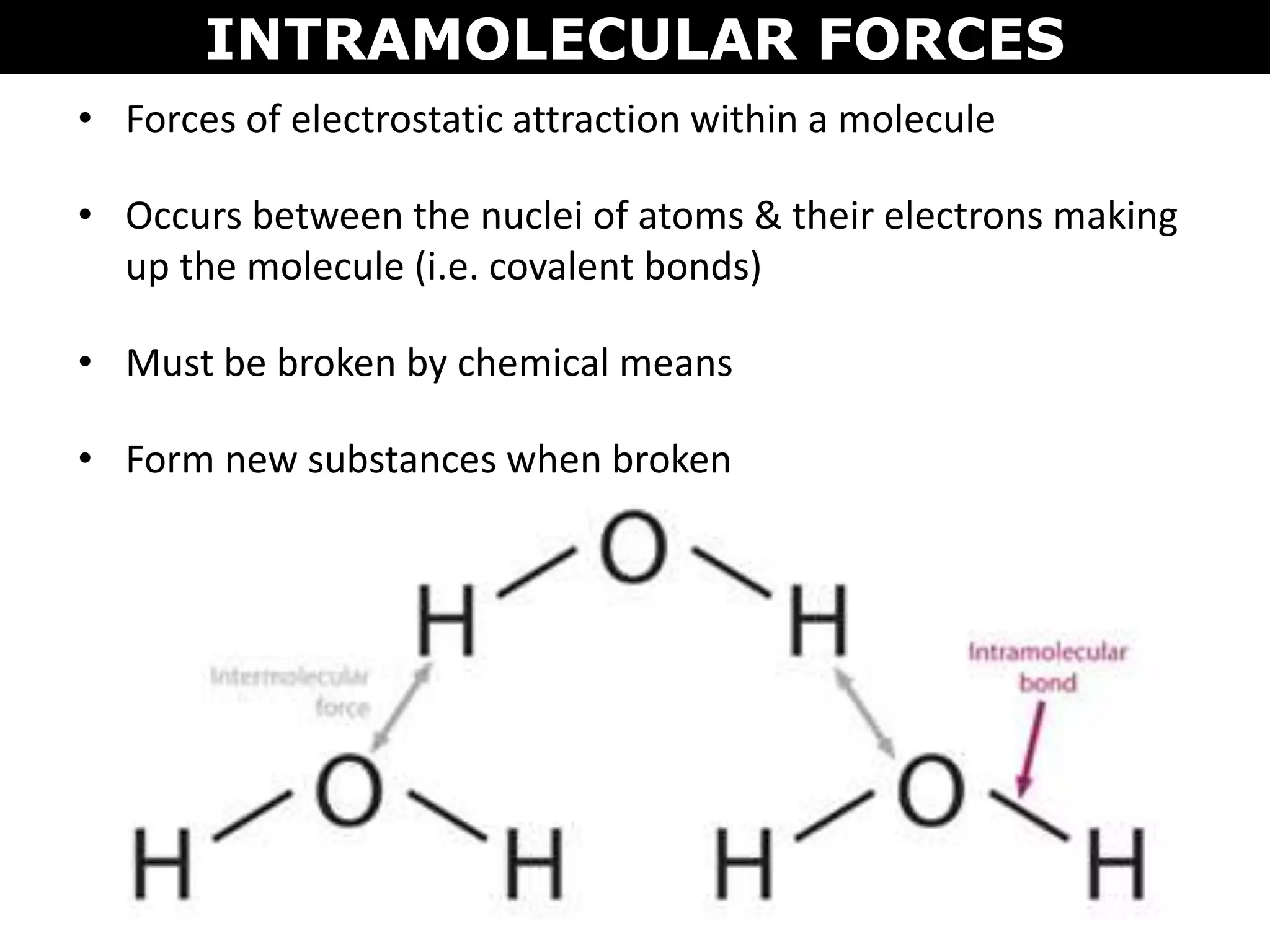
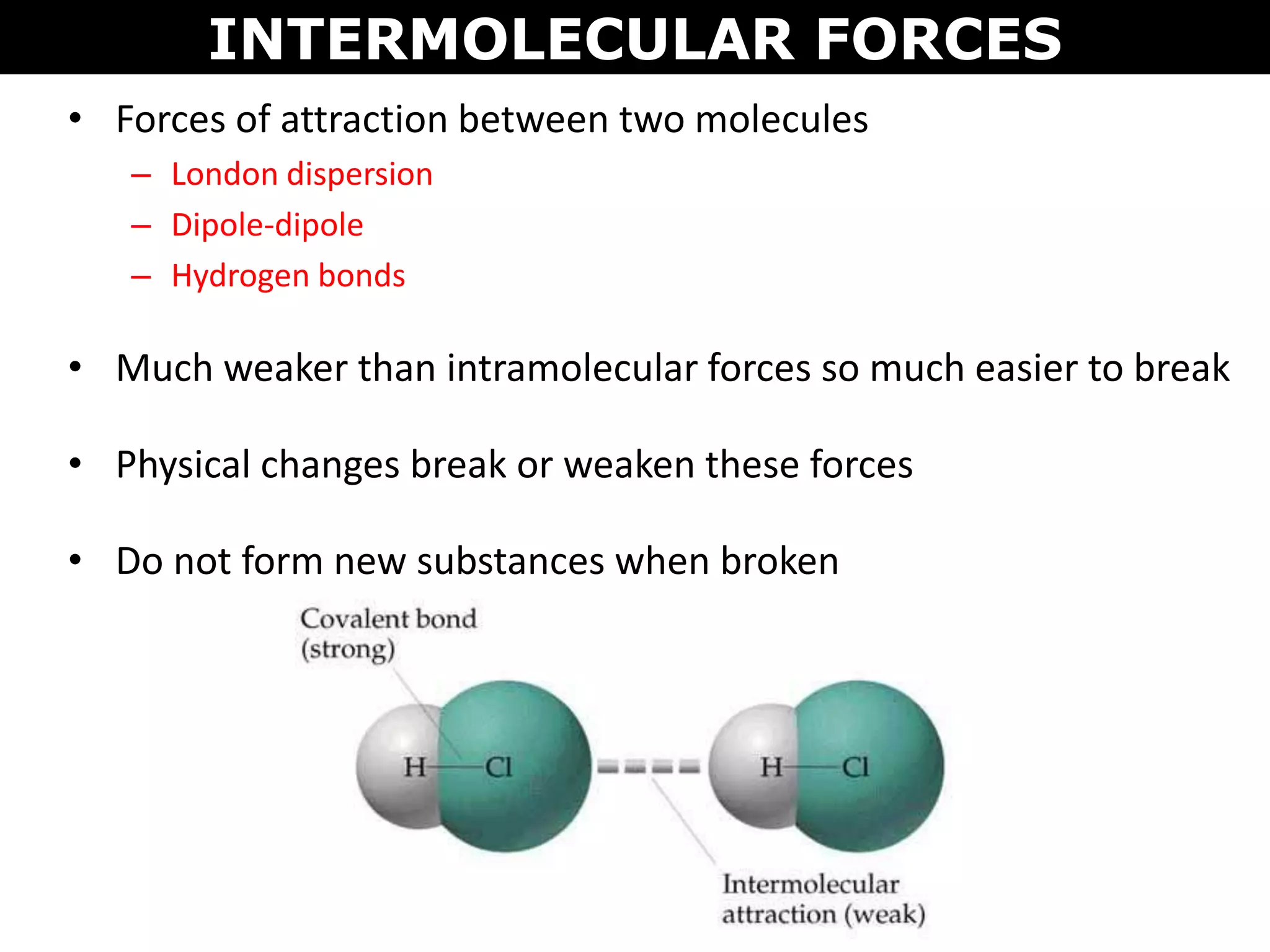
