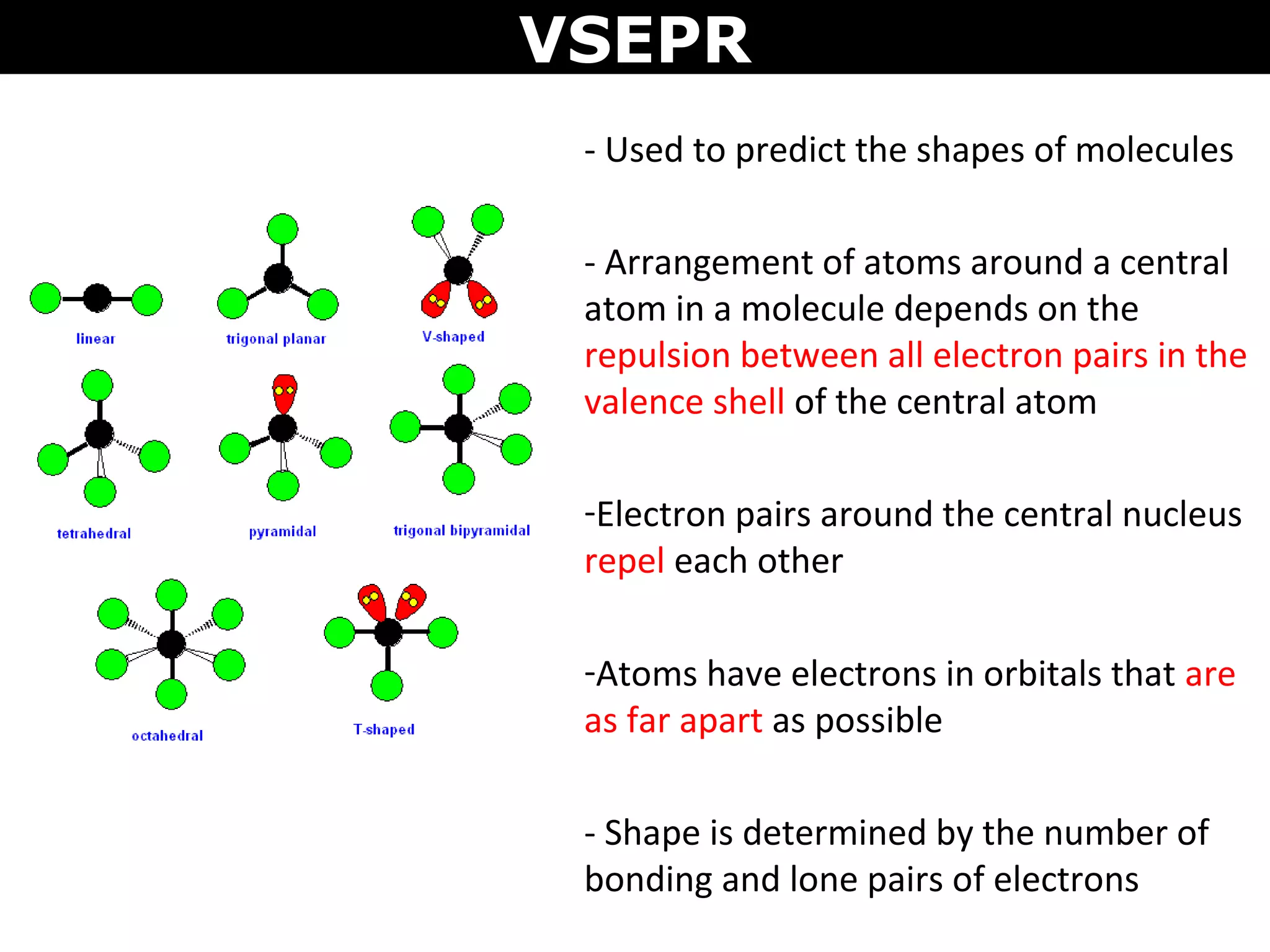
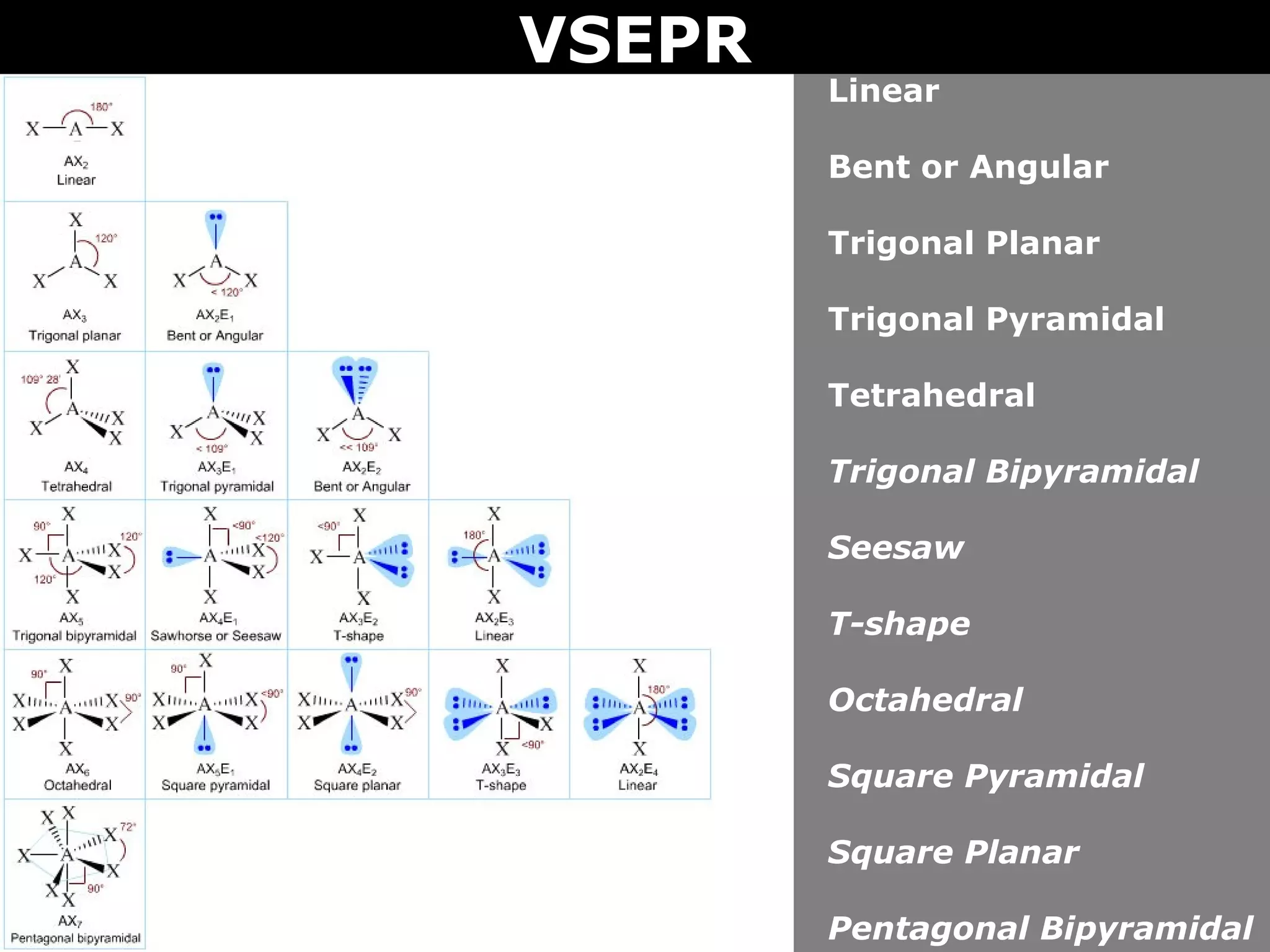
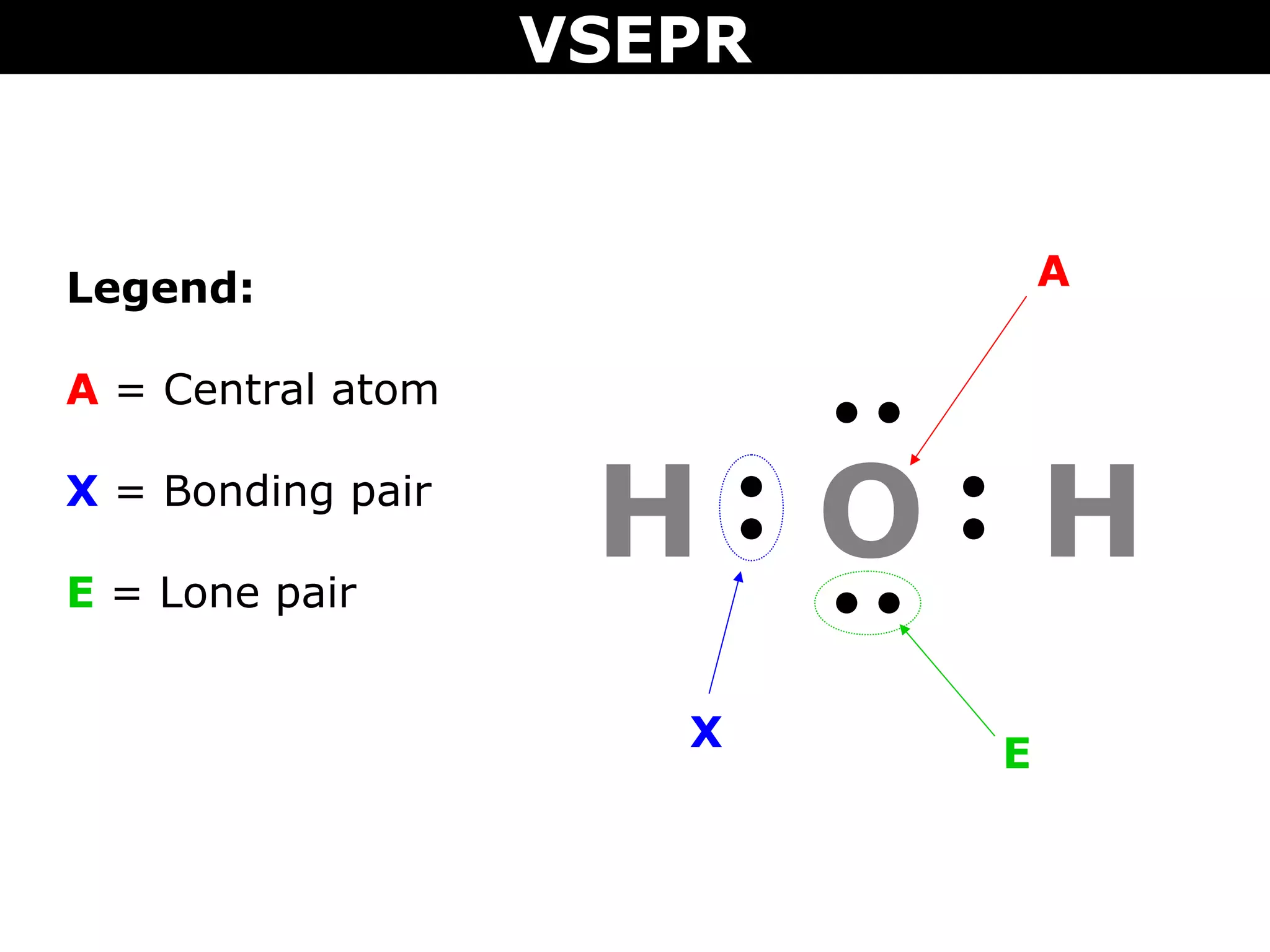
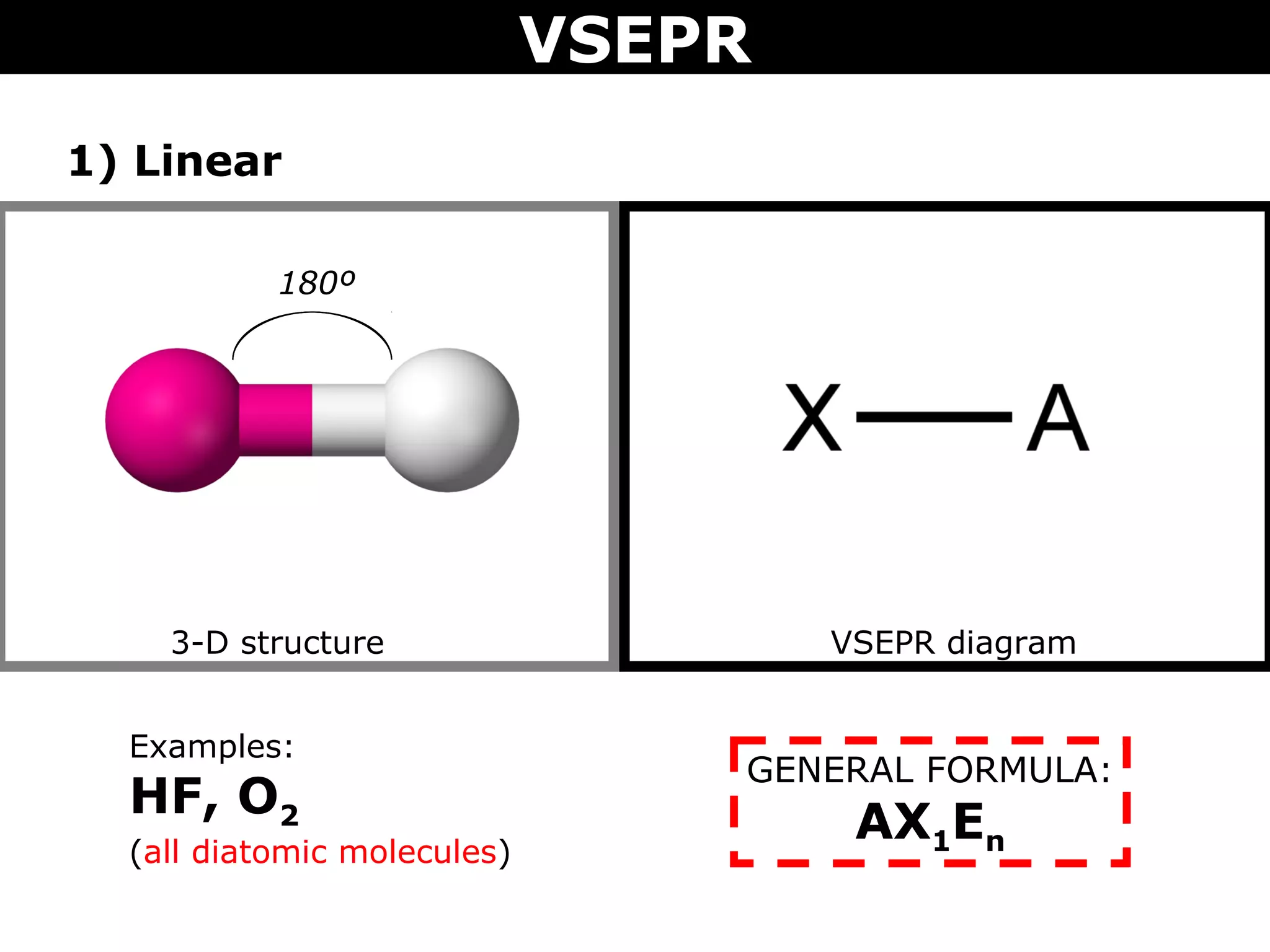
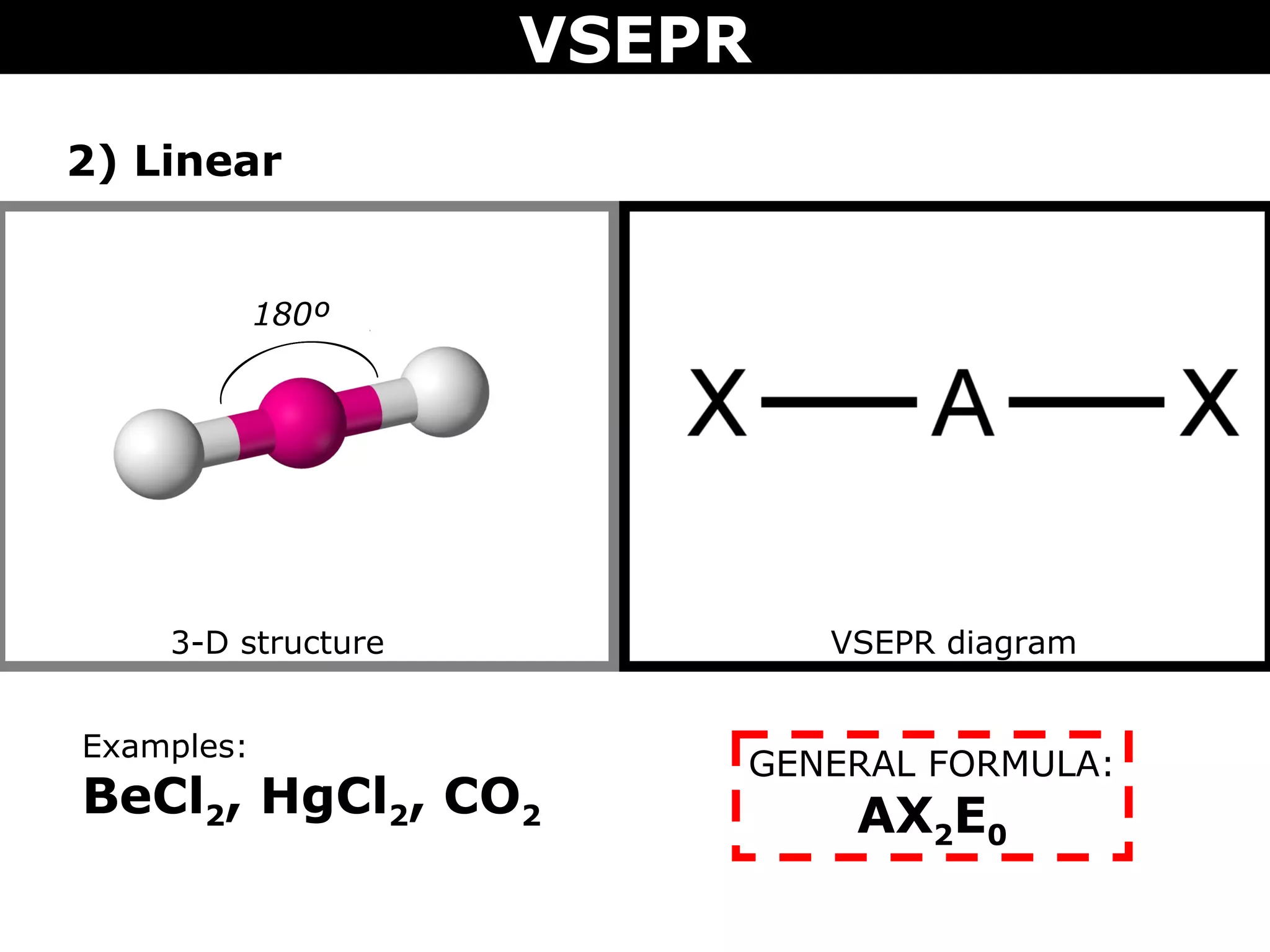
