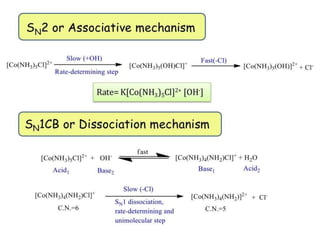
This document discusses acid and base hydrolysis in octahedral complexes. It covers factors that affect the rate of acid hydrolysis, including the charge on the complex, steric hindrance effects, and the strength of the leaving group. A higher positive charge, more steric hindrance, or stronger metal-leaving group bond each decrease the rate of acid hydrolysis according to first-order kinetics through a dissociative SN1 mechanism. Base hydrolysis of octahedral complexes can proceed by either associative SN2 or dissociative SN1 pathways depending on conditions.








![2.Effect of crowding ( steric hindrance )
An increase in the steric crowding around the metal ion
preferably favors a dissociative nucleophilic substitution
SN1 mechanism
For example, when we consider the [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+
complex, the NH3 molecule in [Co(NH3)5Cl]2+ complex
ion are replaced by ethylenediaamine (en) the rate of
acid hydrolysis of the complex is decreases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/70chxqqwrs6u5mypd7wo-octahedral-complexes-altaf-hussain-sem-1-230202154449-fe17b63a/85/Acid-Base-Hydrolysis-in-Octahedral-Complexes-9-320.jpg)