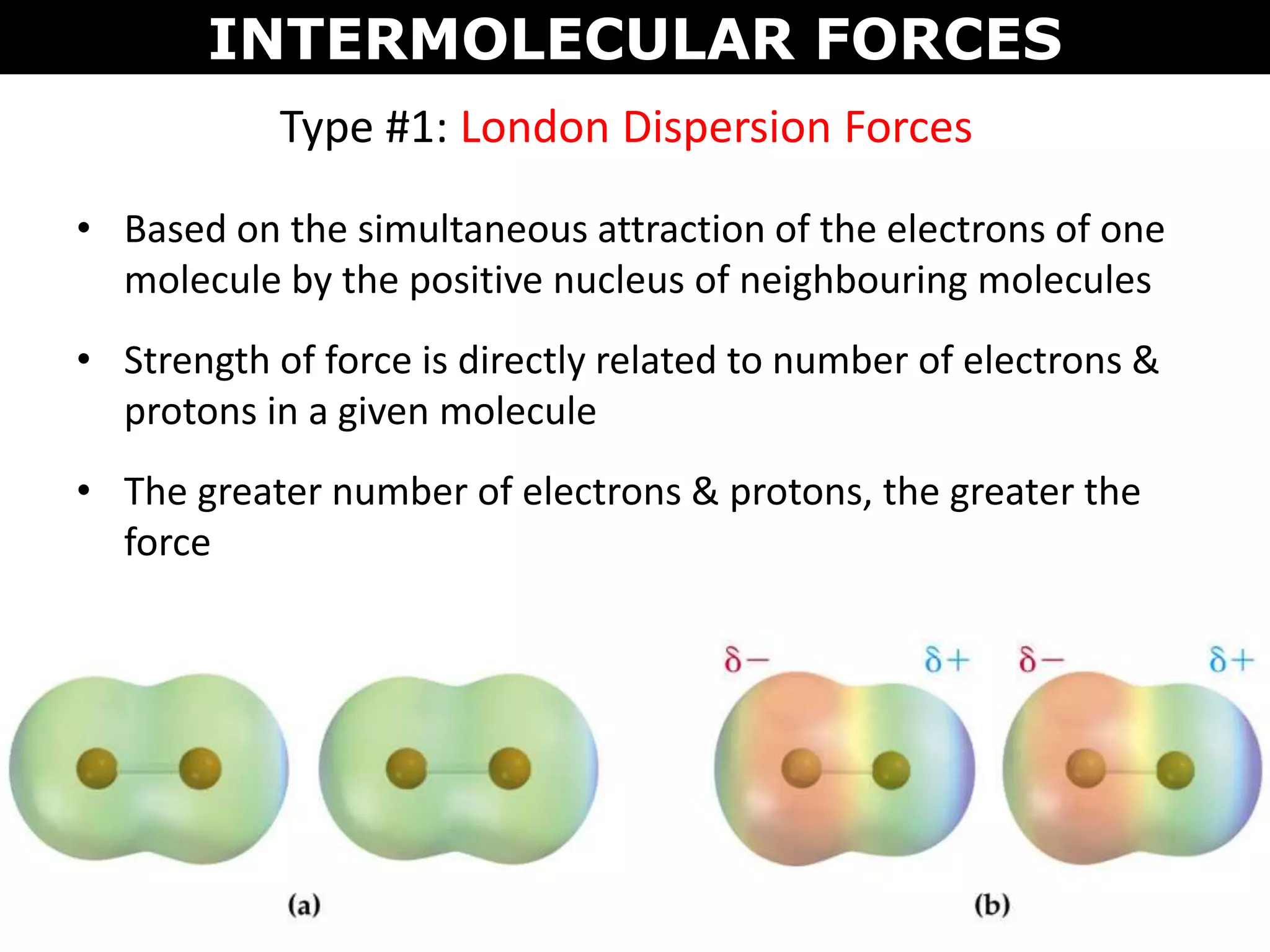
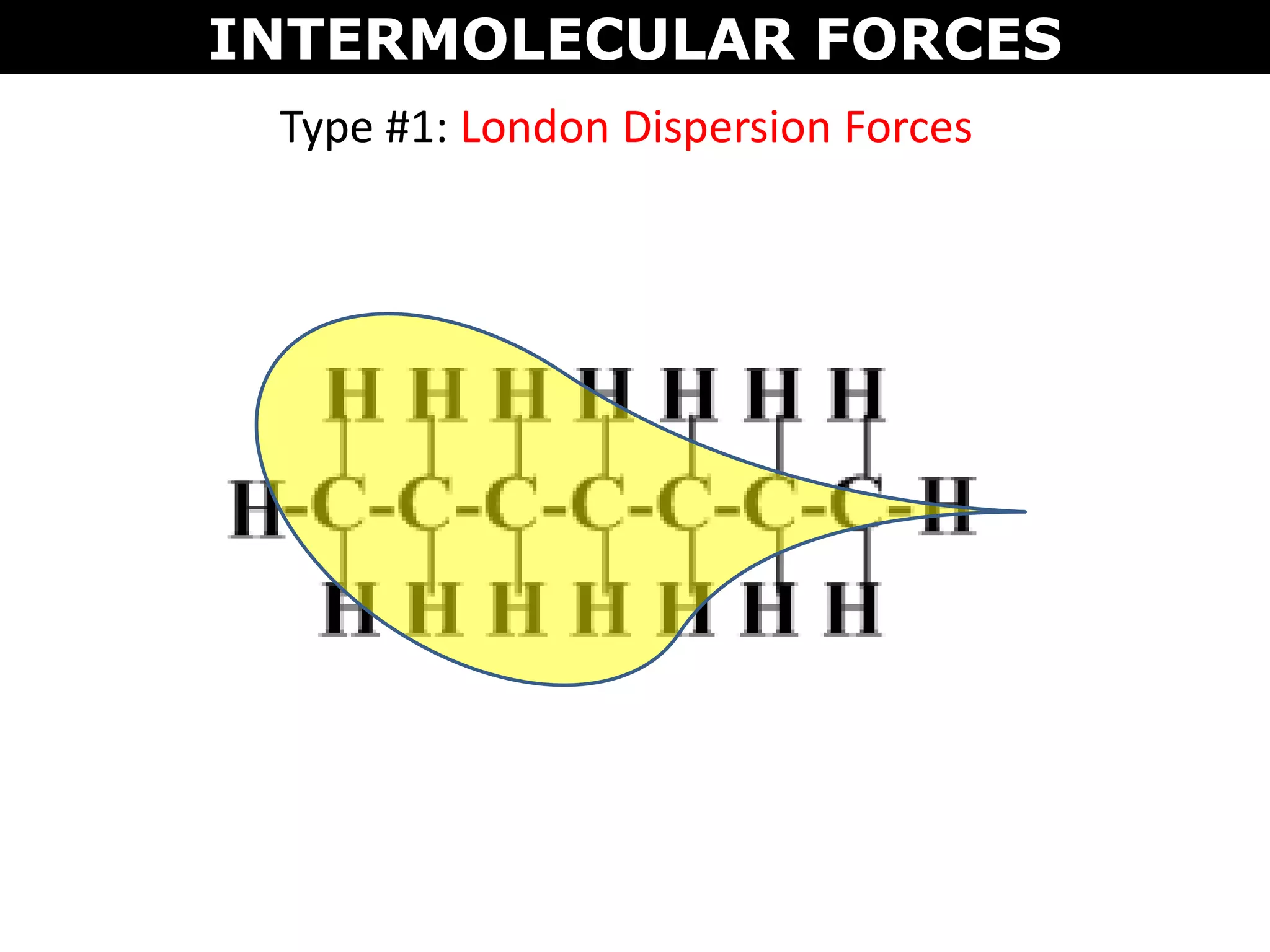
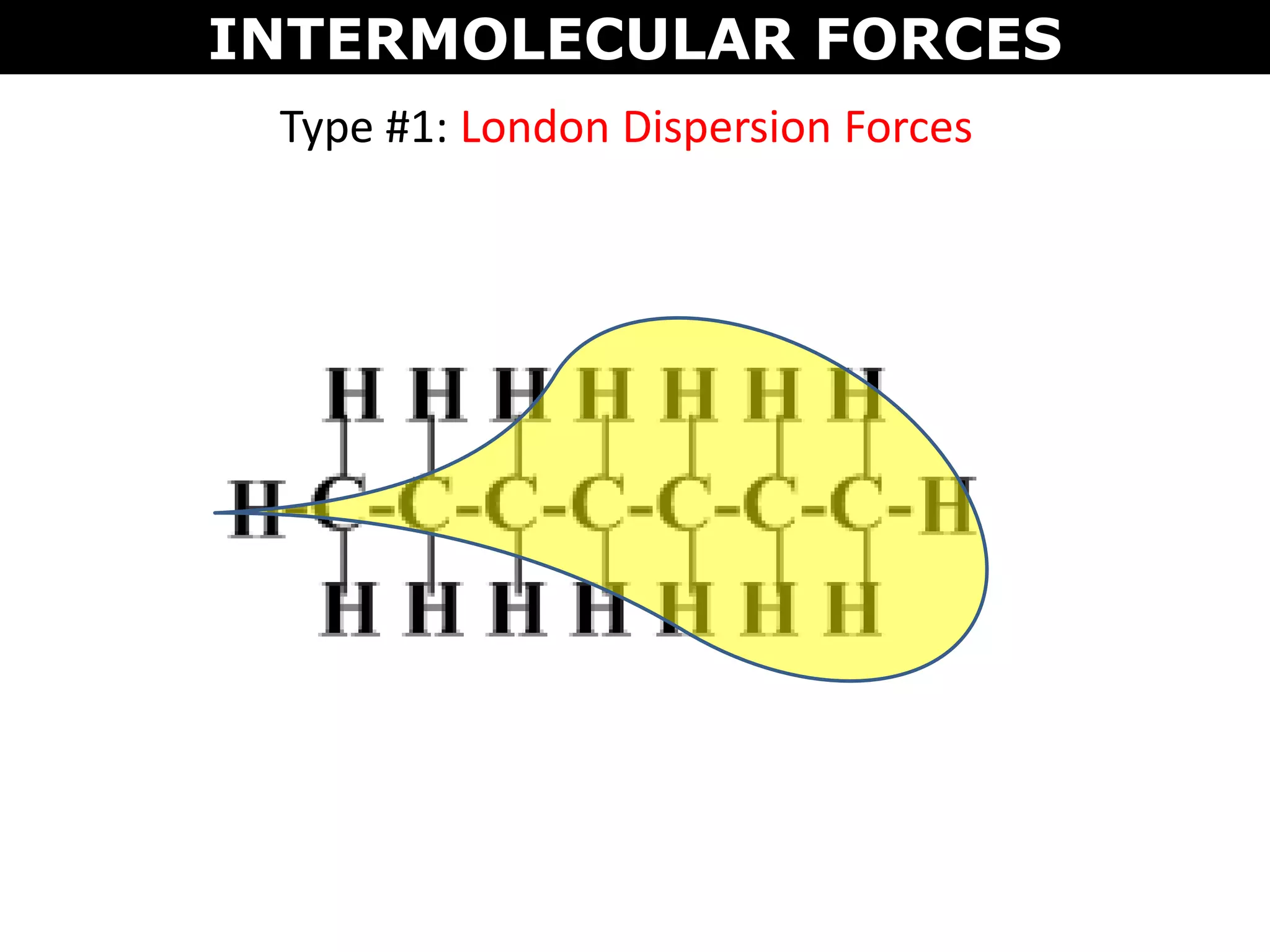