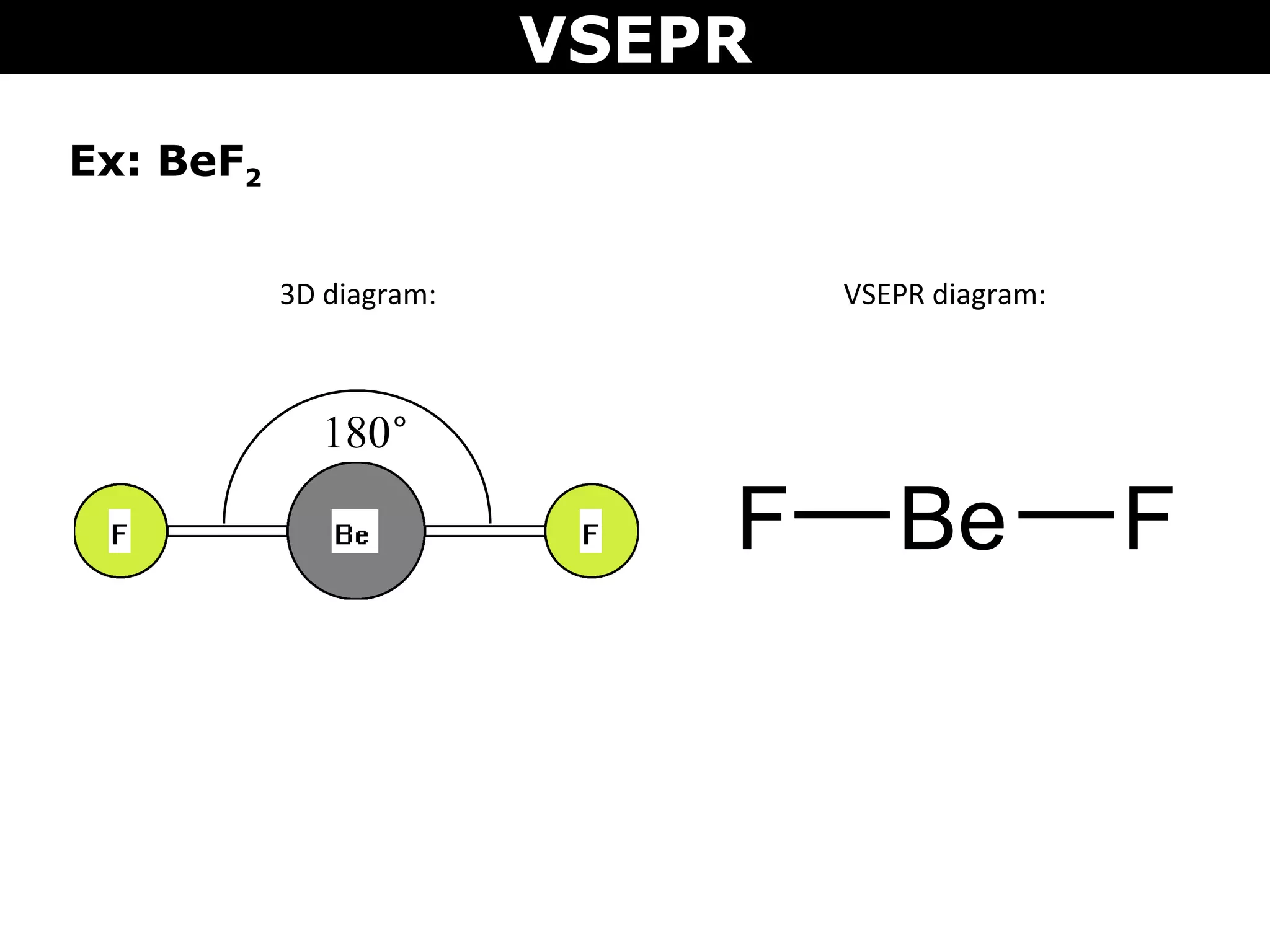
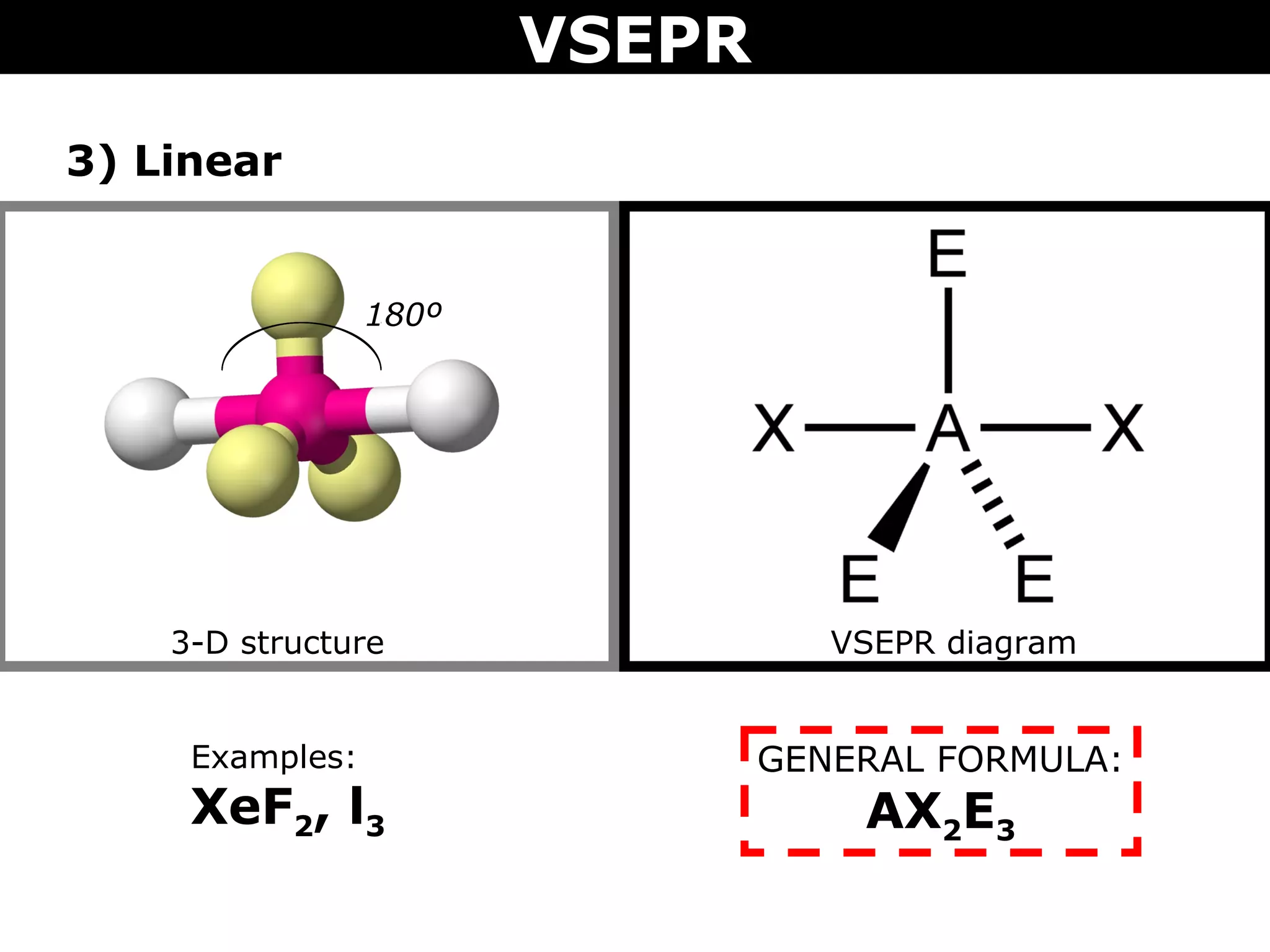
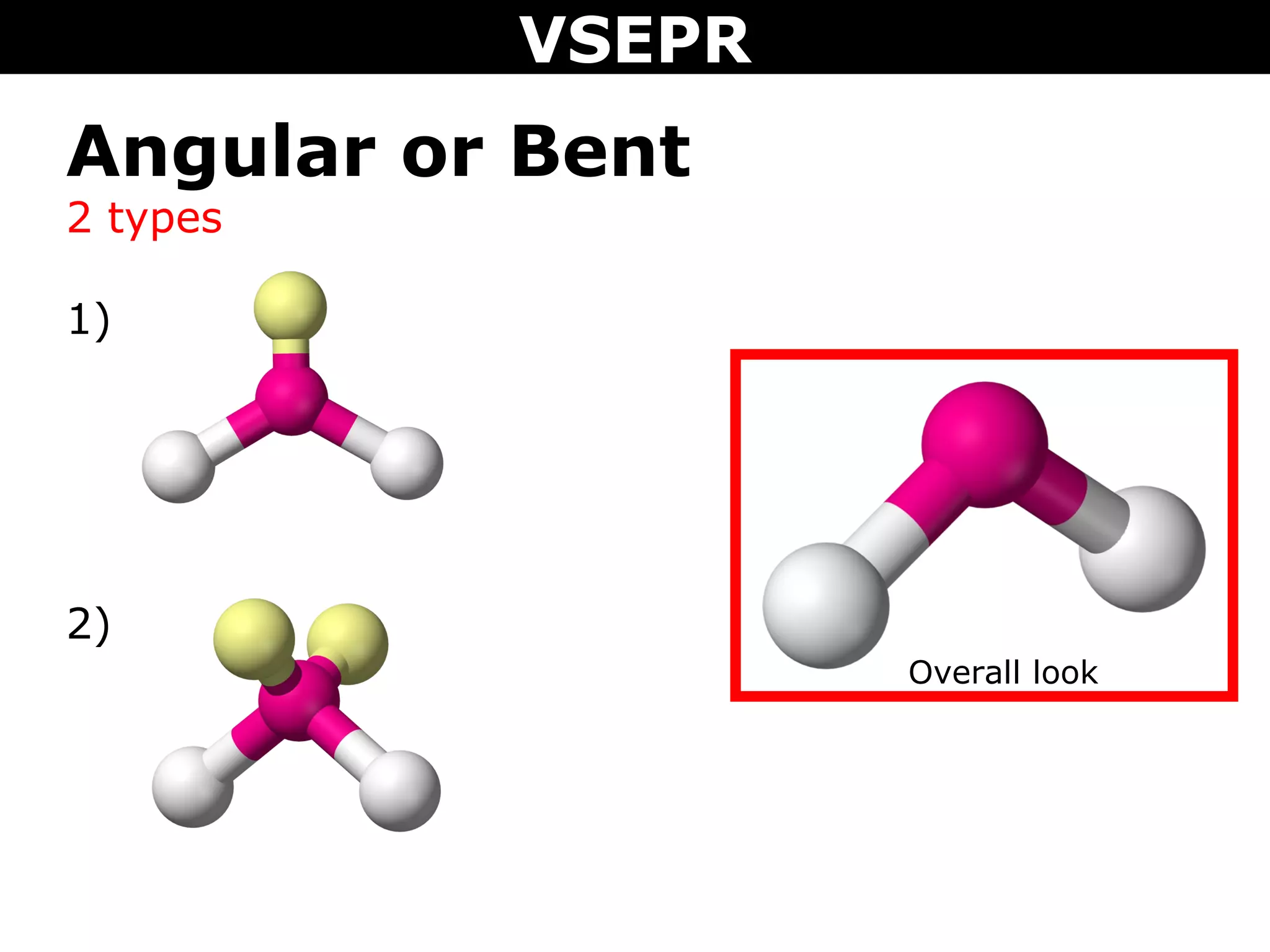
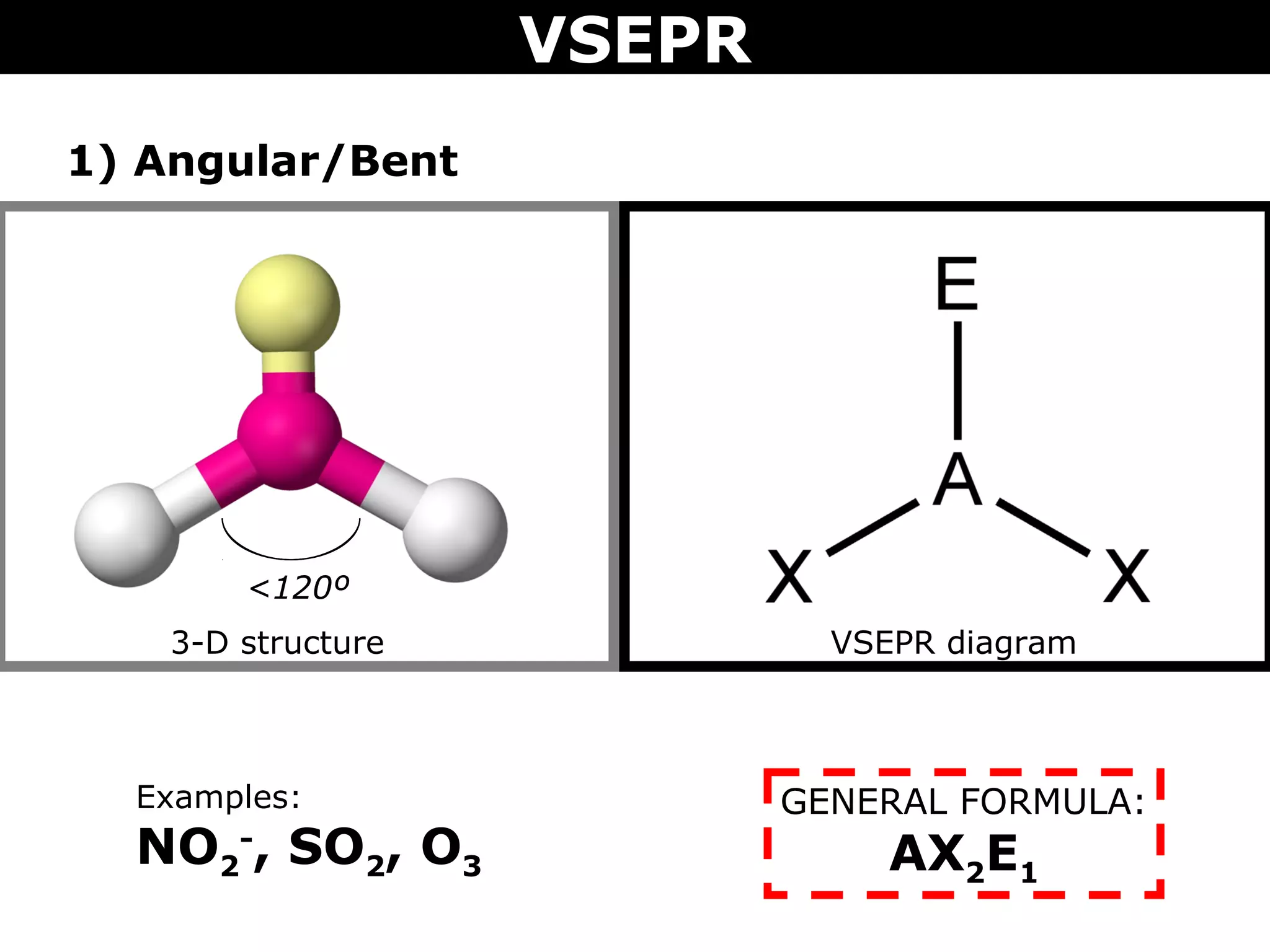
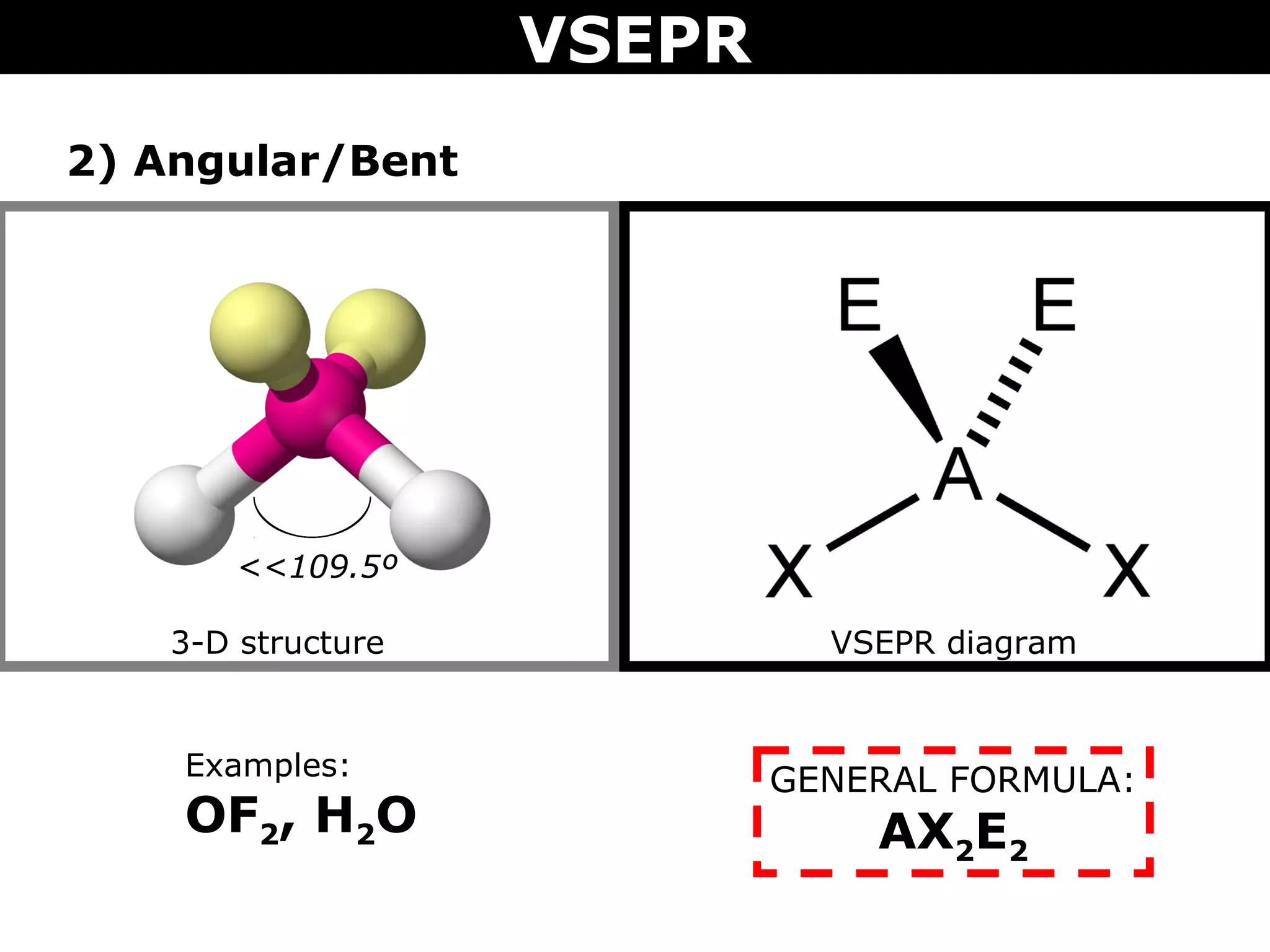
