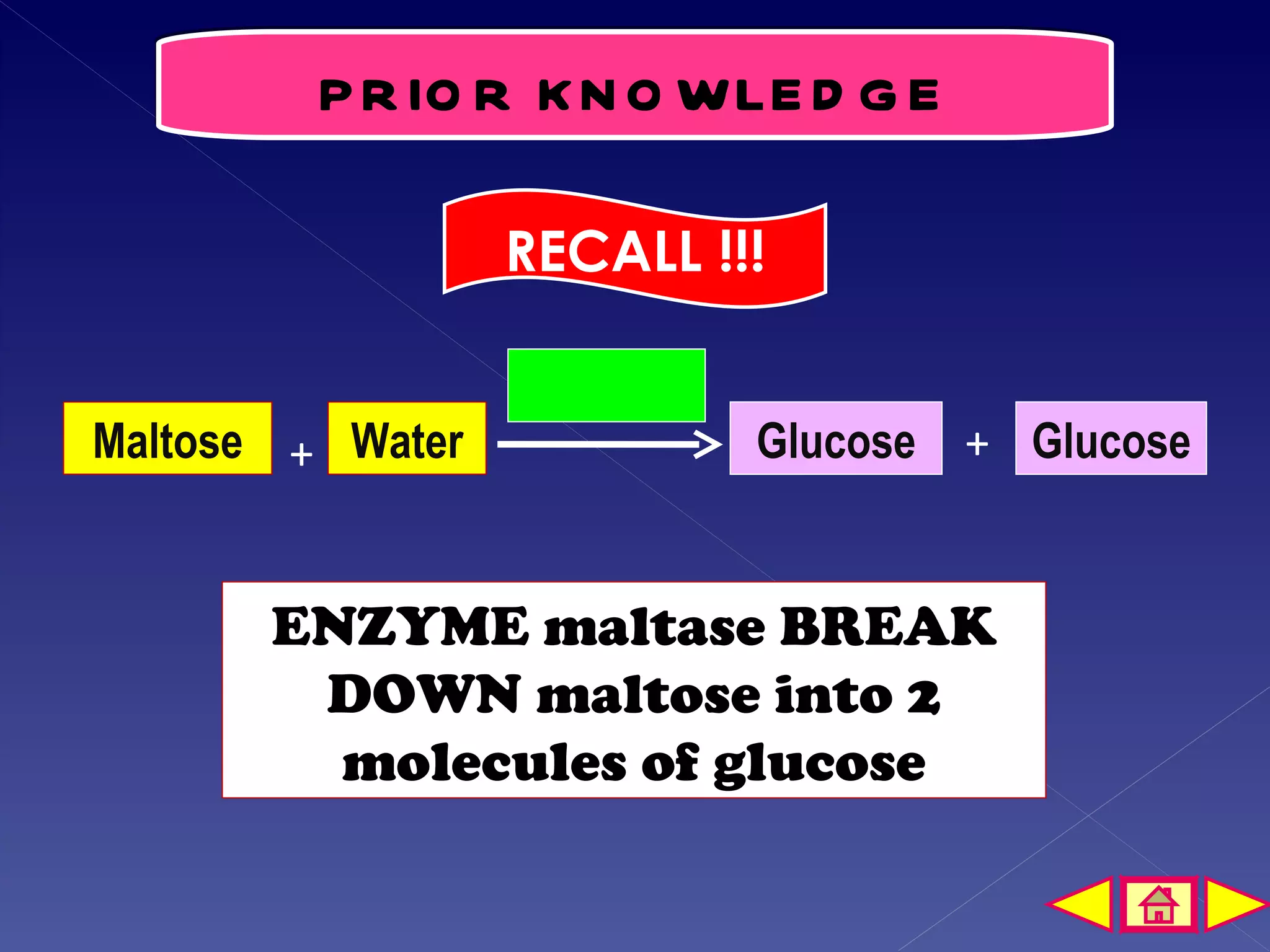
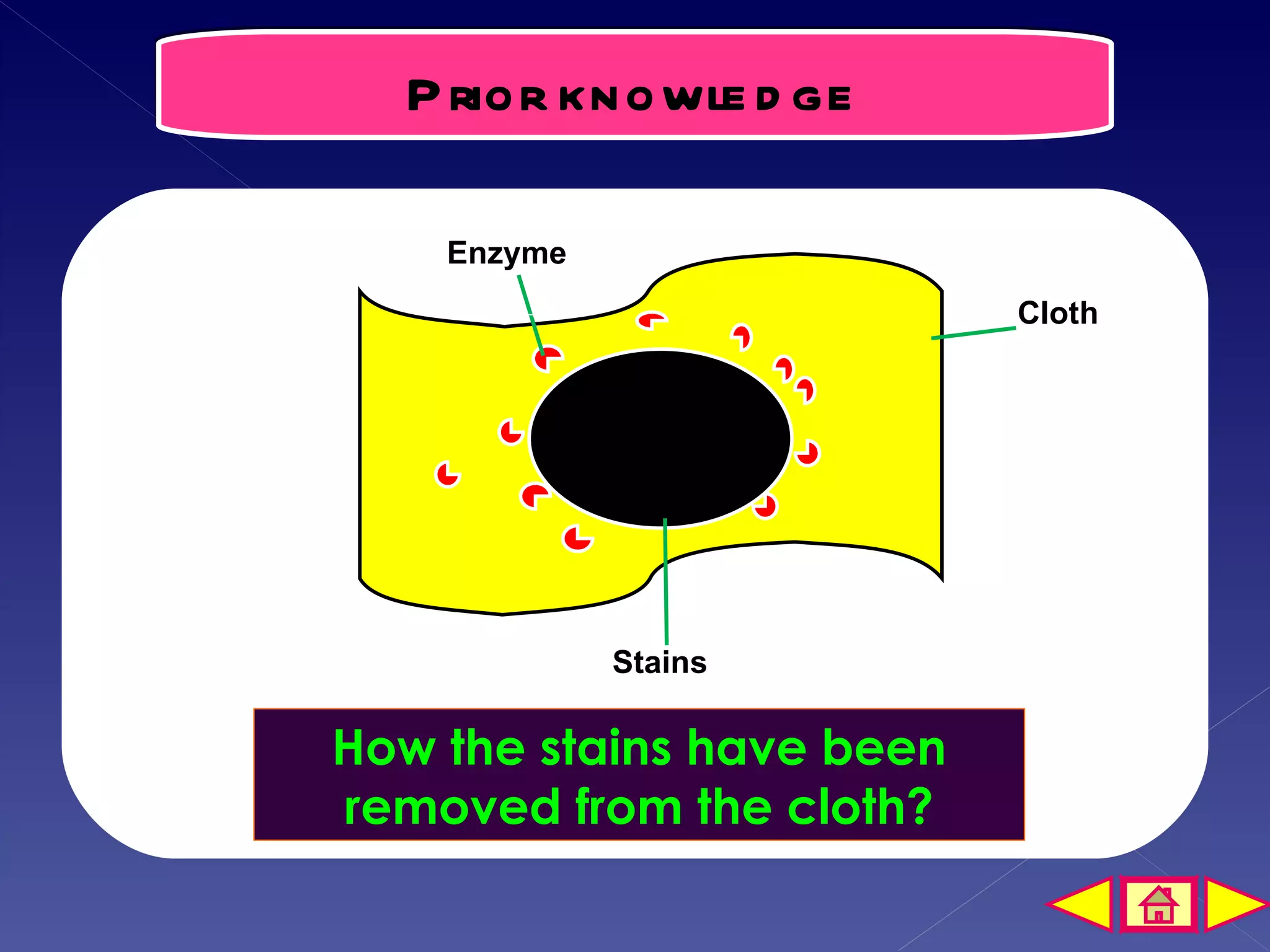
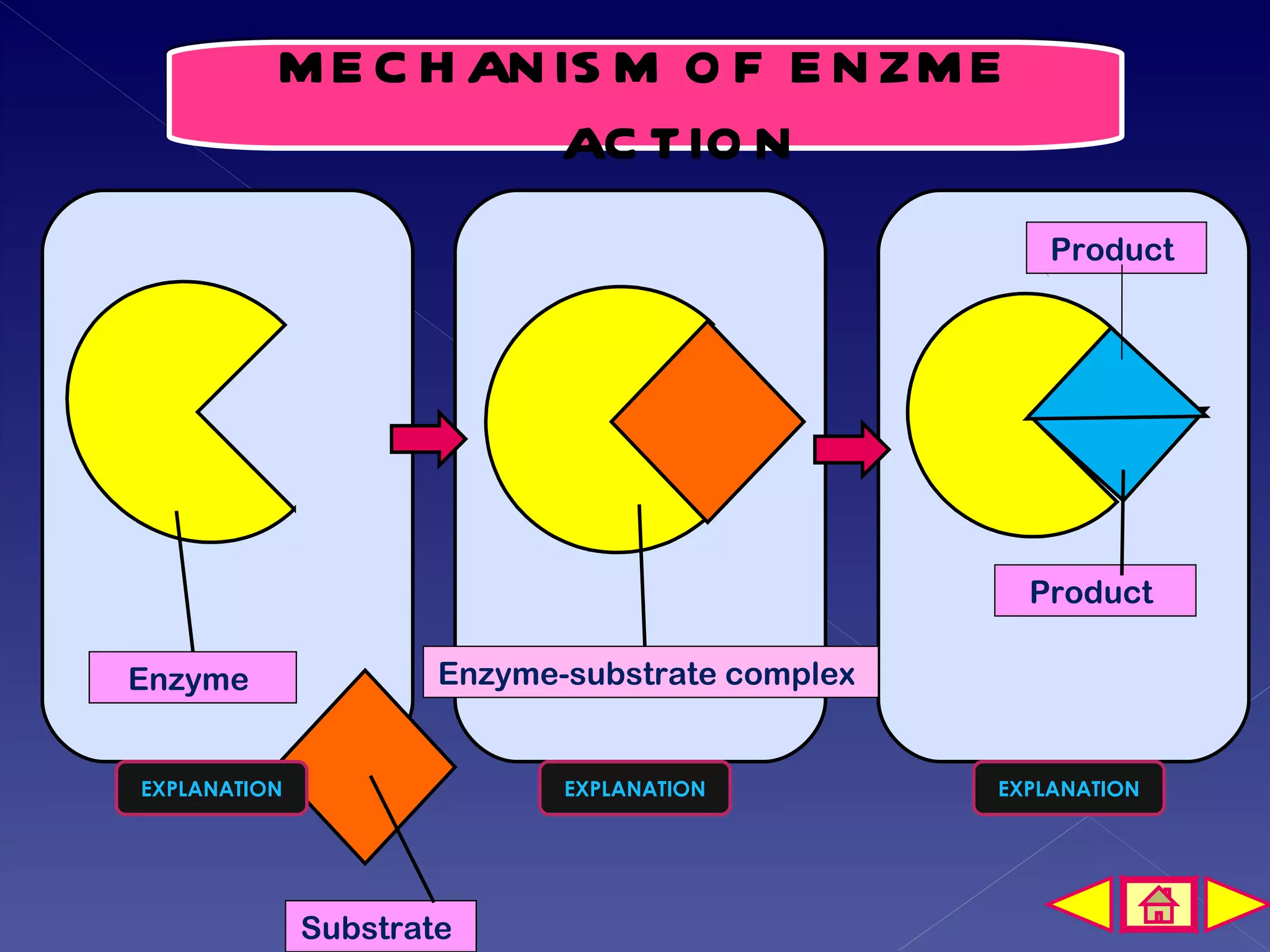
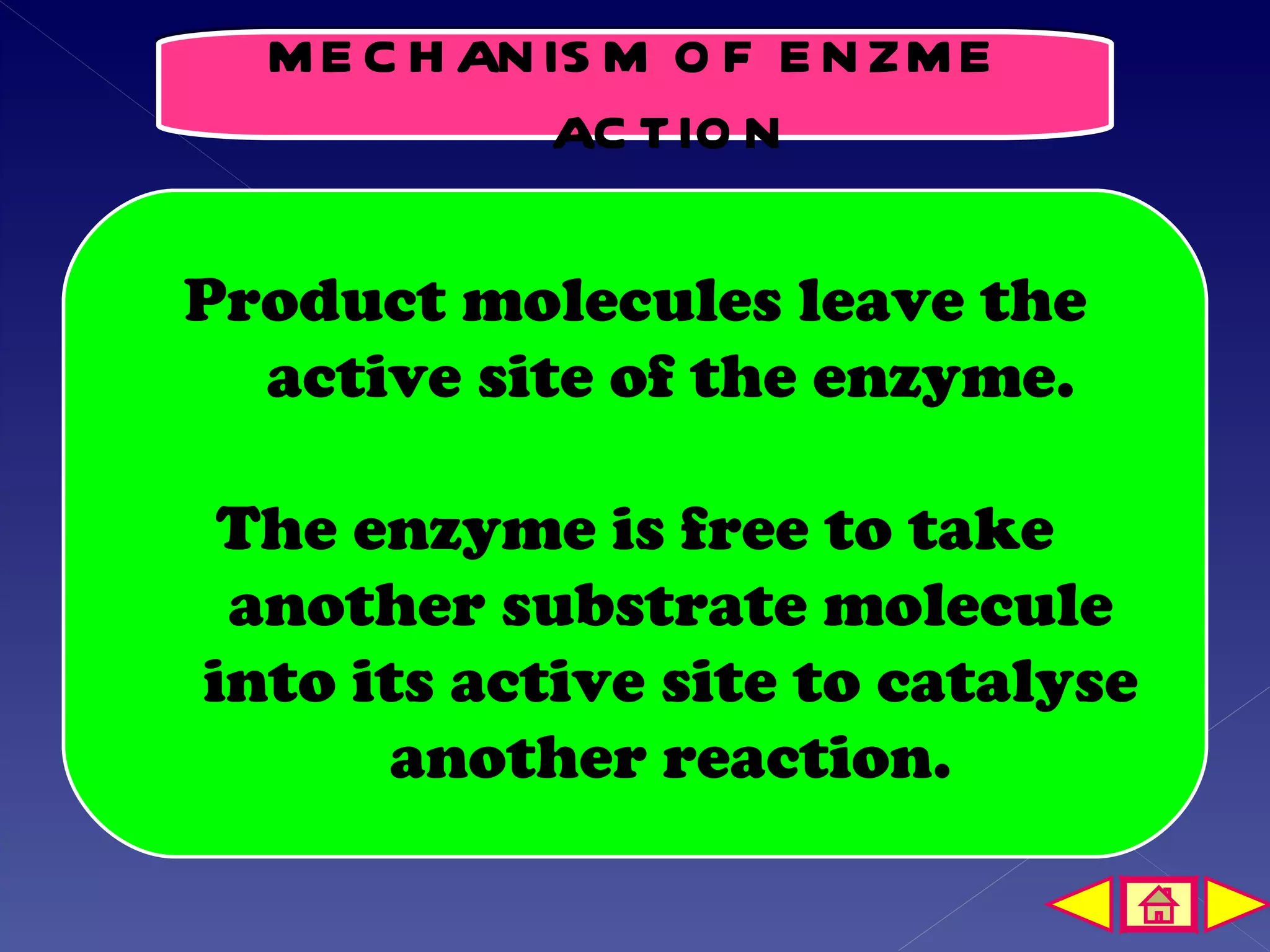