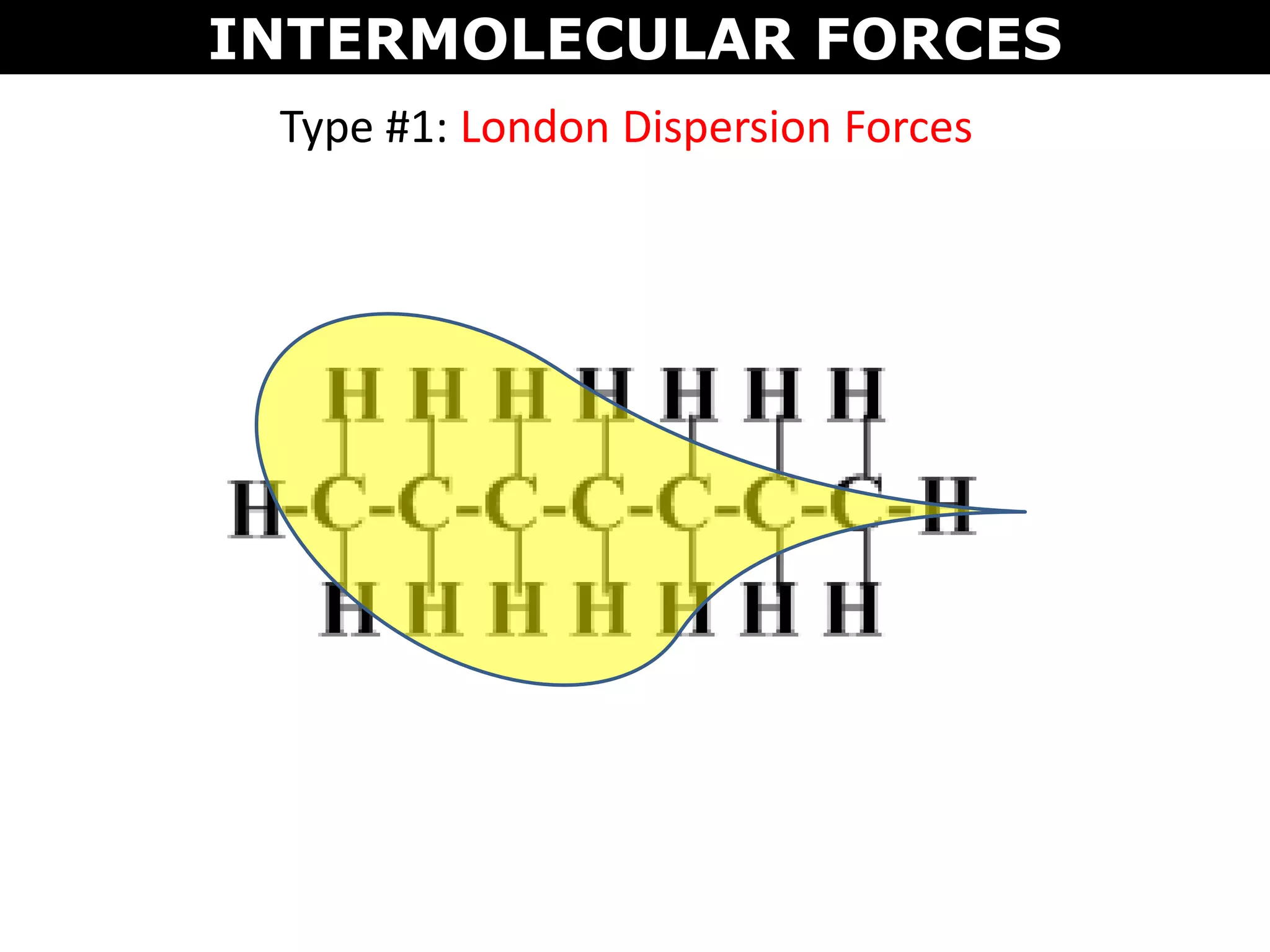
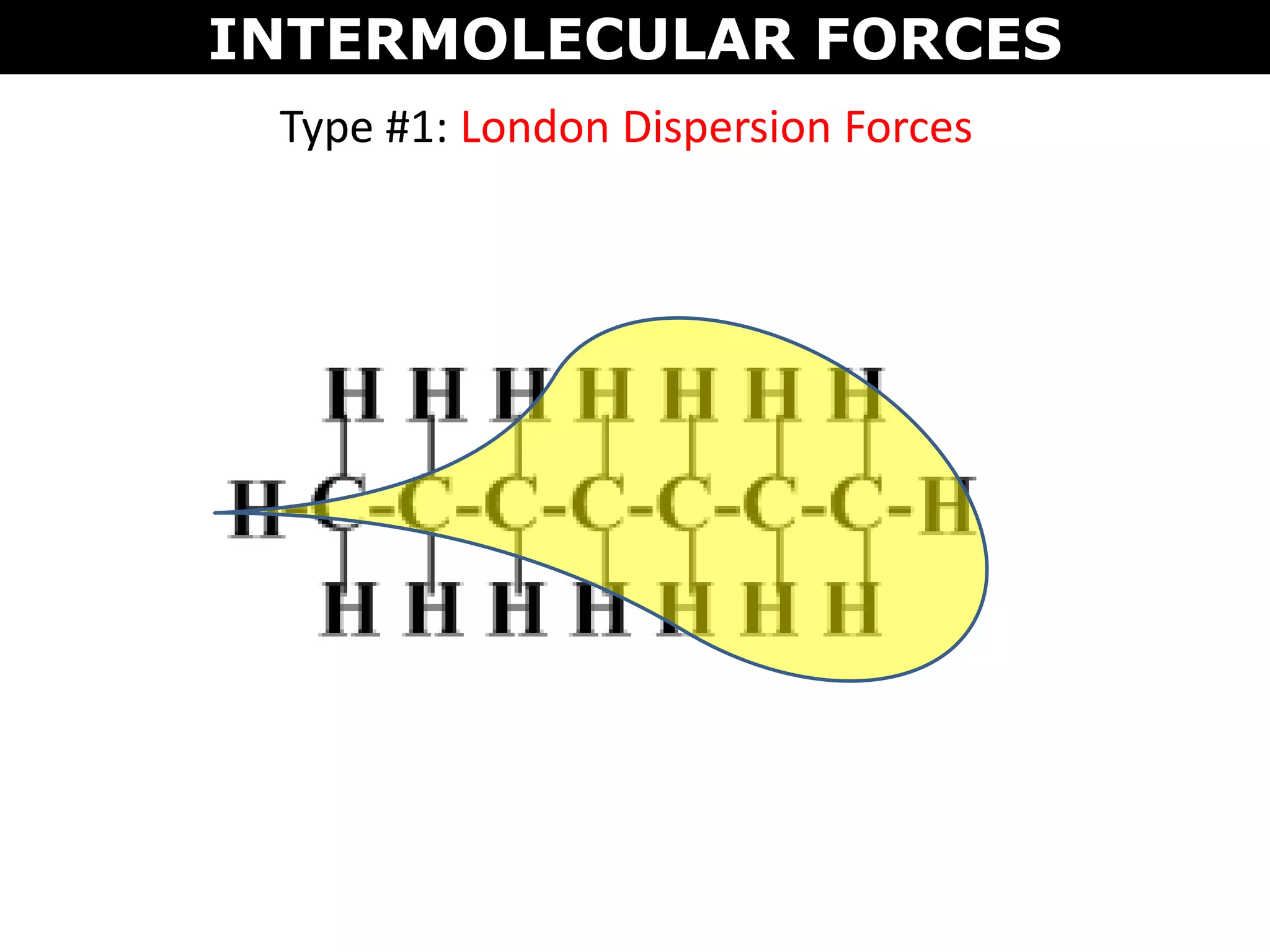
