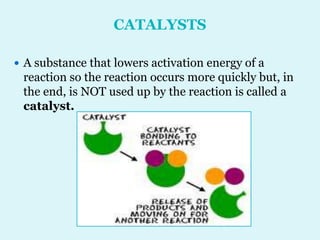
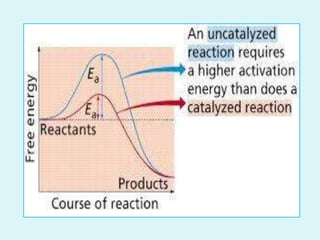
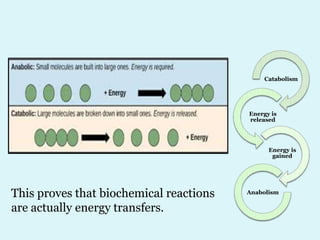
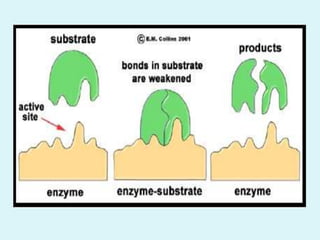
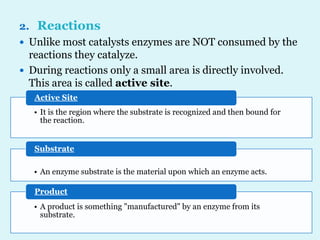
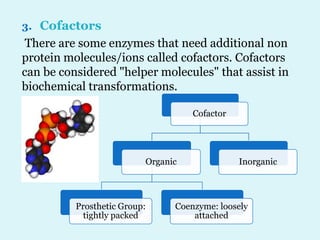
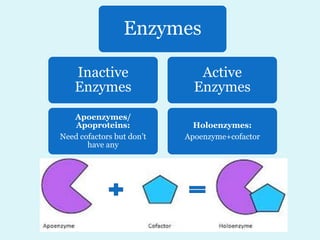
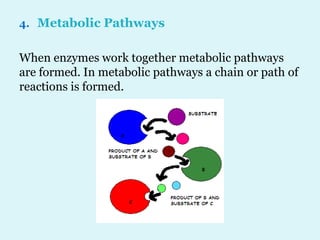
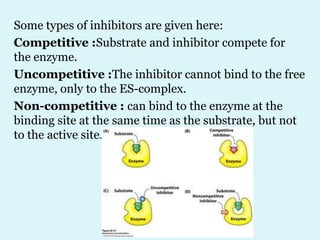
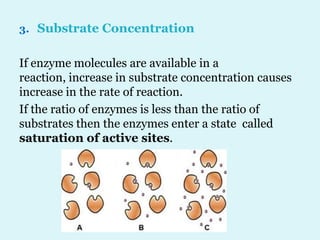
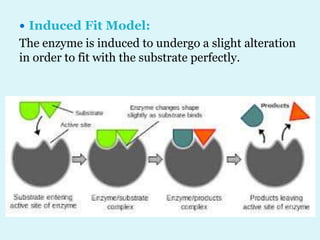
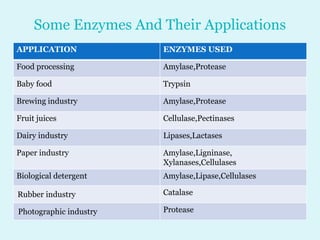
Enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions in living organisms. They are usually proteins that lower the activation energy of reactions and bring substrates together in the correct orientation. Enzymes work through specific active sites and are not consumed by reactions. They are affected by factors like temperature, pH, and substrate concentration. The lock and key and induced fit models describe how enzymes specifically interact with substrates. Enzymes have many uses in industries like food processing, brewing, paper production, and detergents.