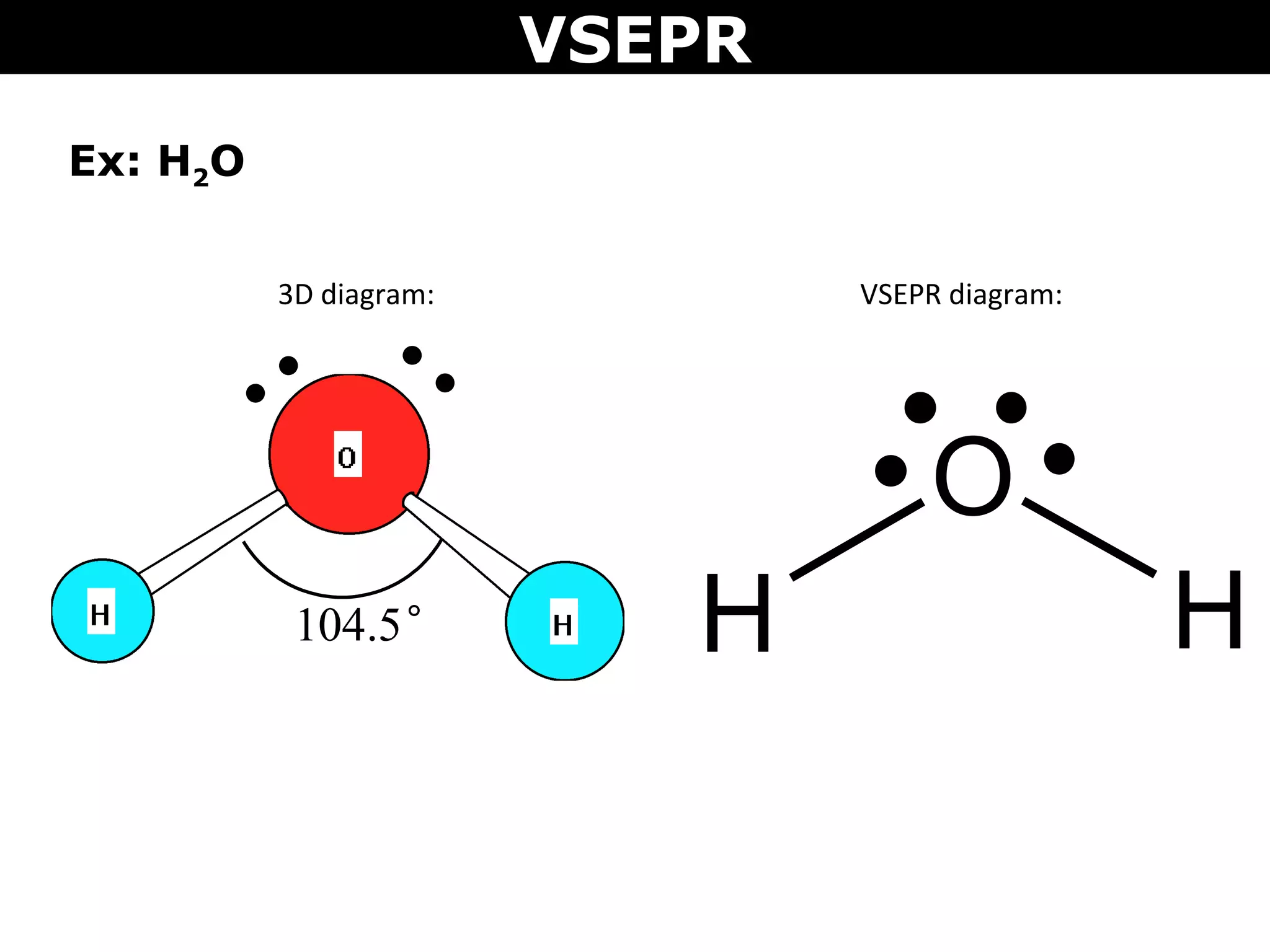
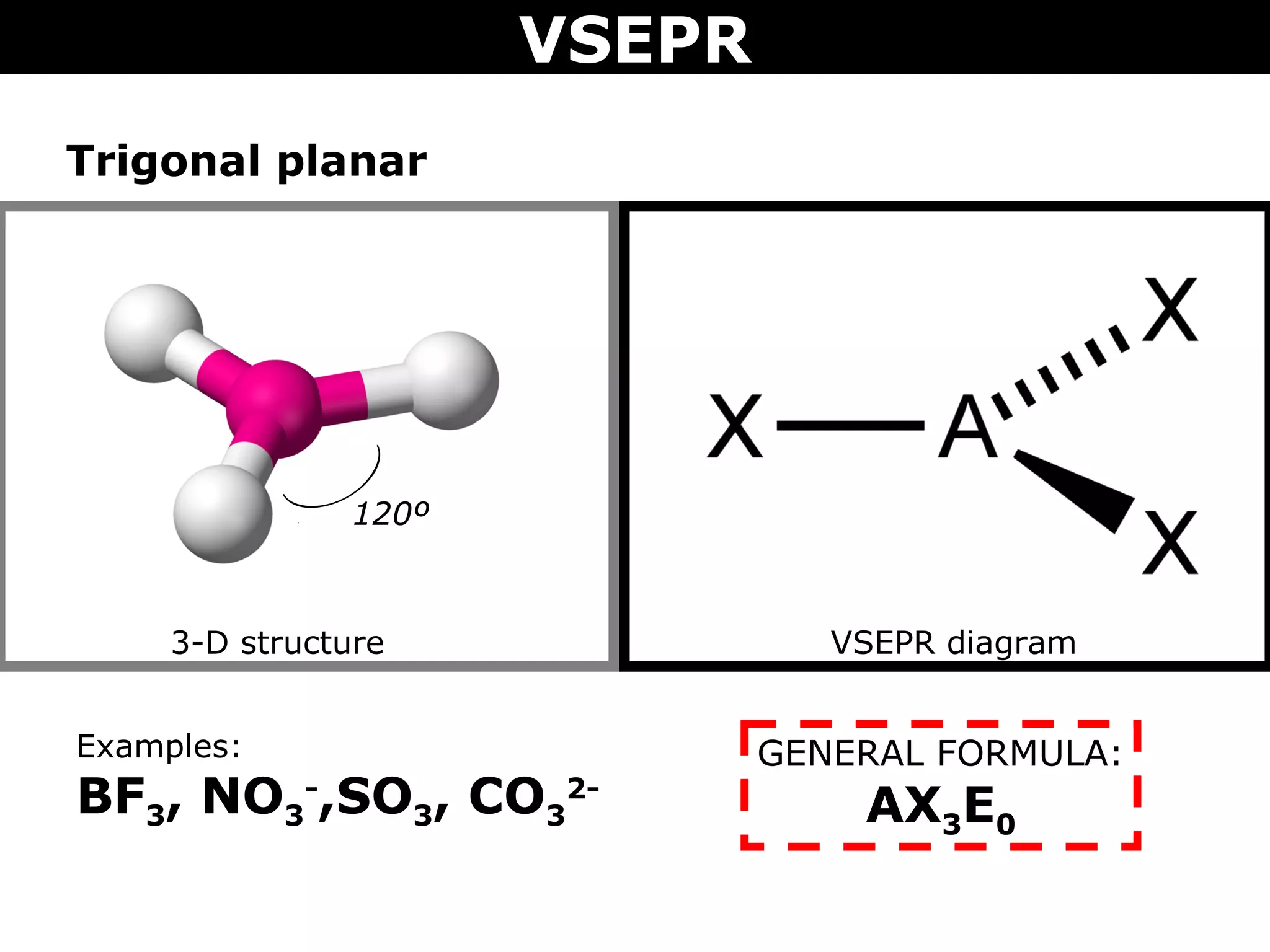
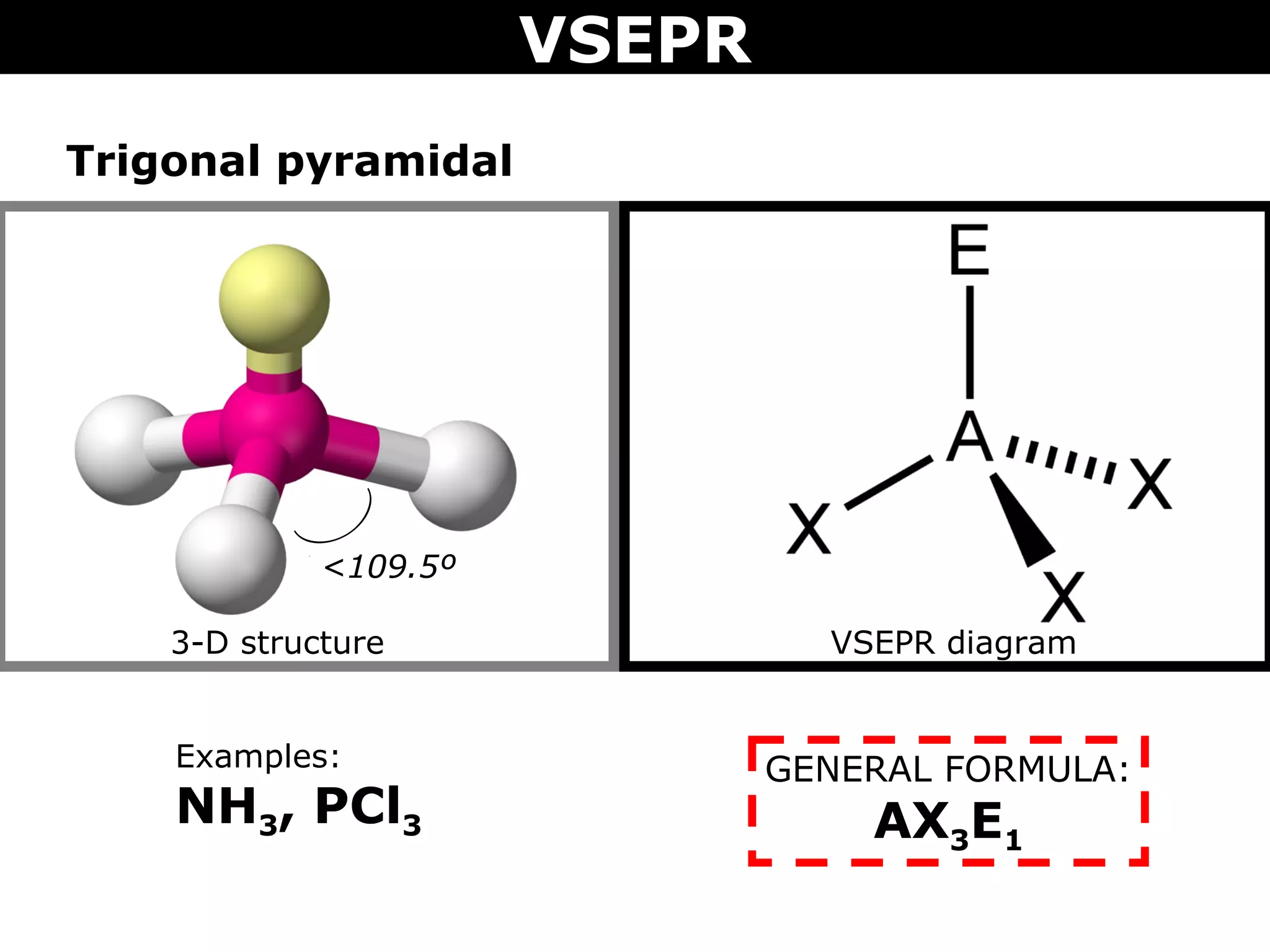
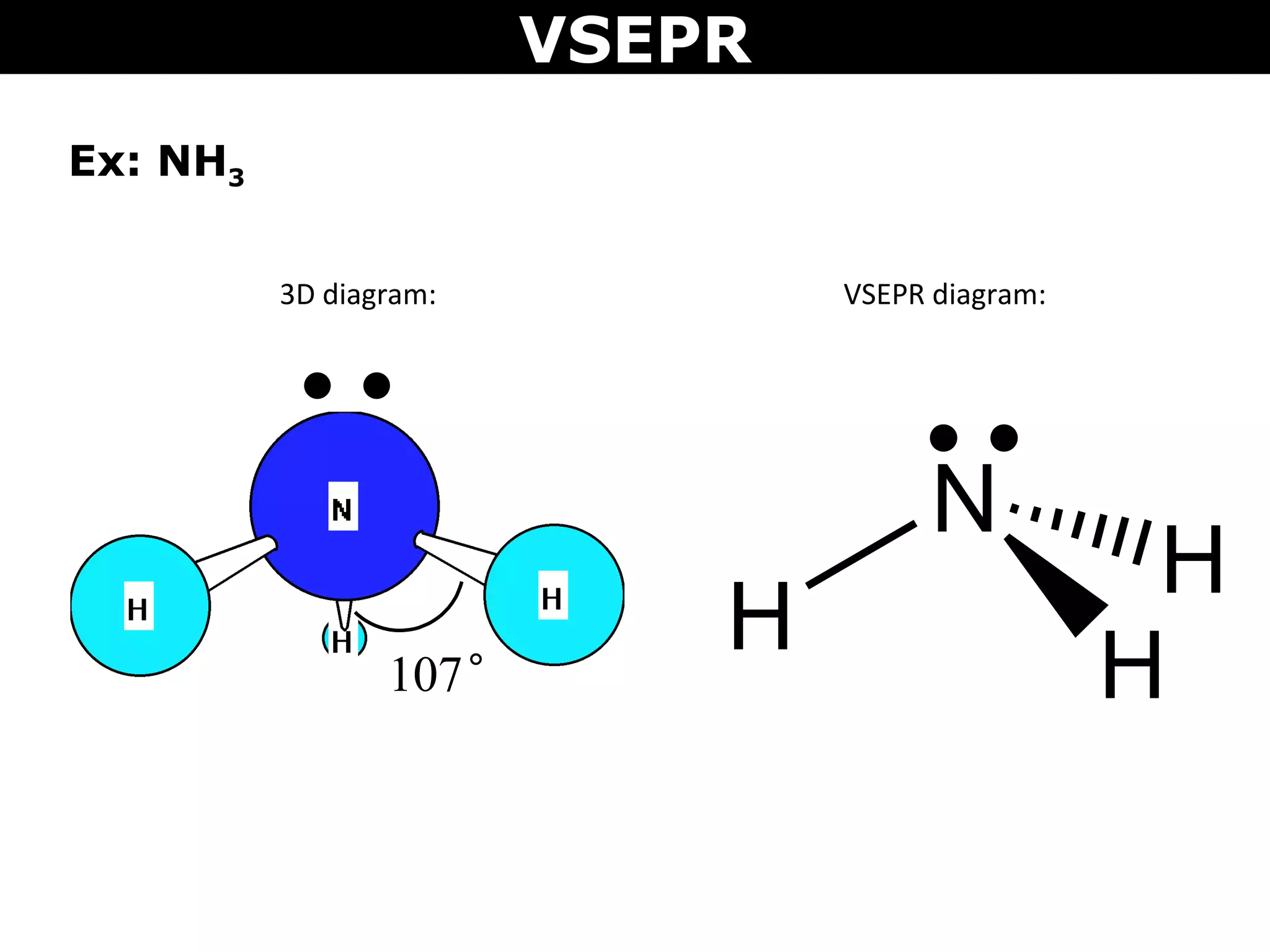
