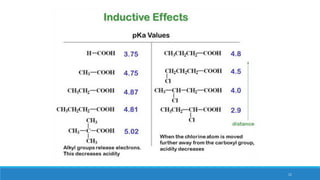
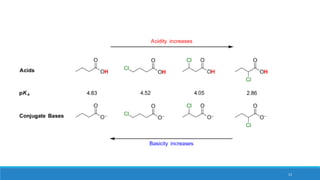
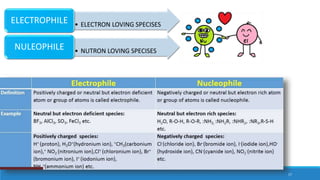
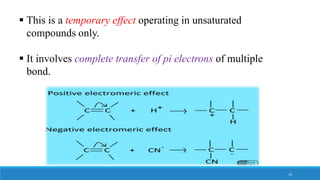
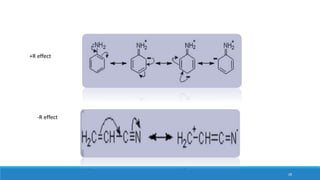
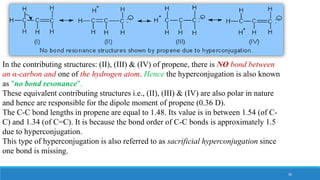
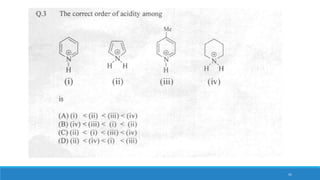
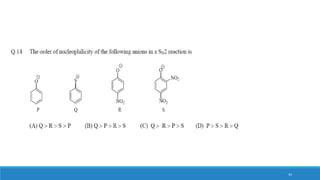
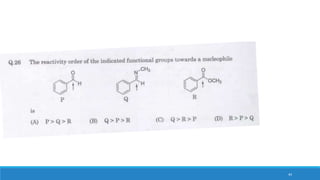
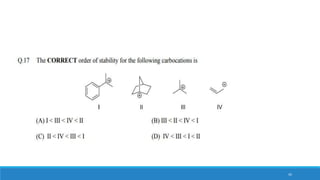
The document outlines fundamental concepts in organic chemistry, focusing on inductive, electromeric, resonance, and hyperconjugation effects. It explains how these effects influence properties such as acidity, basicity, and the stability of molecules. Additionally, it provides detailed applications and comparative analysis of these effects in chemical reactions.