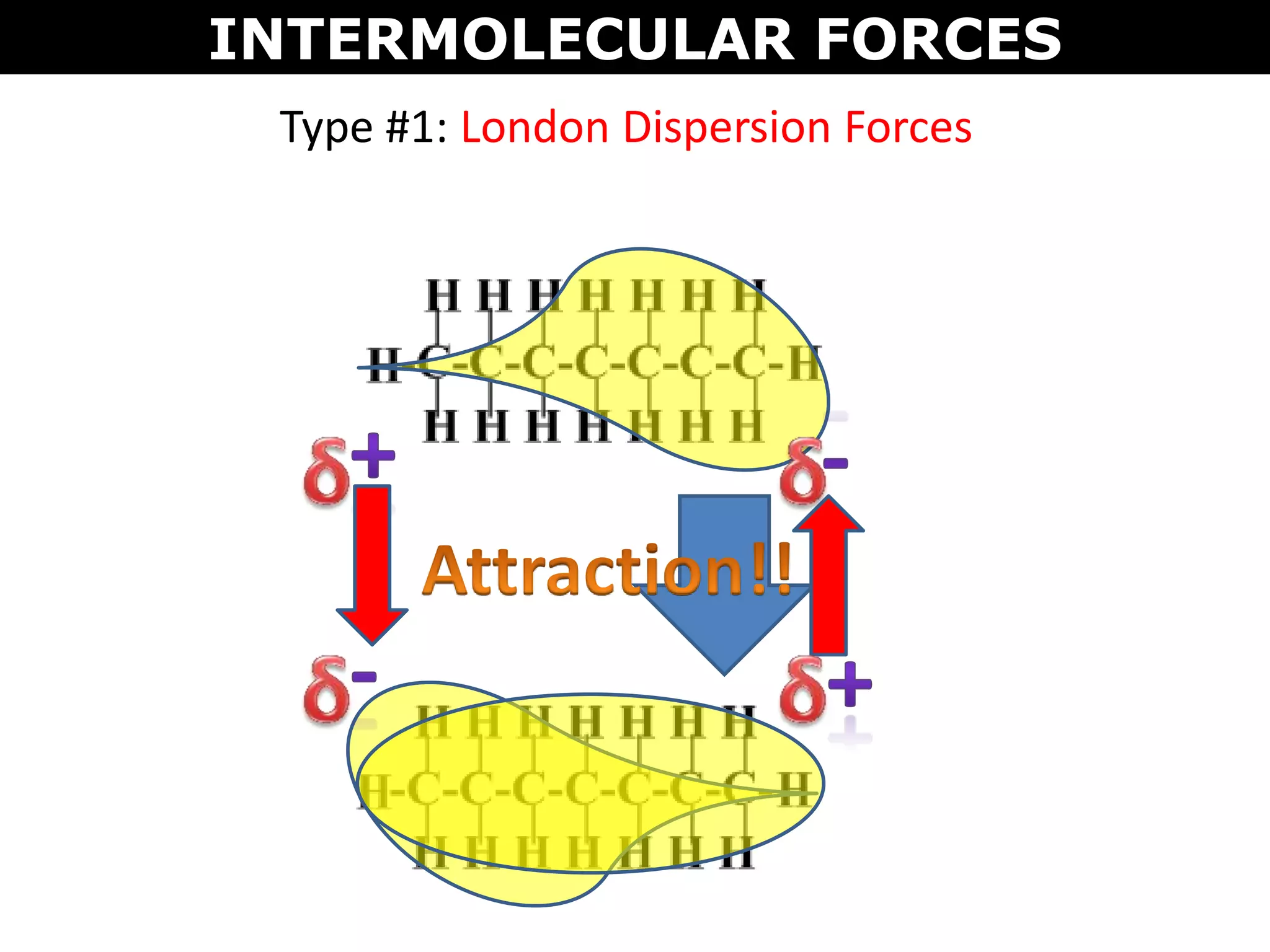
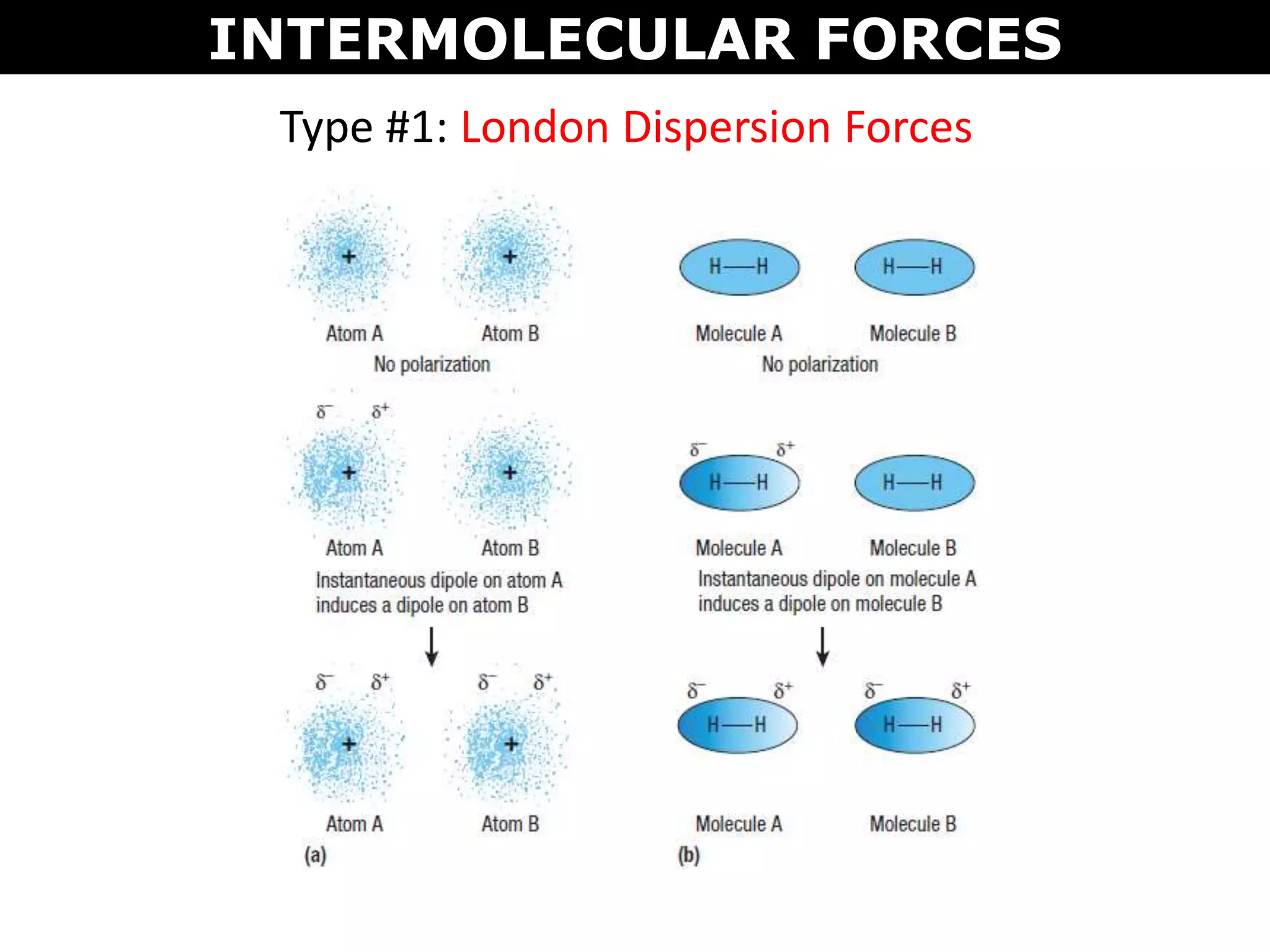
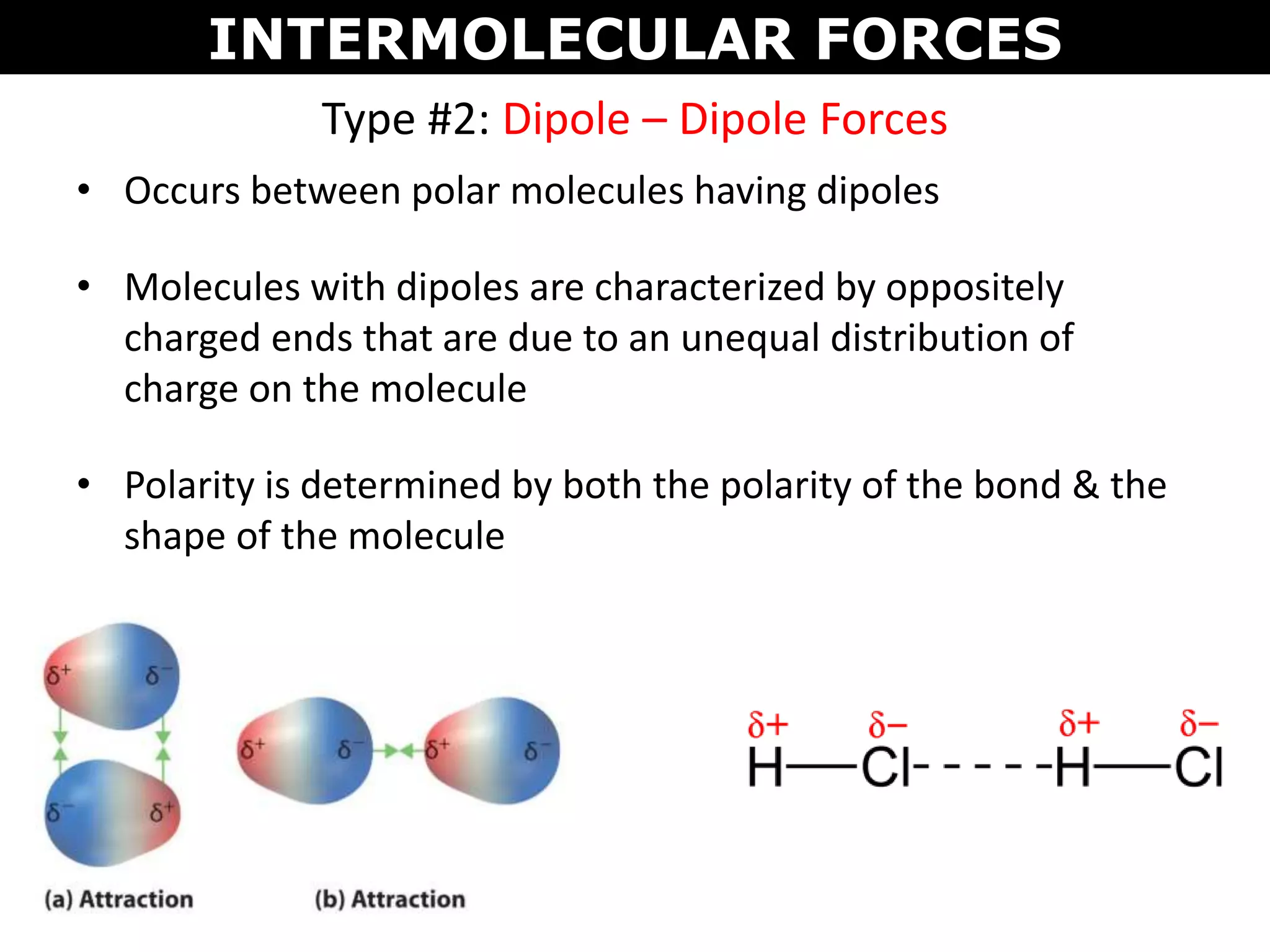