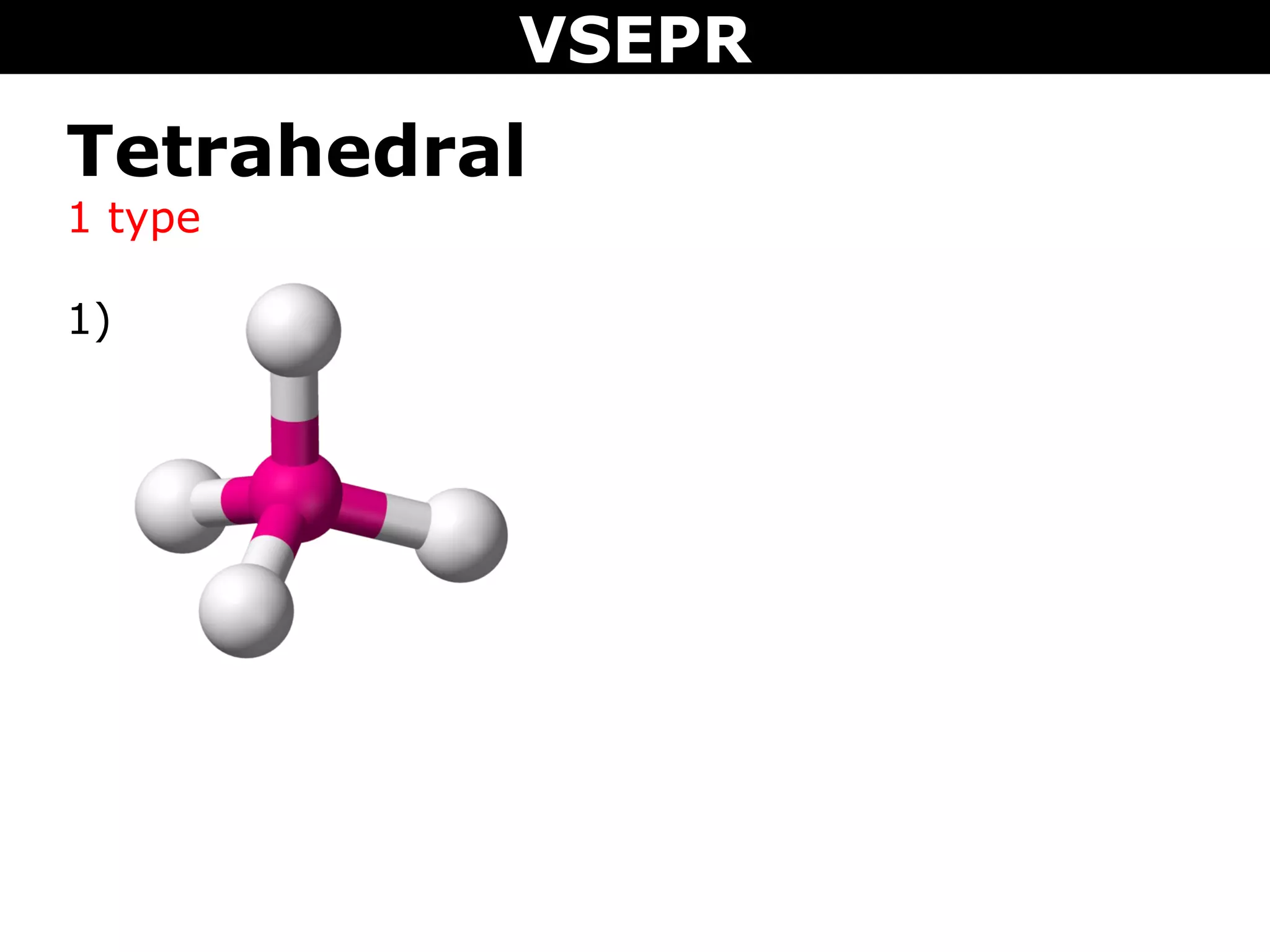
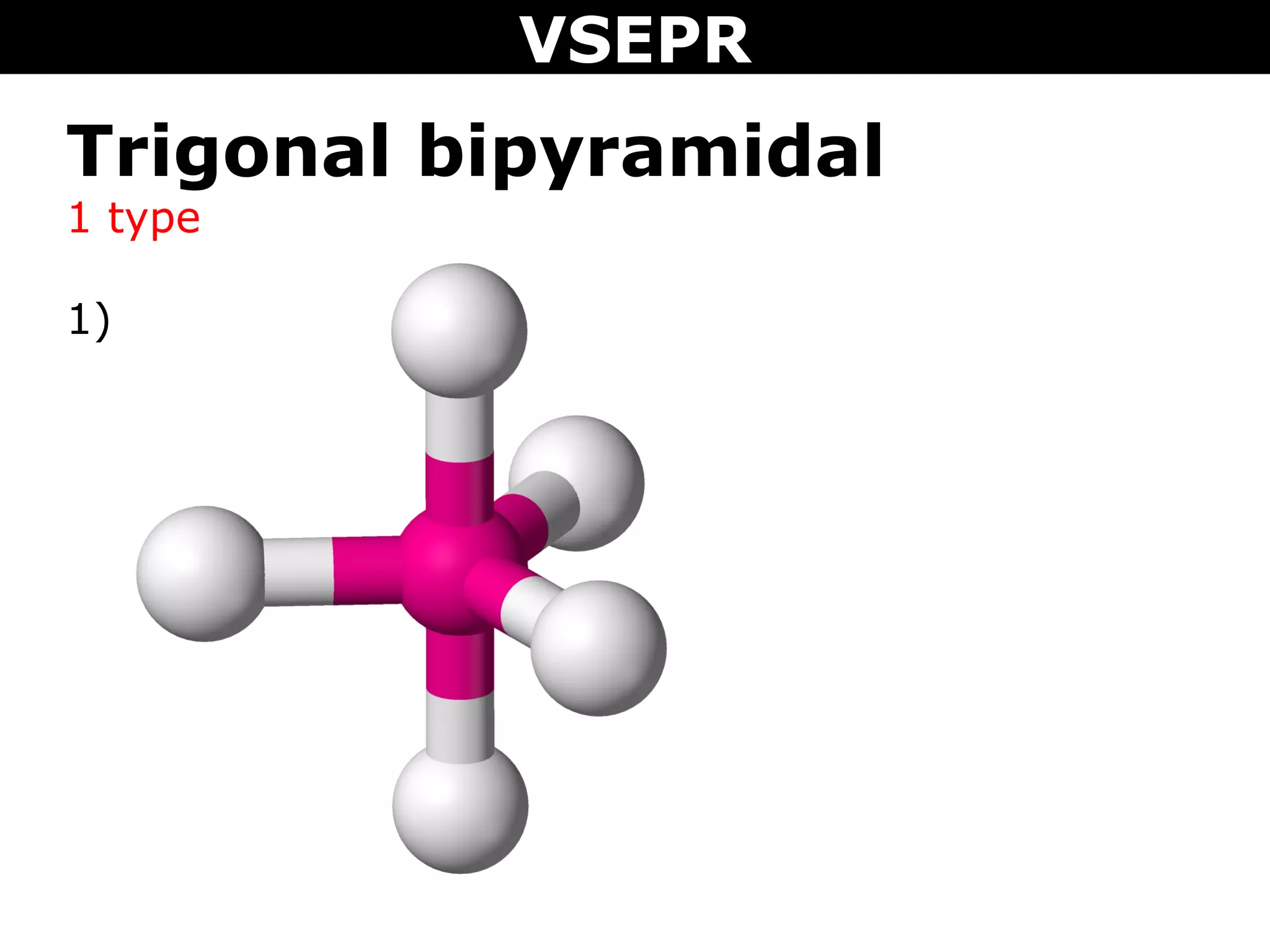
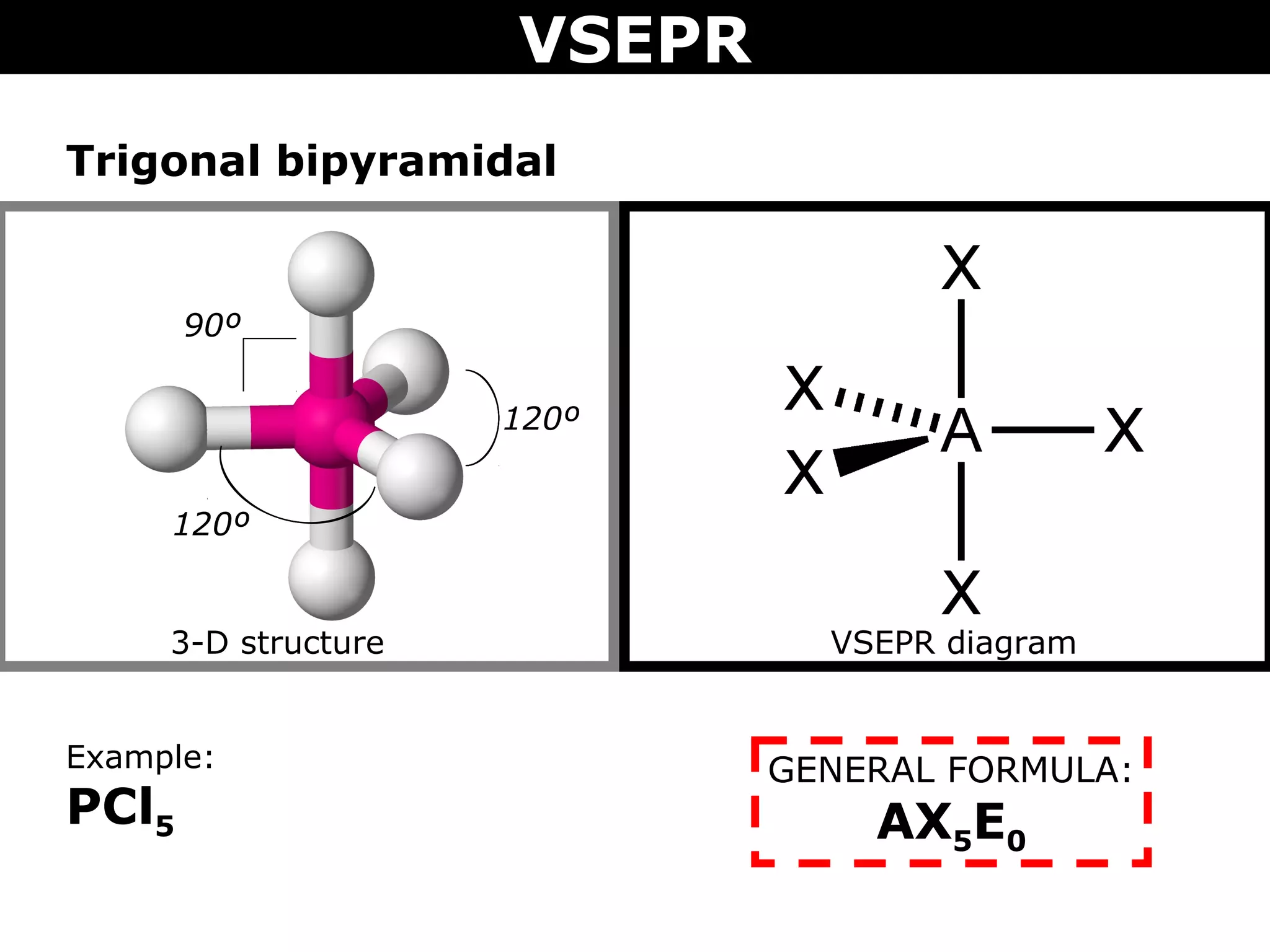
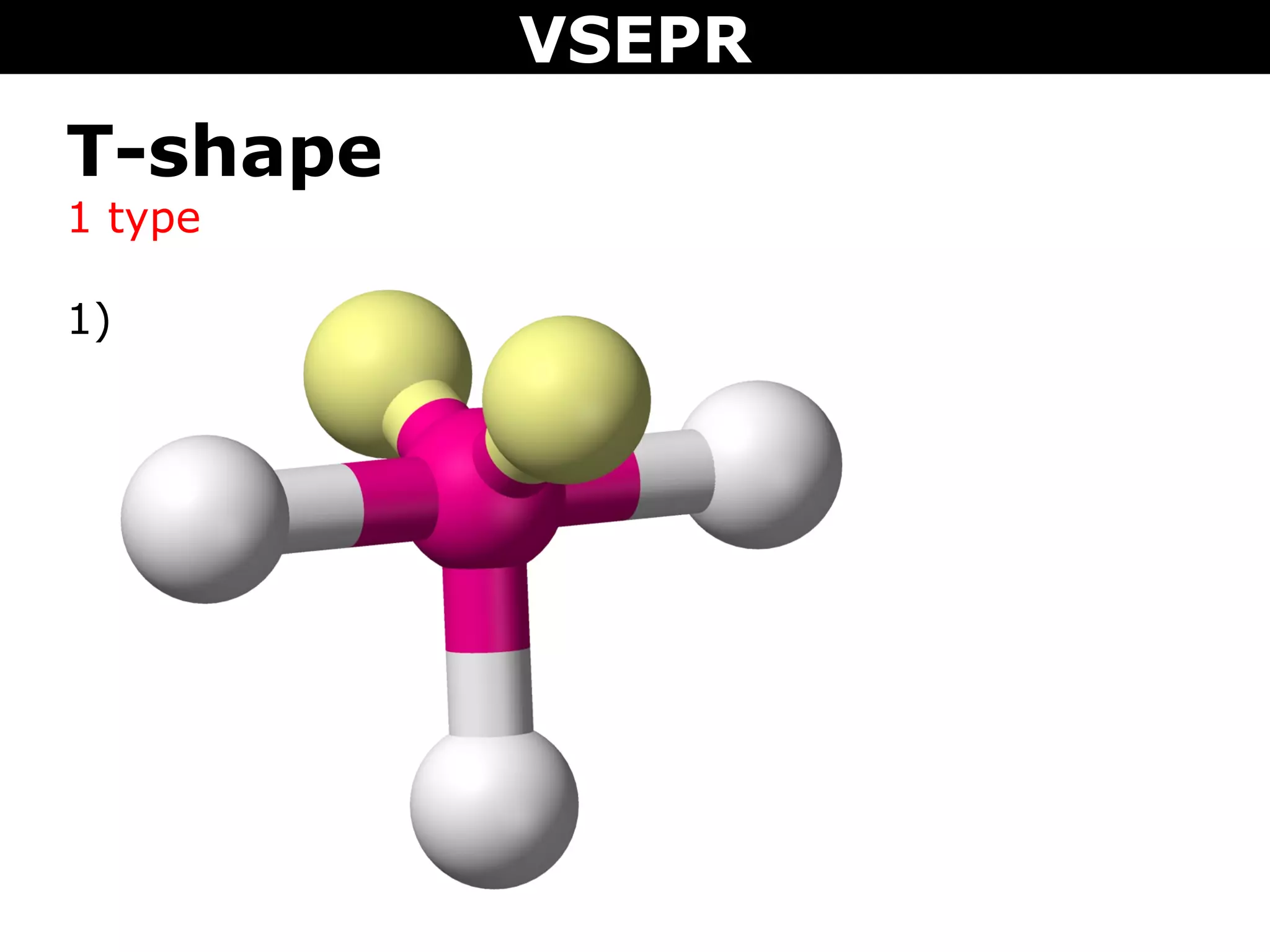
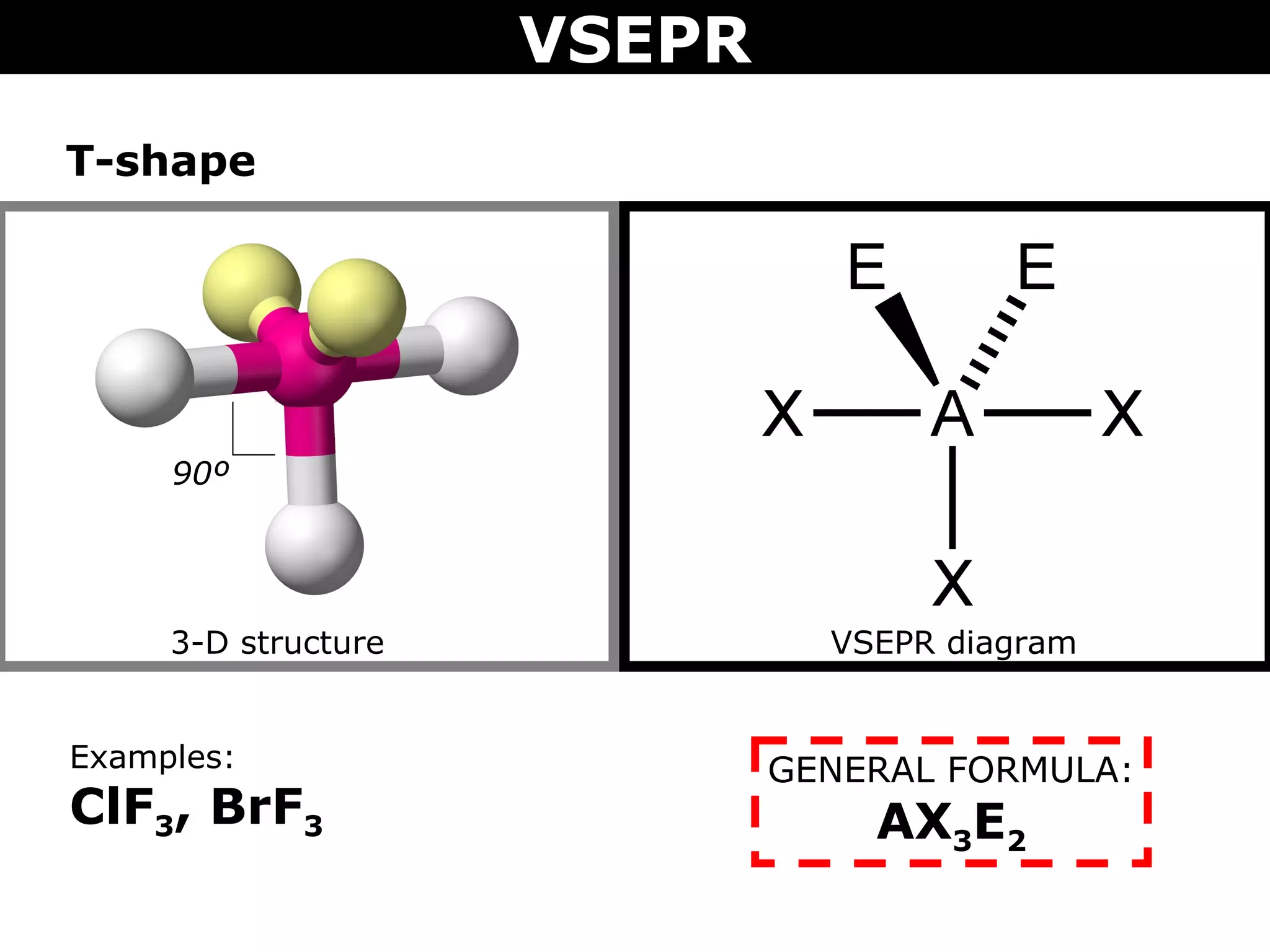
