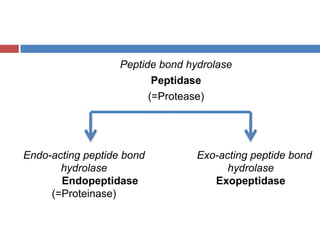
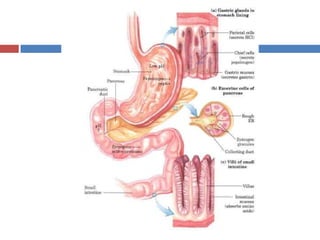
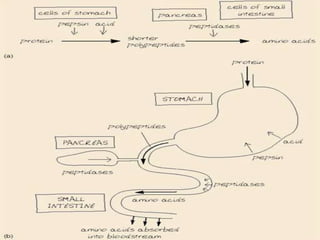
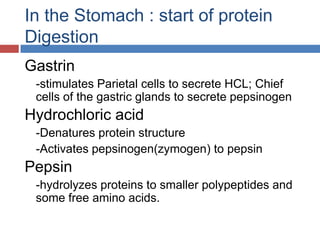
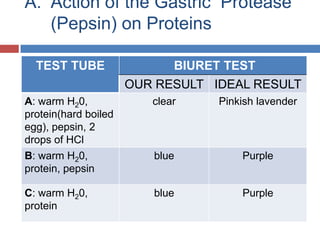
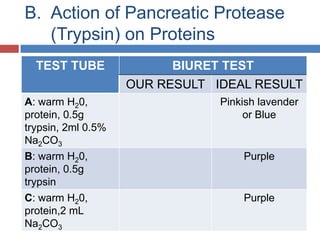
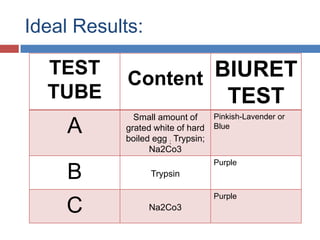
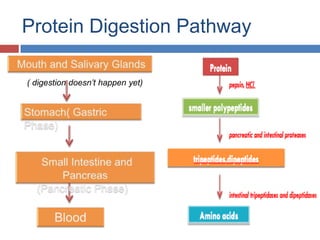
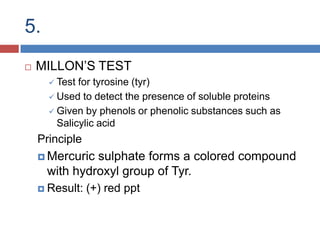
Protein digestion is a two-step process involving enzymes in the stomach and small intestine. In the stomach, pepsin breaks down proteins into smaller polypeptides and some amino acids. In the small intestine, proteases like trypsin and peptidases further break down polypeptides into dipeptides and individual amino acids, which are then absorbed. Tests like Biuret can detect the presence of proteins and the completeness of digestion. Factors like pH, temperature, and inhibitors affect the efficiency of protein digestion.