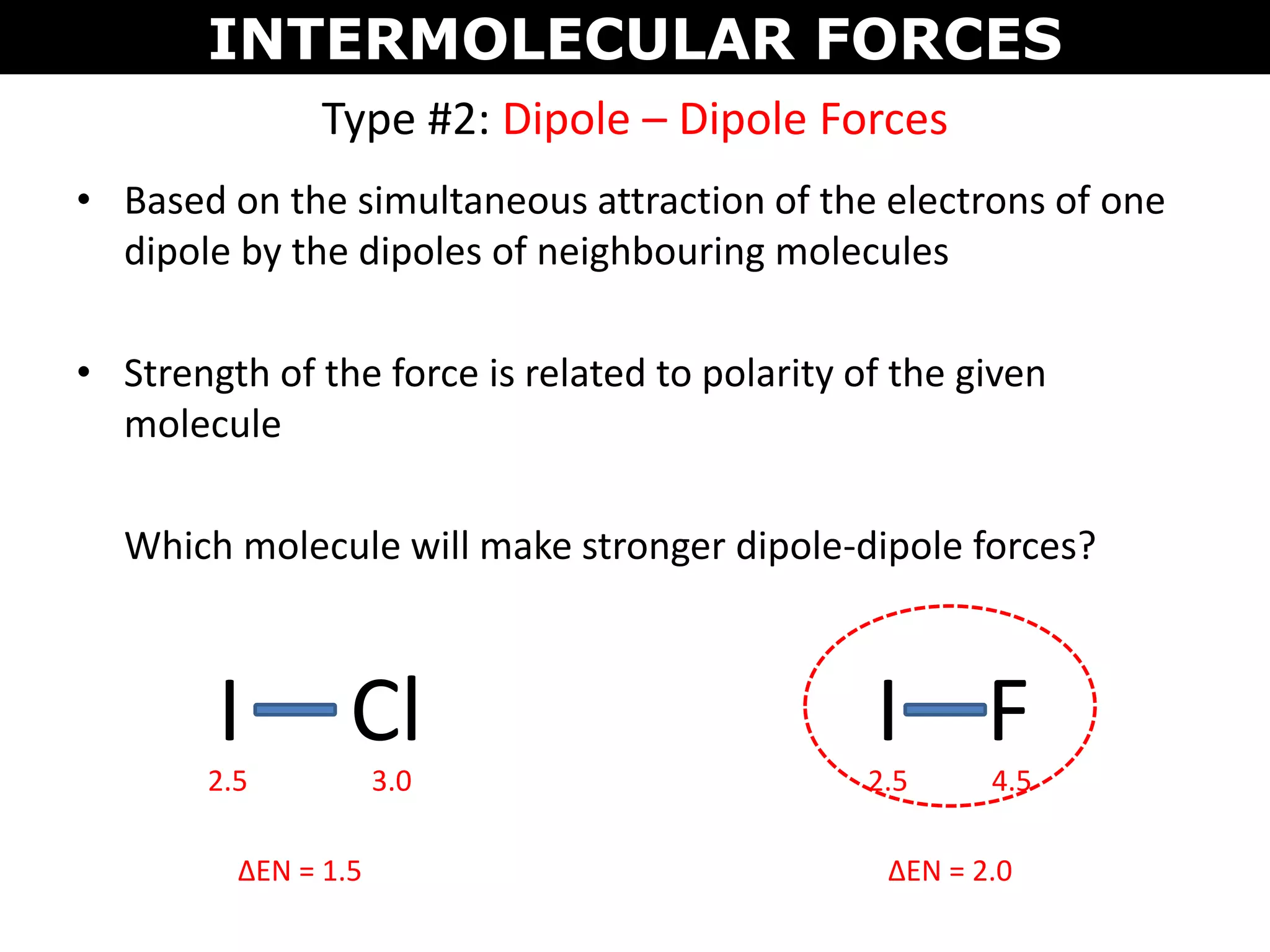
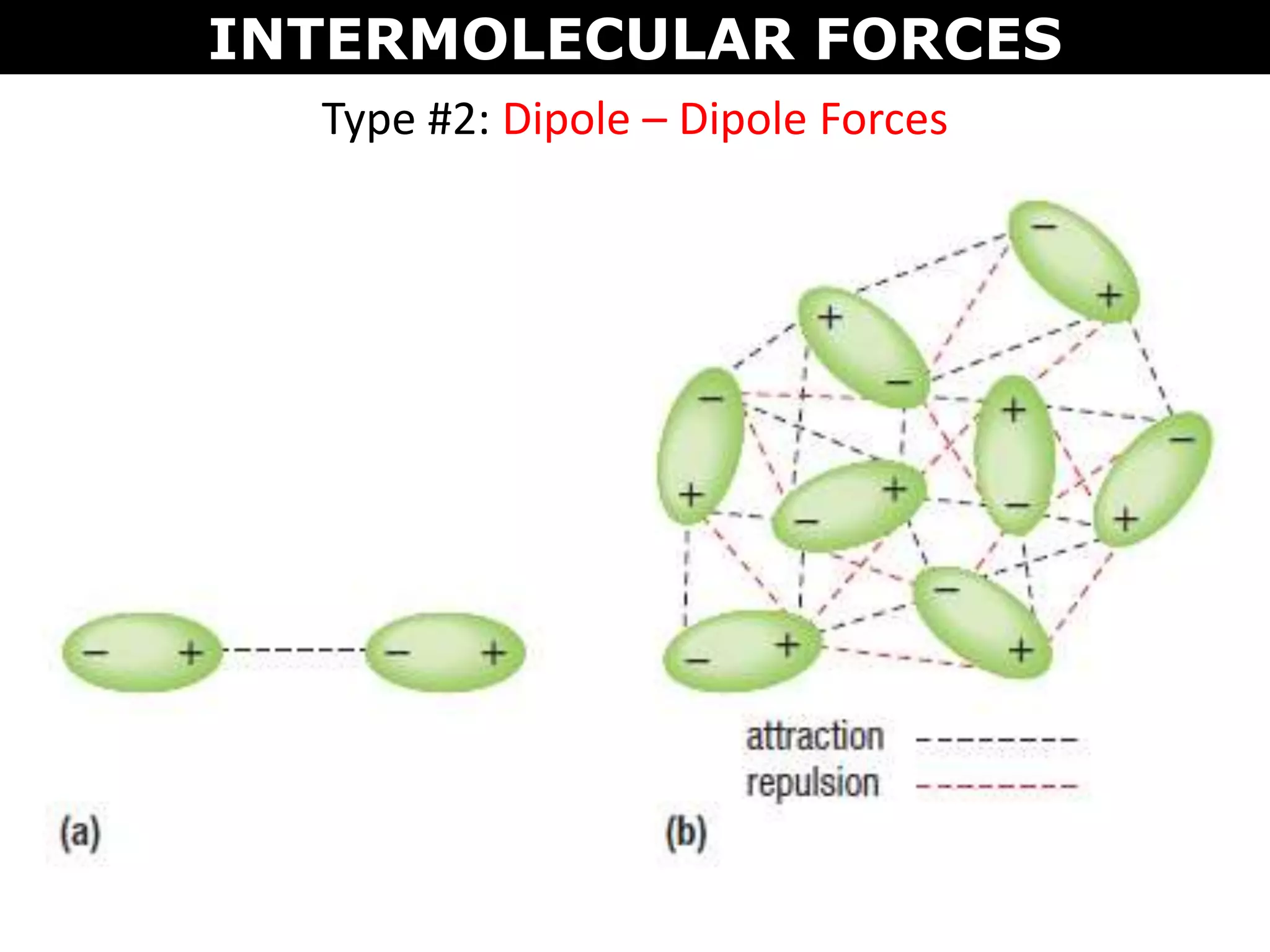
