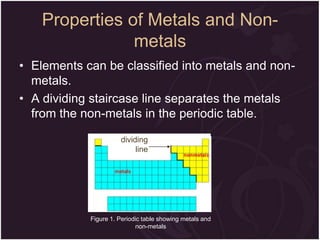
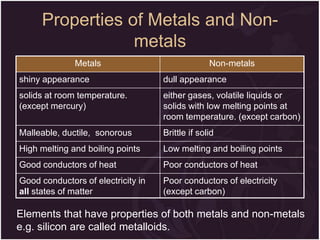
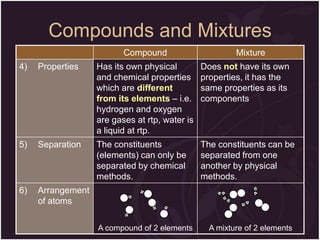
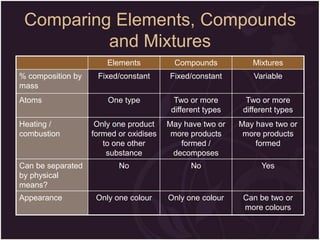
This document describes the key differences between elements, compounds, and mixtures. It states that elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down further, while compounds are formed by a chemical reaction and have a fixed composition. Mixtures have a variable composition and do not undergo chemical changes. Examples of each are provided. The document also discusses the properties of metals and nonmetals, and provides exercises to test the understanding of these concepts.