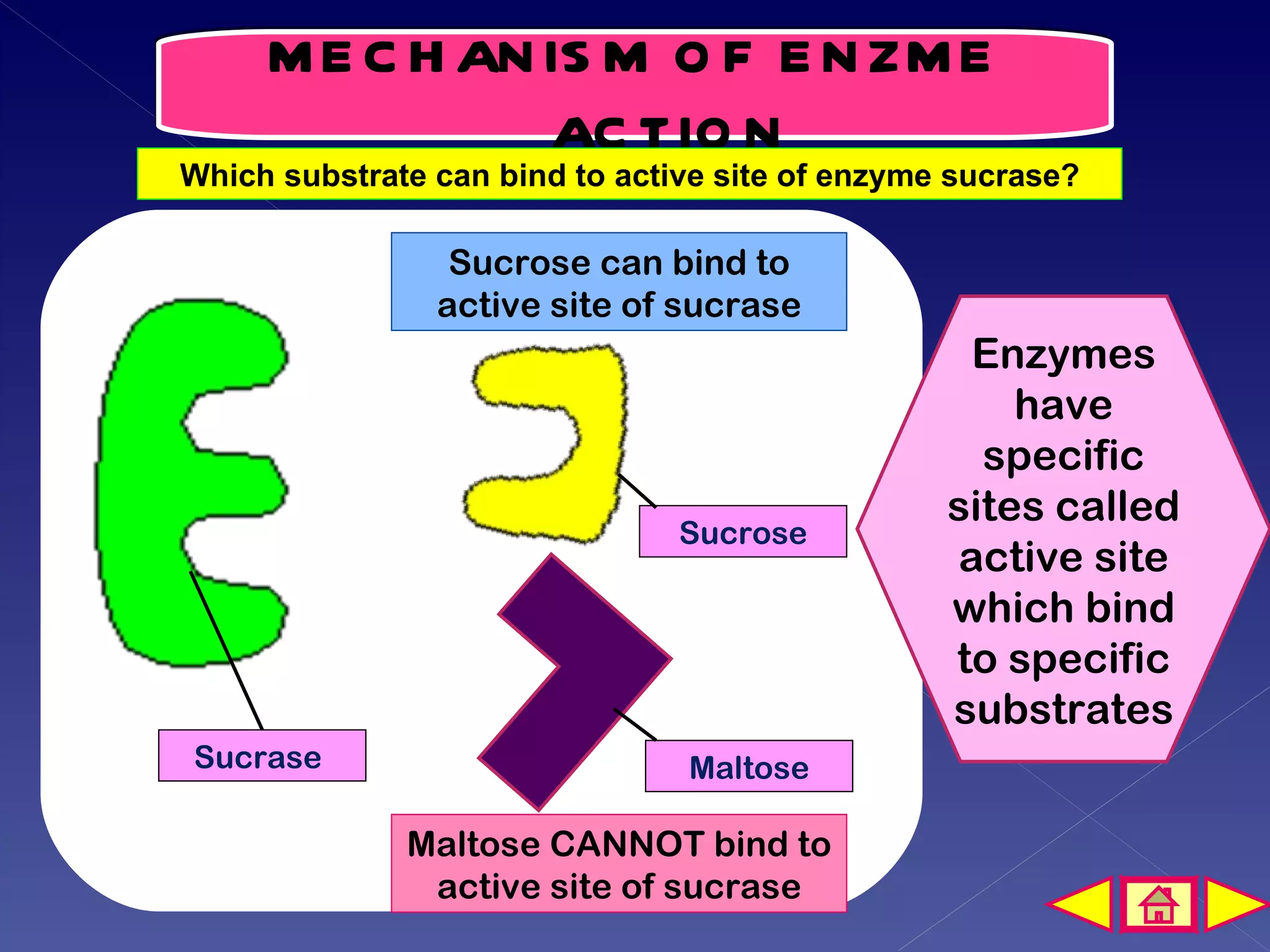
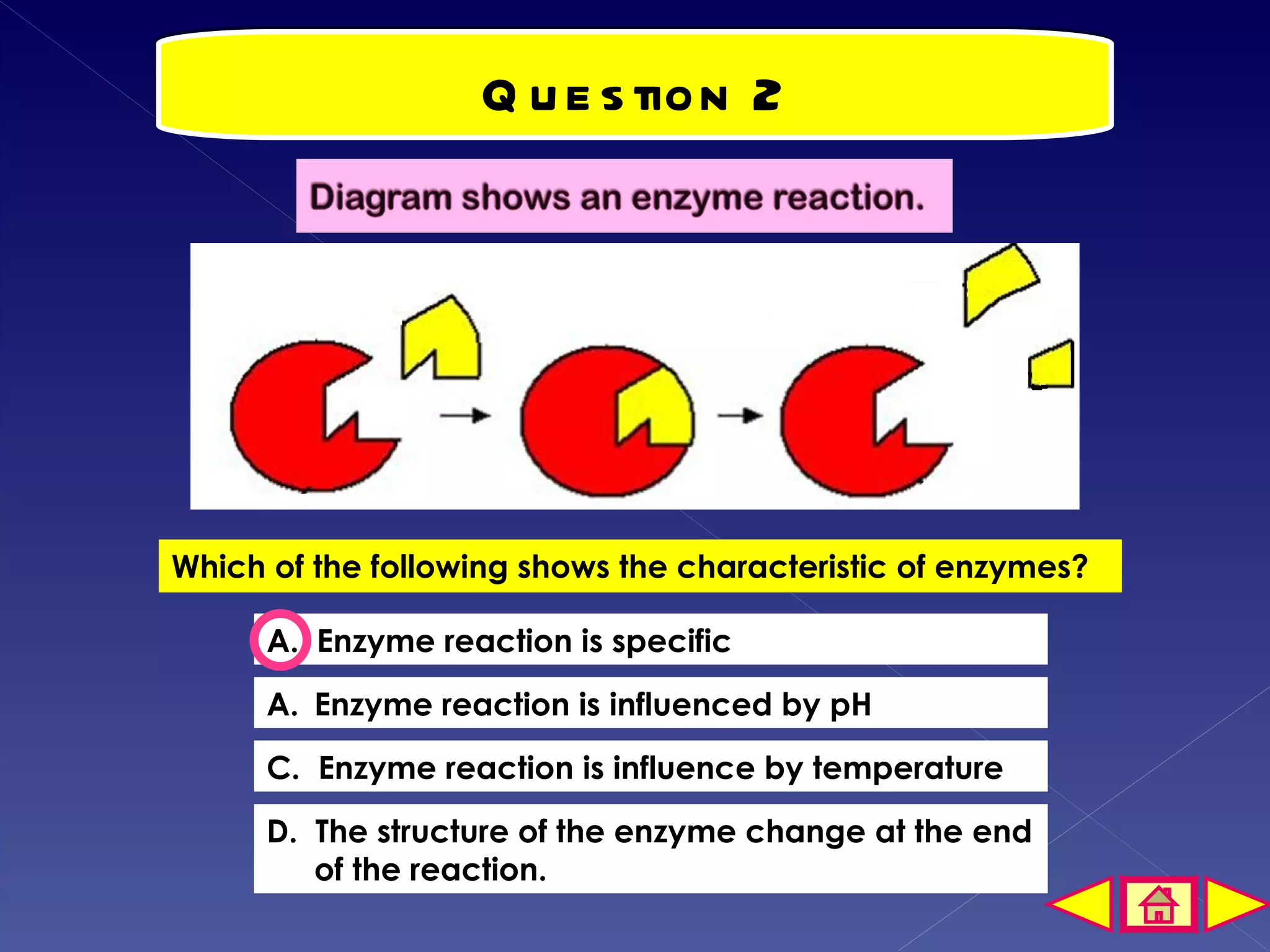
This document discusses the mechanism of enzyme action through a learning outcome and several sections. It begins with introducing the topic of enzyme mechanisms and defining enzymes as biological catalysts for cellular reactions. It then explains the "lock and key" hypothesis for enzyme action, where a specific substrate molecule binds to the active site of an enzyme, forming an unstable enzyme-substrate complex. This allows the substrate to be converted into products, which then leave the active site so the enzyme can catalyze another reaction. The document assessments students' understanding with multiple choice and short answer questions about enzyme specificity and how temperature affects reaction rates.