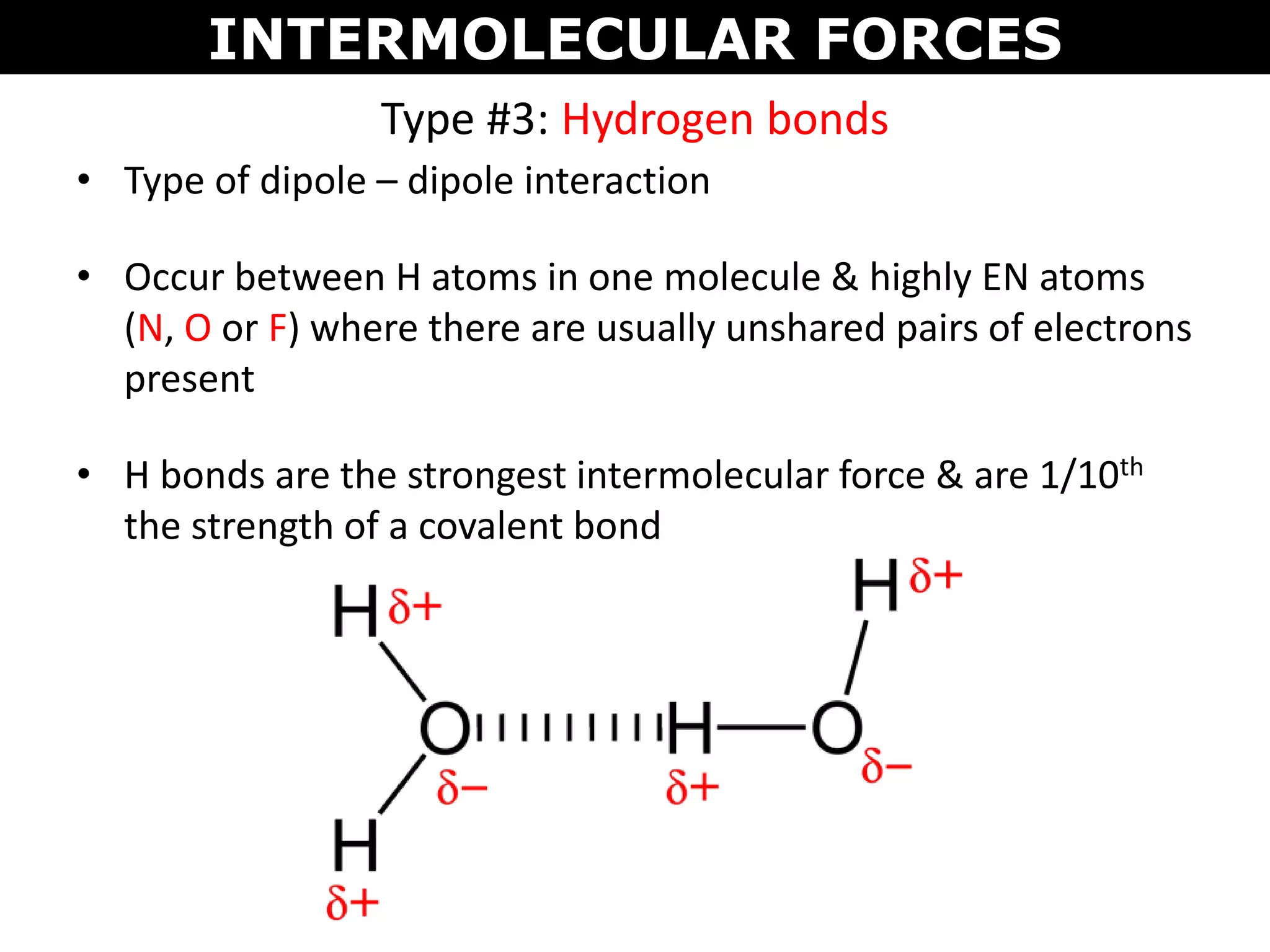
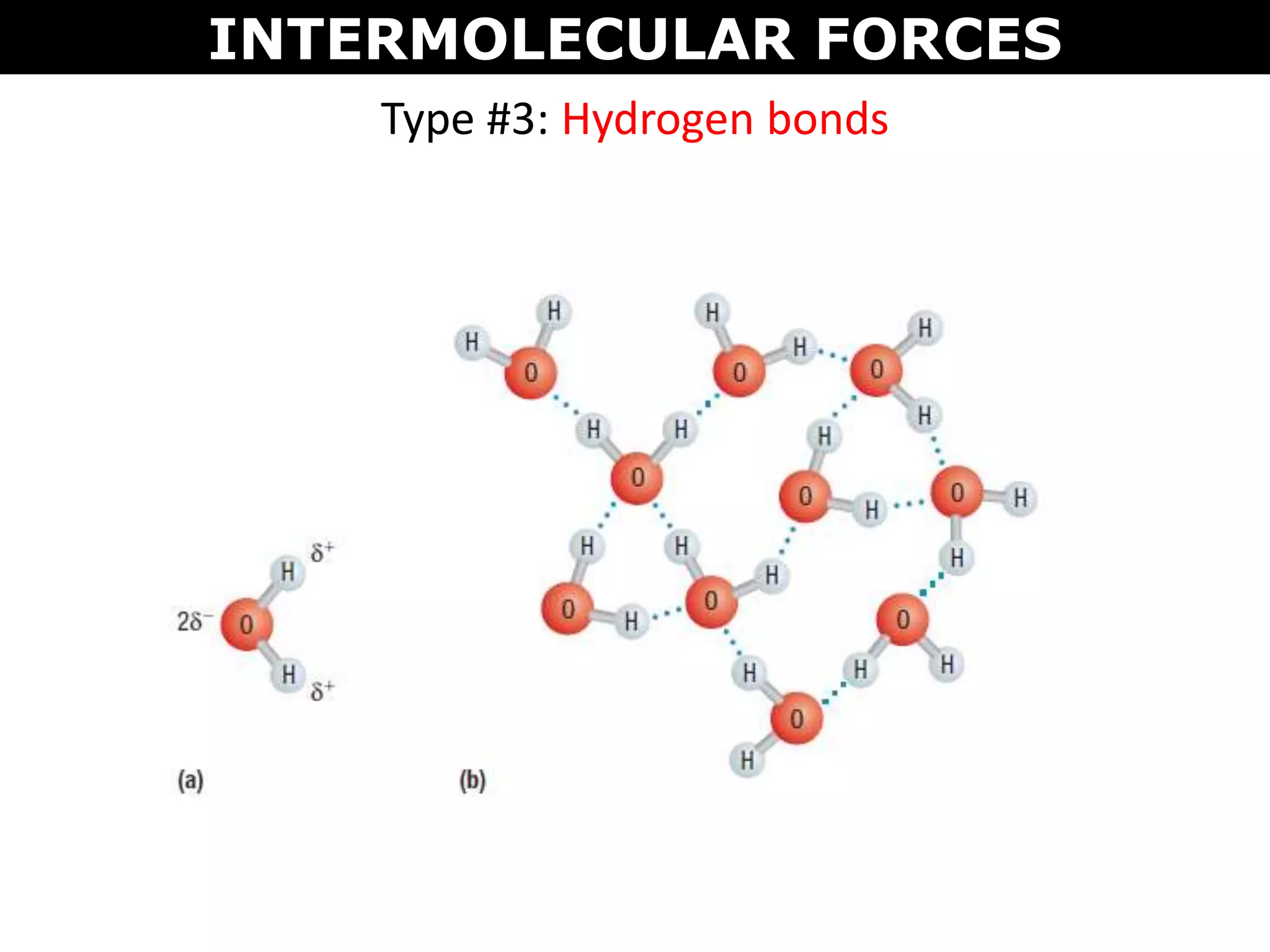