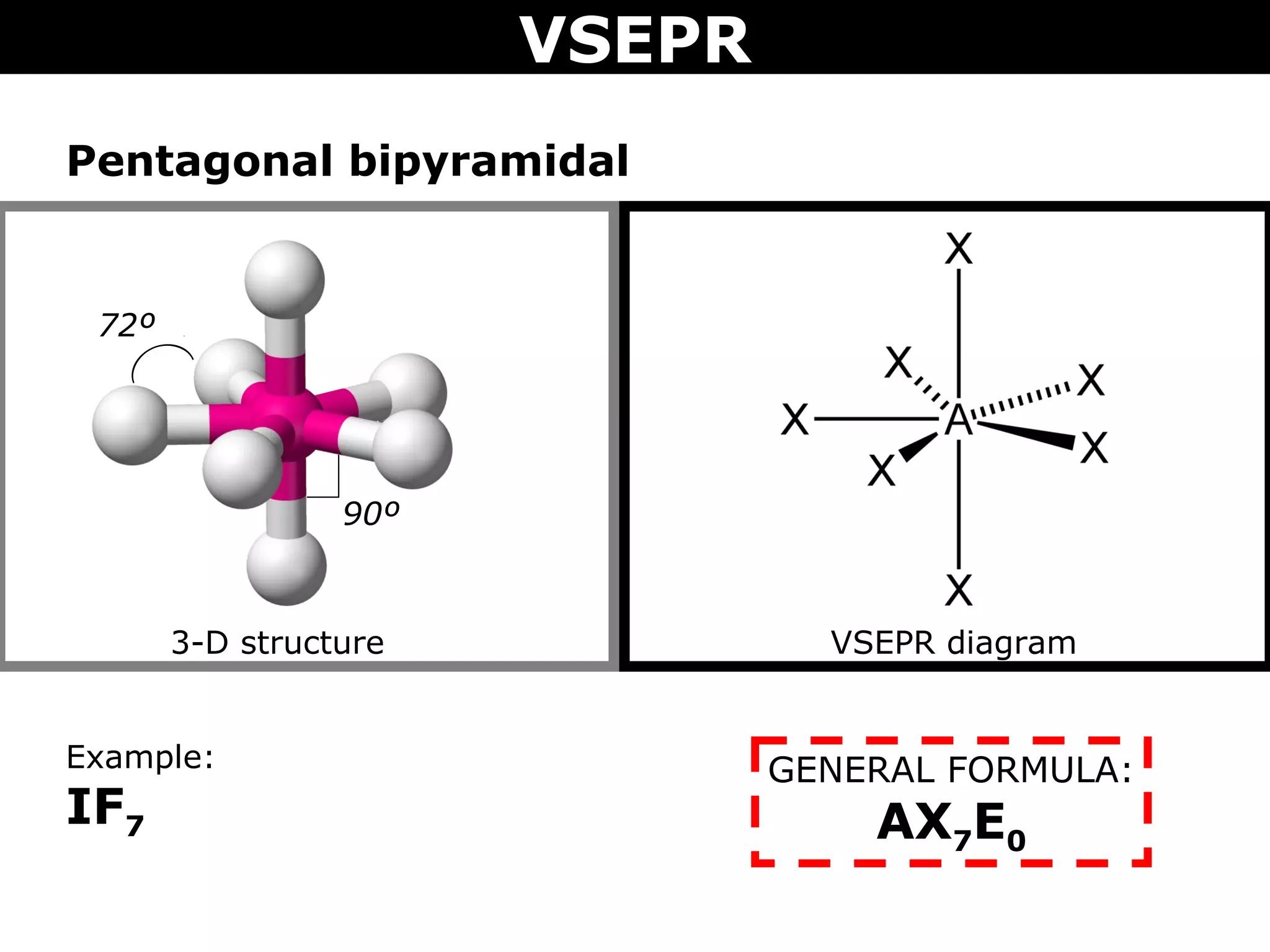
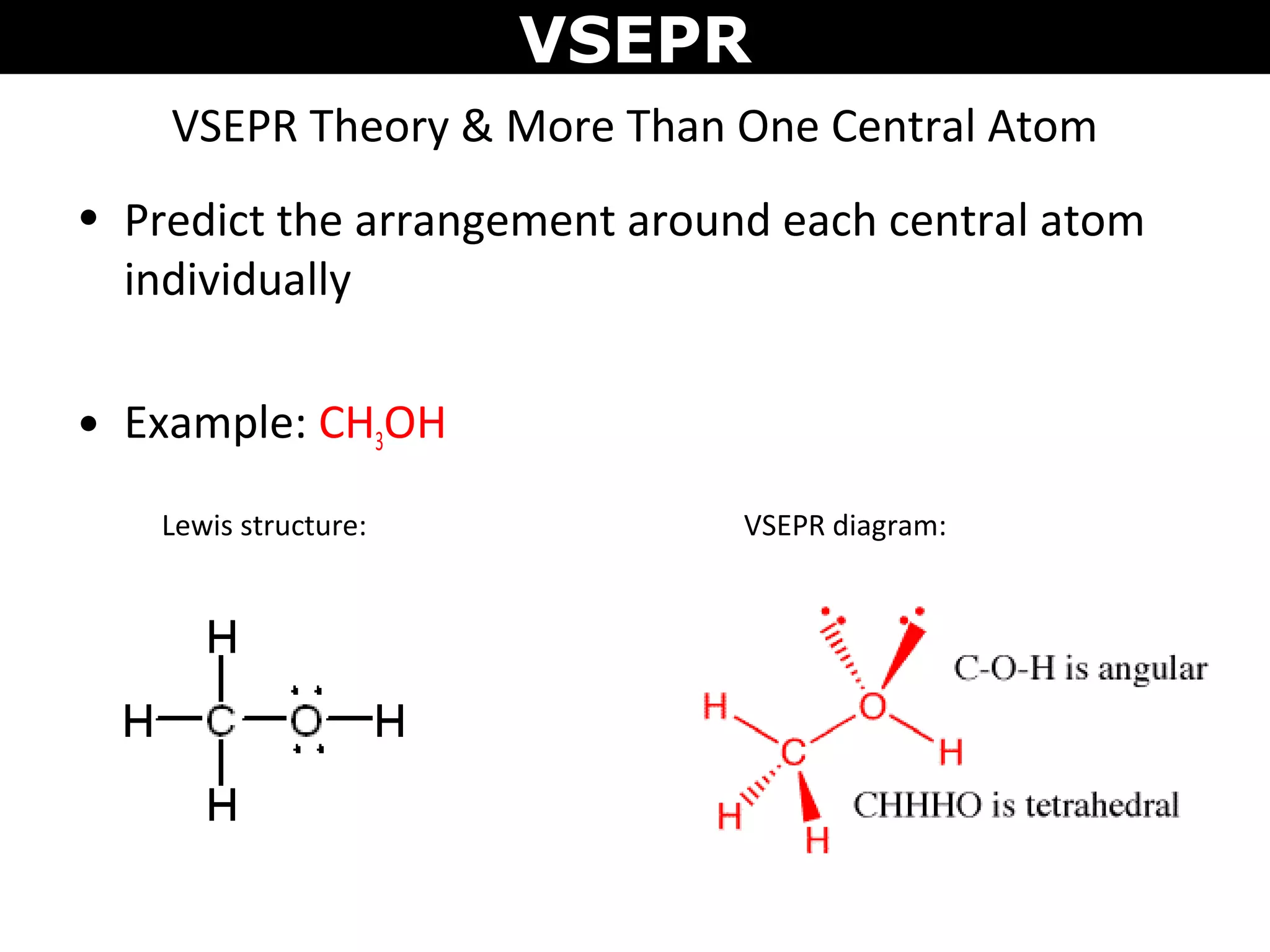
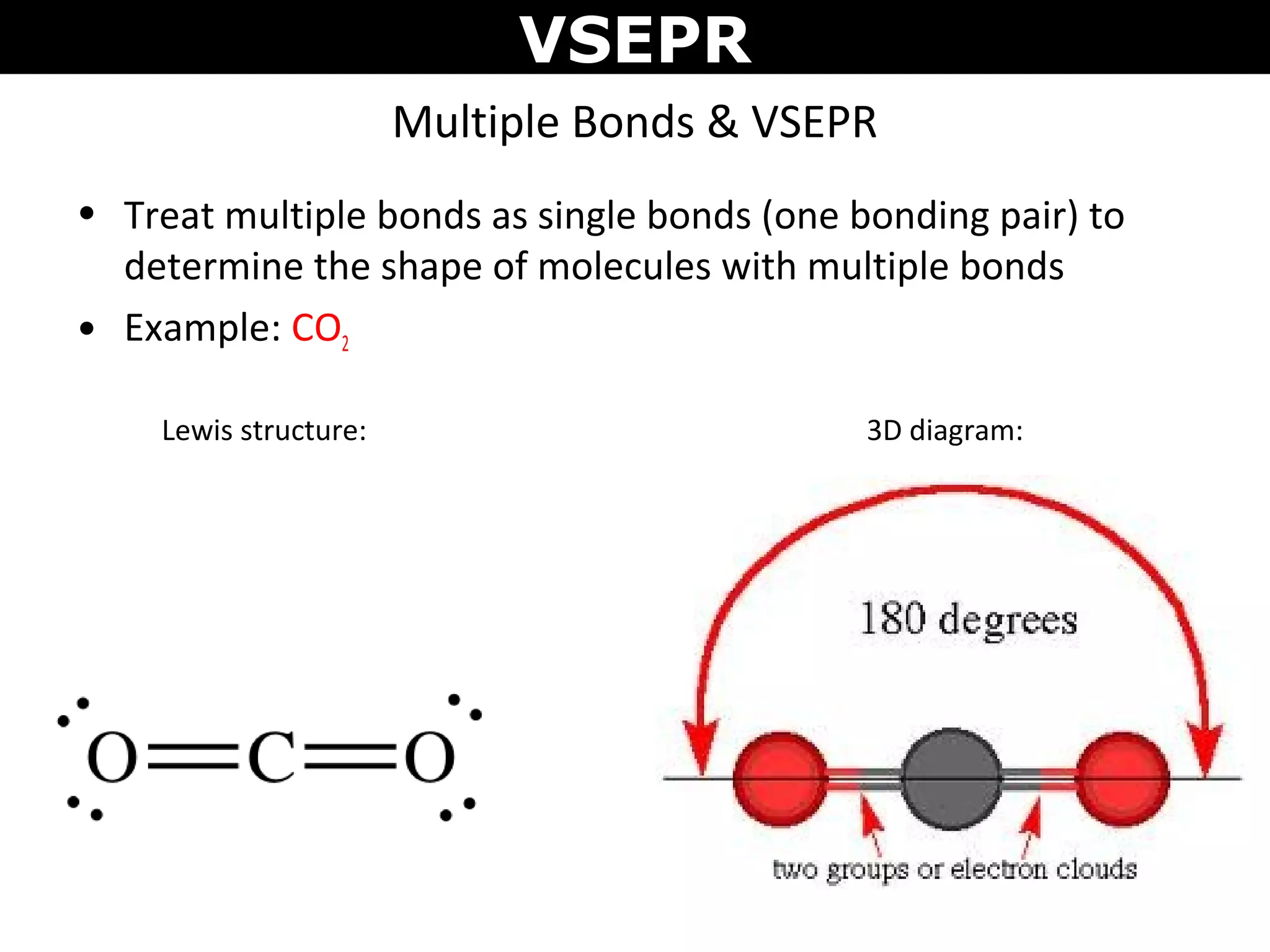
This document provides an overview of Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory, which is used to predict the shapes of molecules based on electron pair repulsion around a central atom. It defines key VSEPR shapes such as linear, bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, and octahedral. Examples are given for each shape along with the general formula and bond angles. The document explains how to apply VSEPR Theory by drawing Lewis structures, counting electron pairs, and determining the molecular shape based on the electron pair arrangement. It also addresses applying VSEPR to molecules with multiple central atoms or multiple bonds.