- Enzymes are biological catalysts made of proteins that speed up chemical reactions without being changed themselves. They work by lowering the activation energy required for reactions.
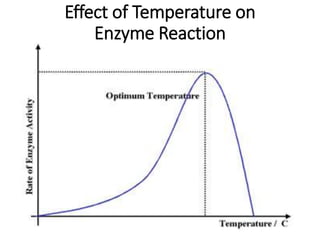
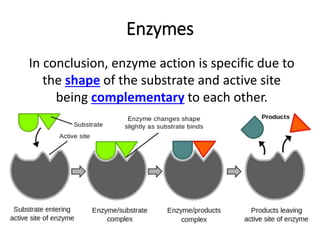
- Enzymes have an active site where substrates bind specifically. The enzyme-substrate complex leads to products. Enzyme activity is affected by temperature and pH. They are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels.
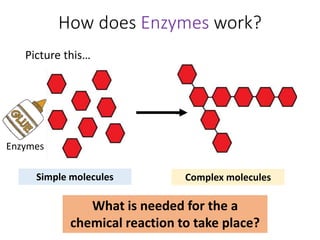
- Enzymes catalyze both the breaking down of large molecules and building up of complex molecules from simpler ones. They are required in small amounts and can catalyze reversible reactions.