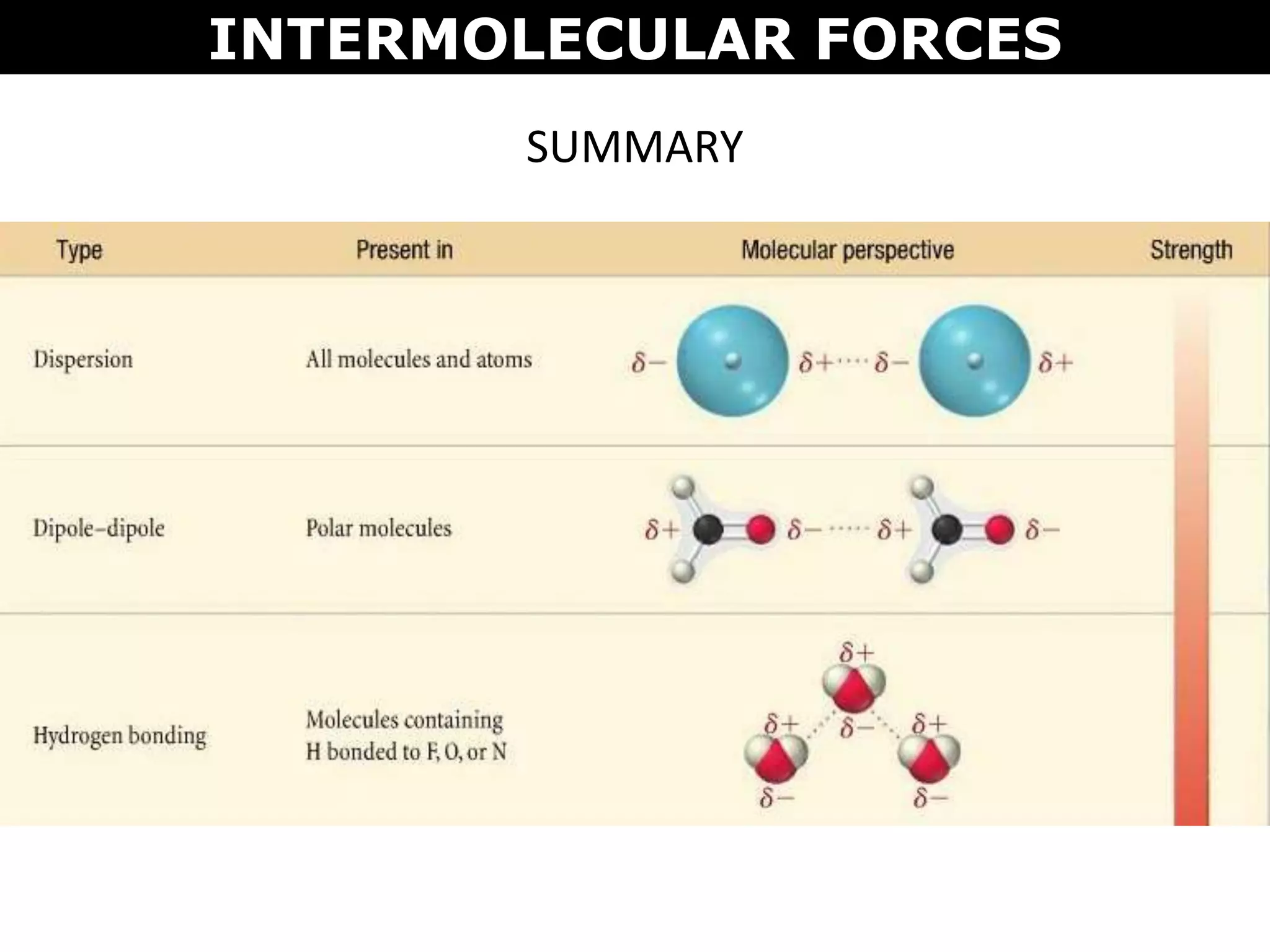
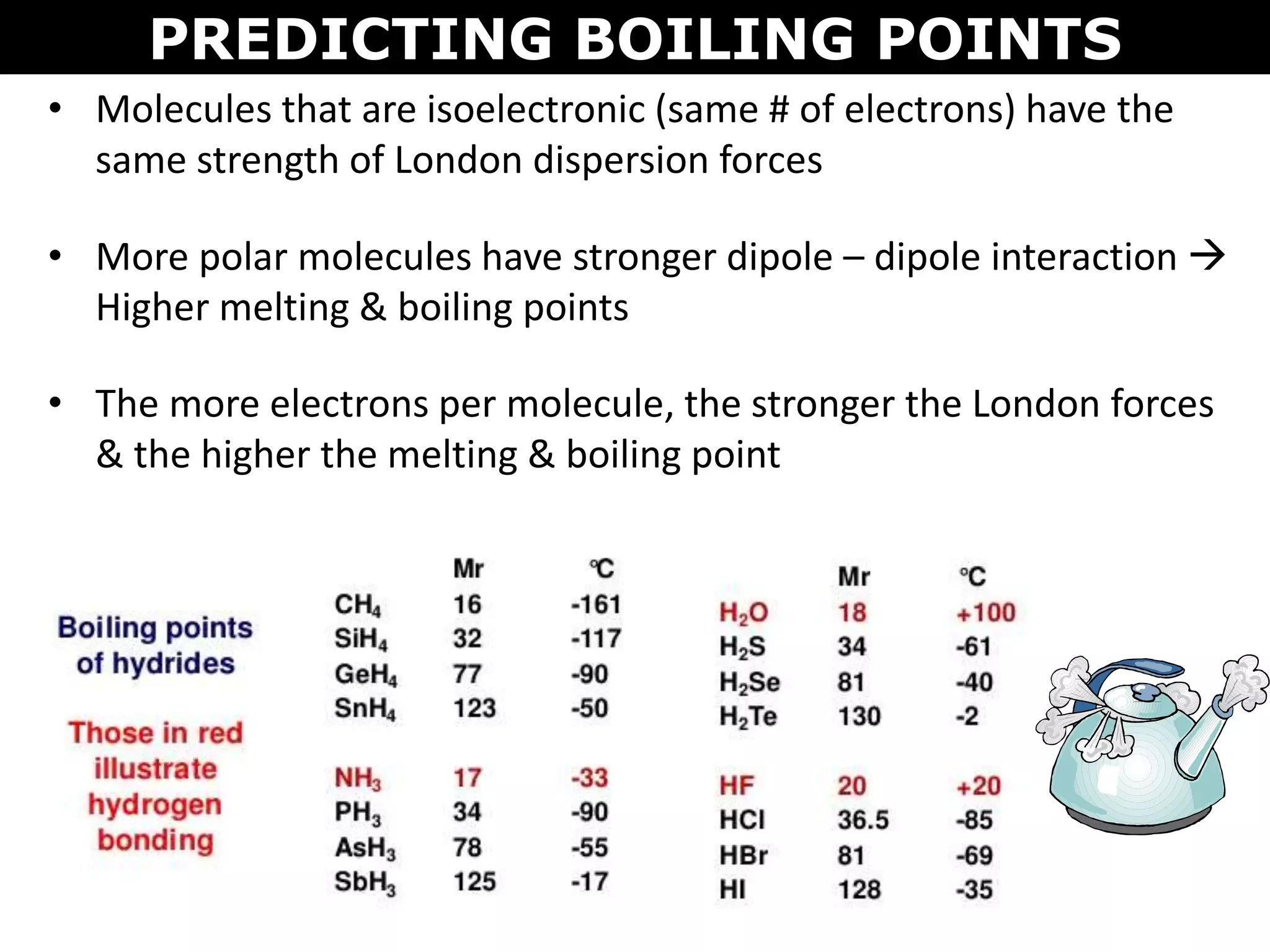
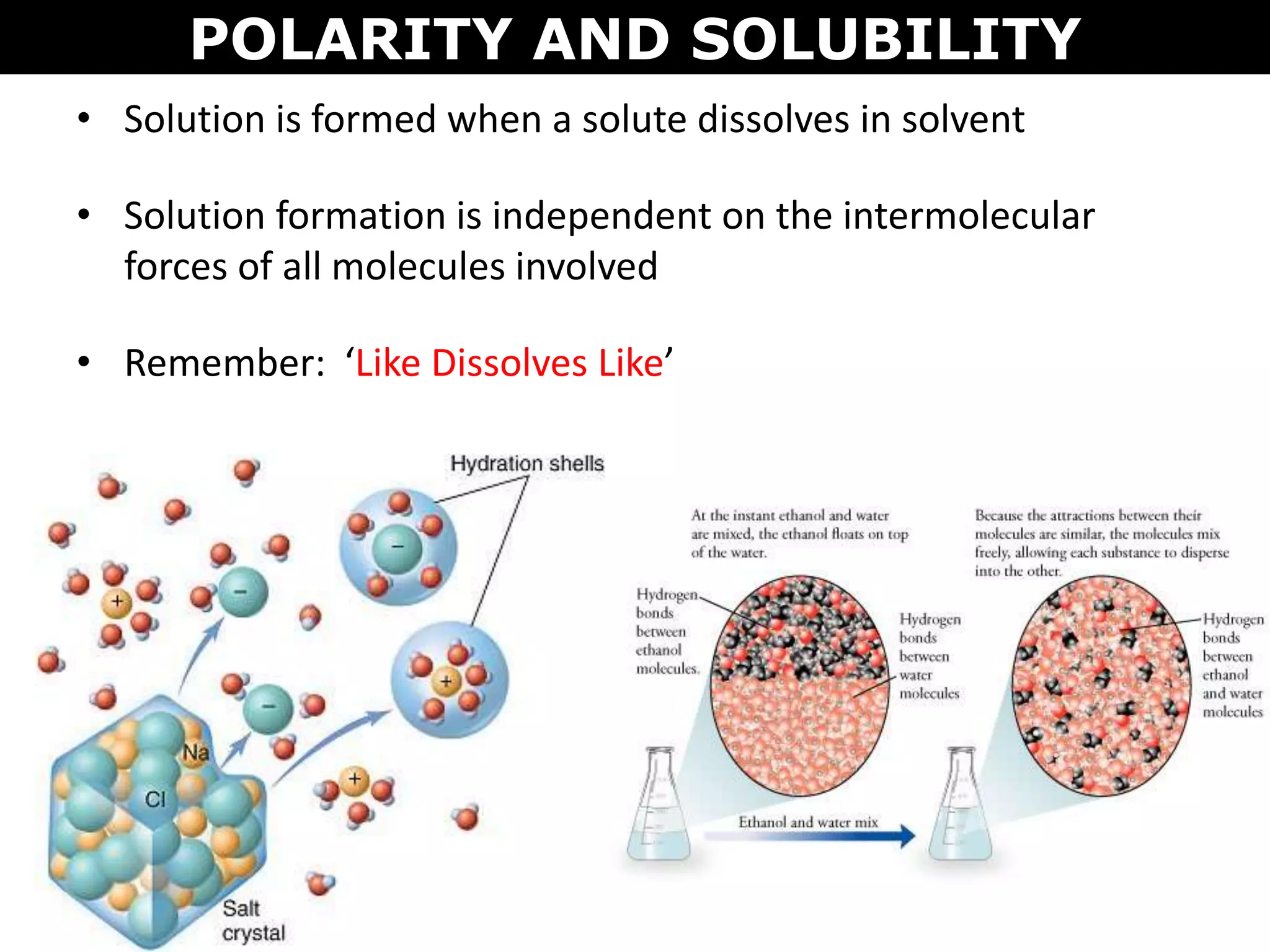
