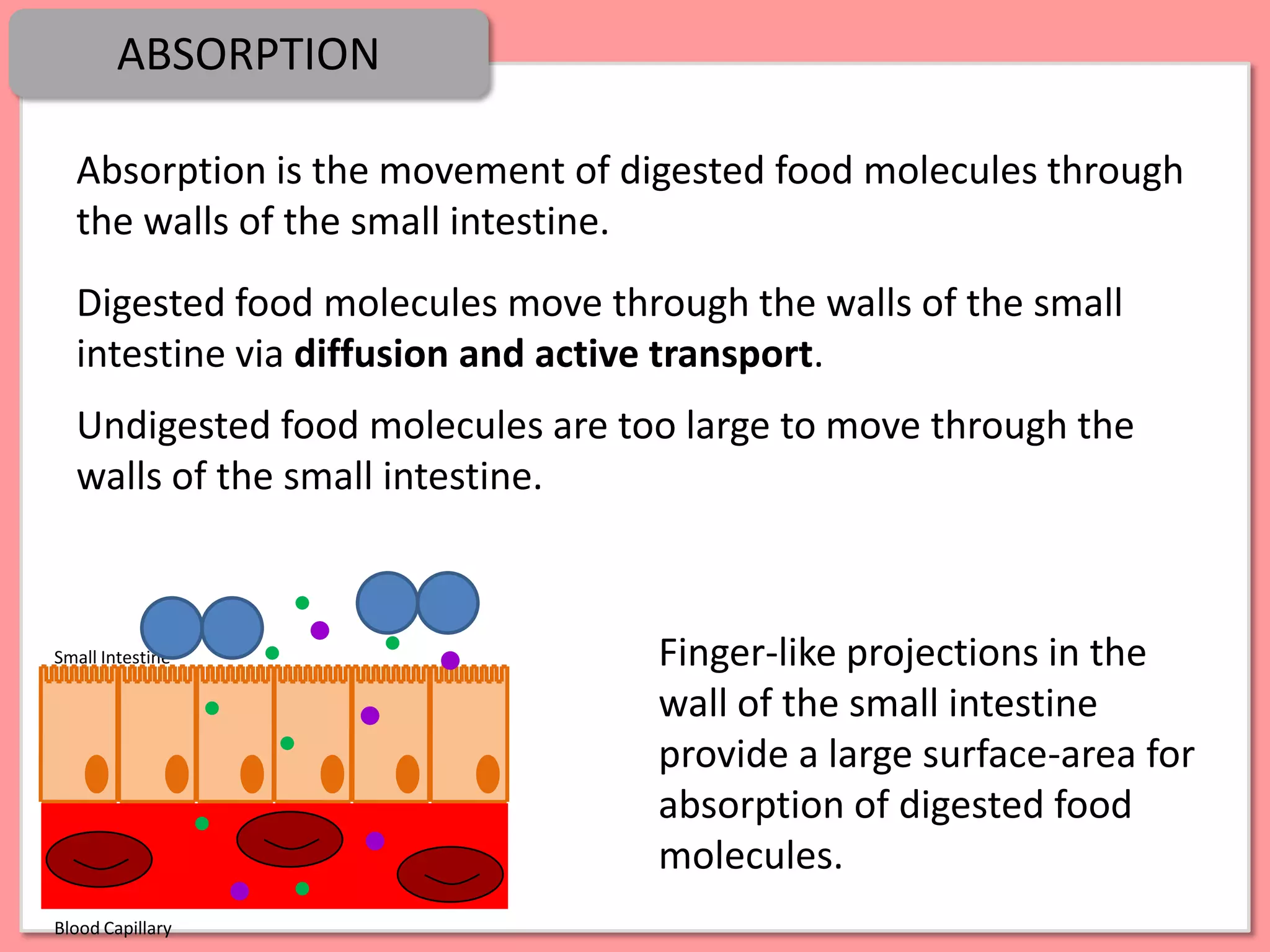
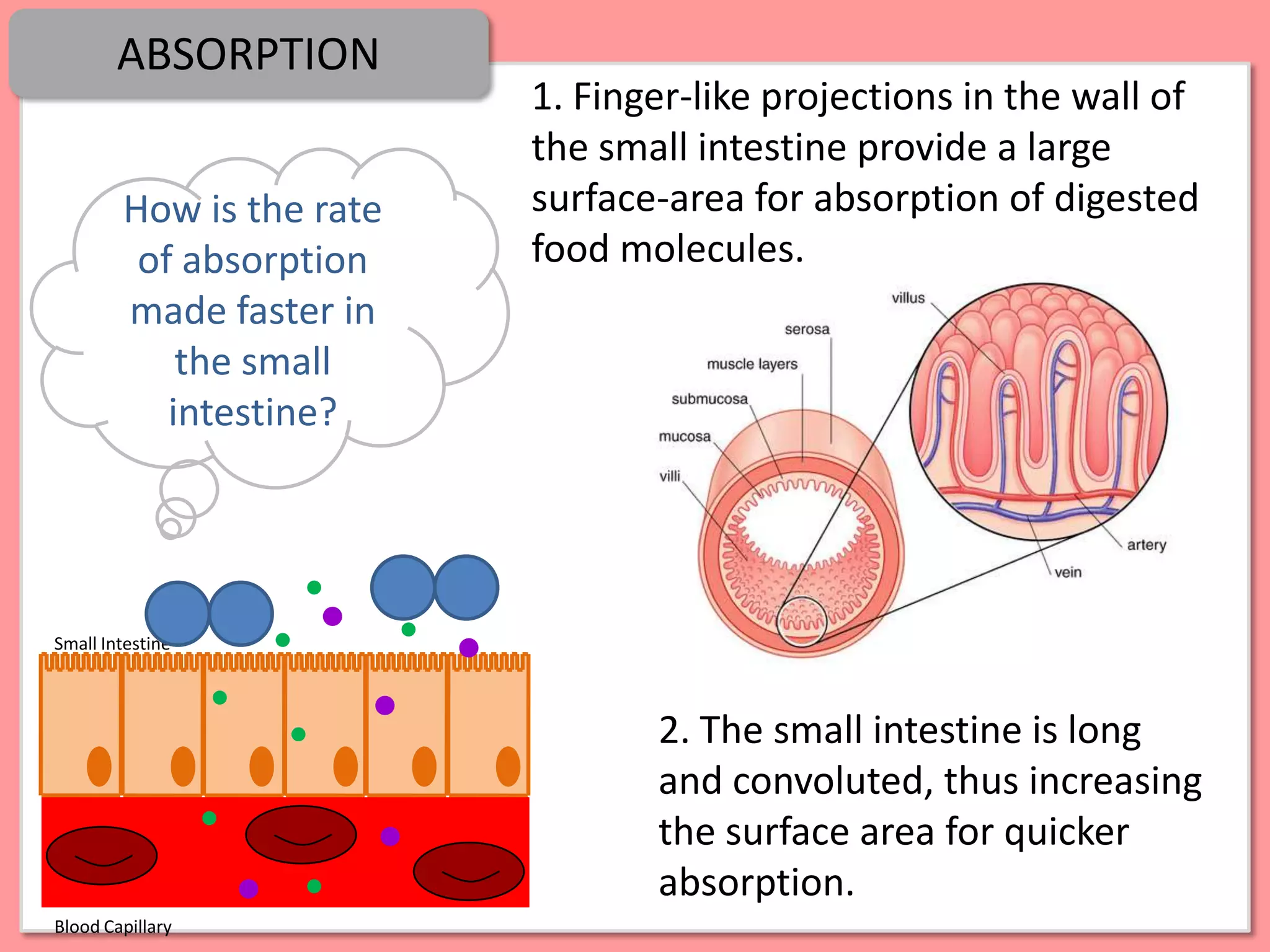
Digestion is the process by which food is broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by cells to provide energy and building materials. Various organs work together to mechanically and chemically break down food, including the mouth, stomach, and small intestine. Enzymes play a key role in digestion by speeding up chemical reactions to break nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into simpler substances like glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids. The small intestine contains villi and microvilli that increase its surface area for absorption of digested nutrients into the bloodstream via diffusion and active transport.