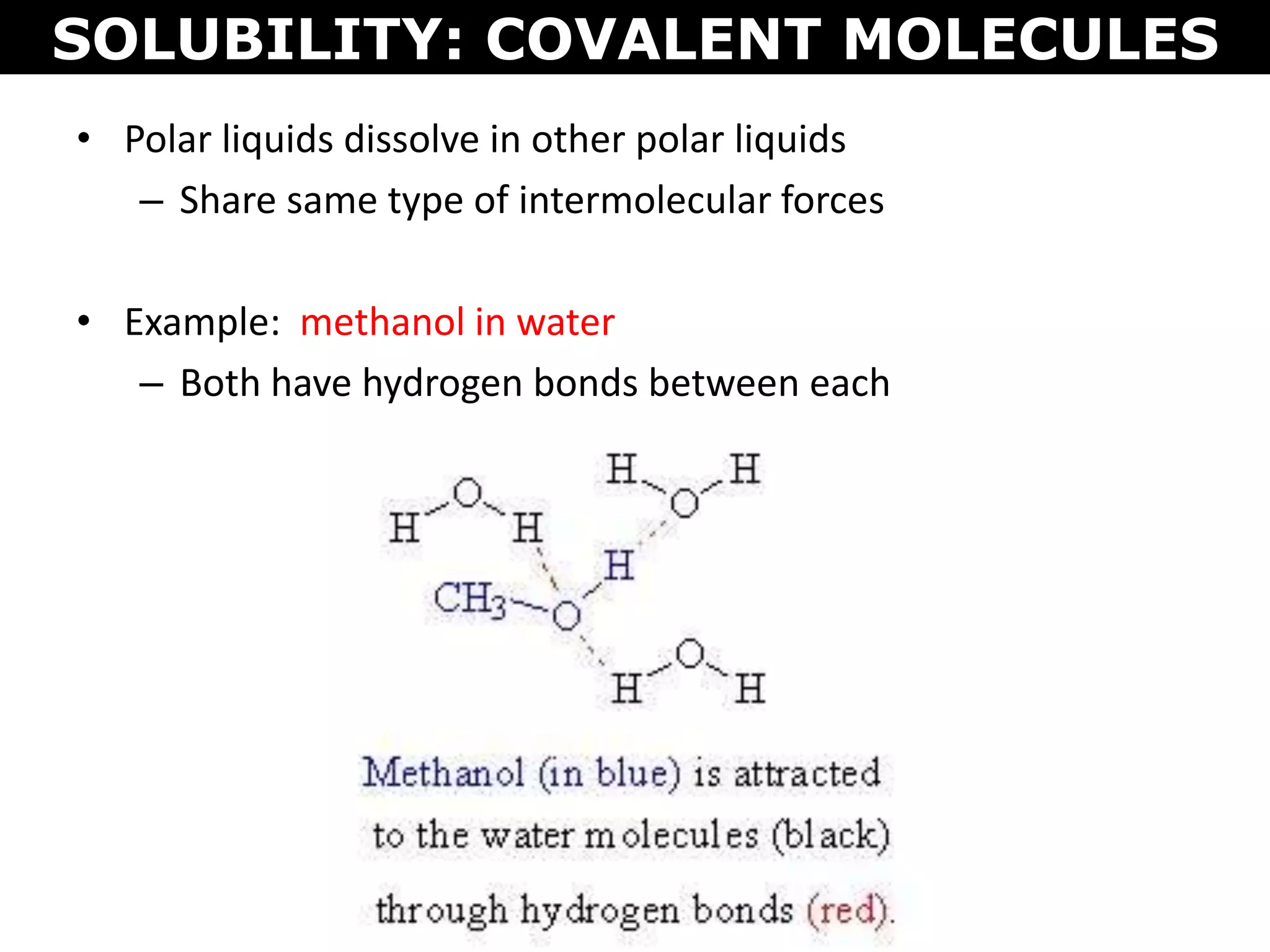
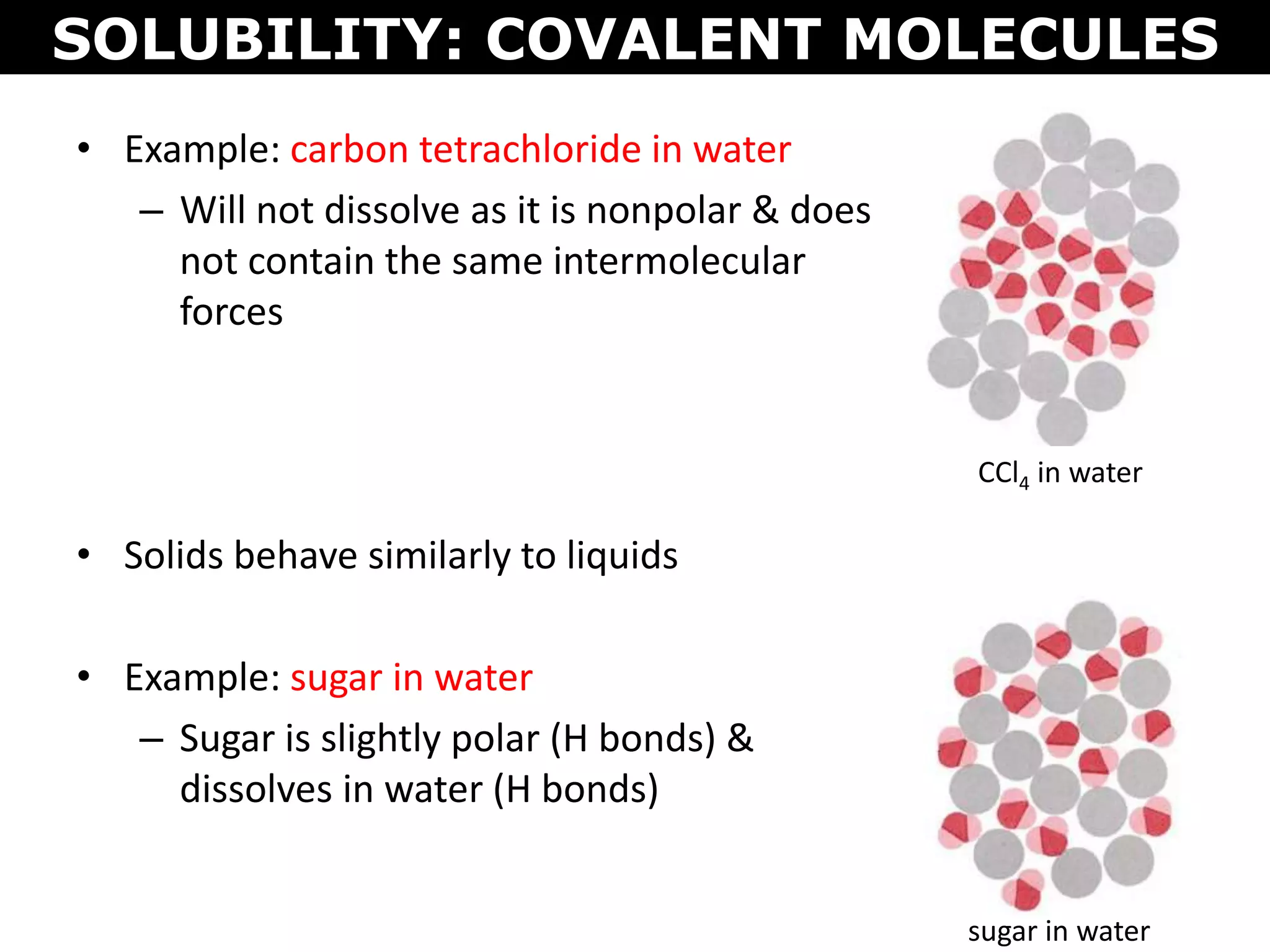
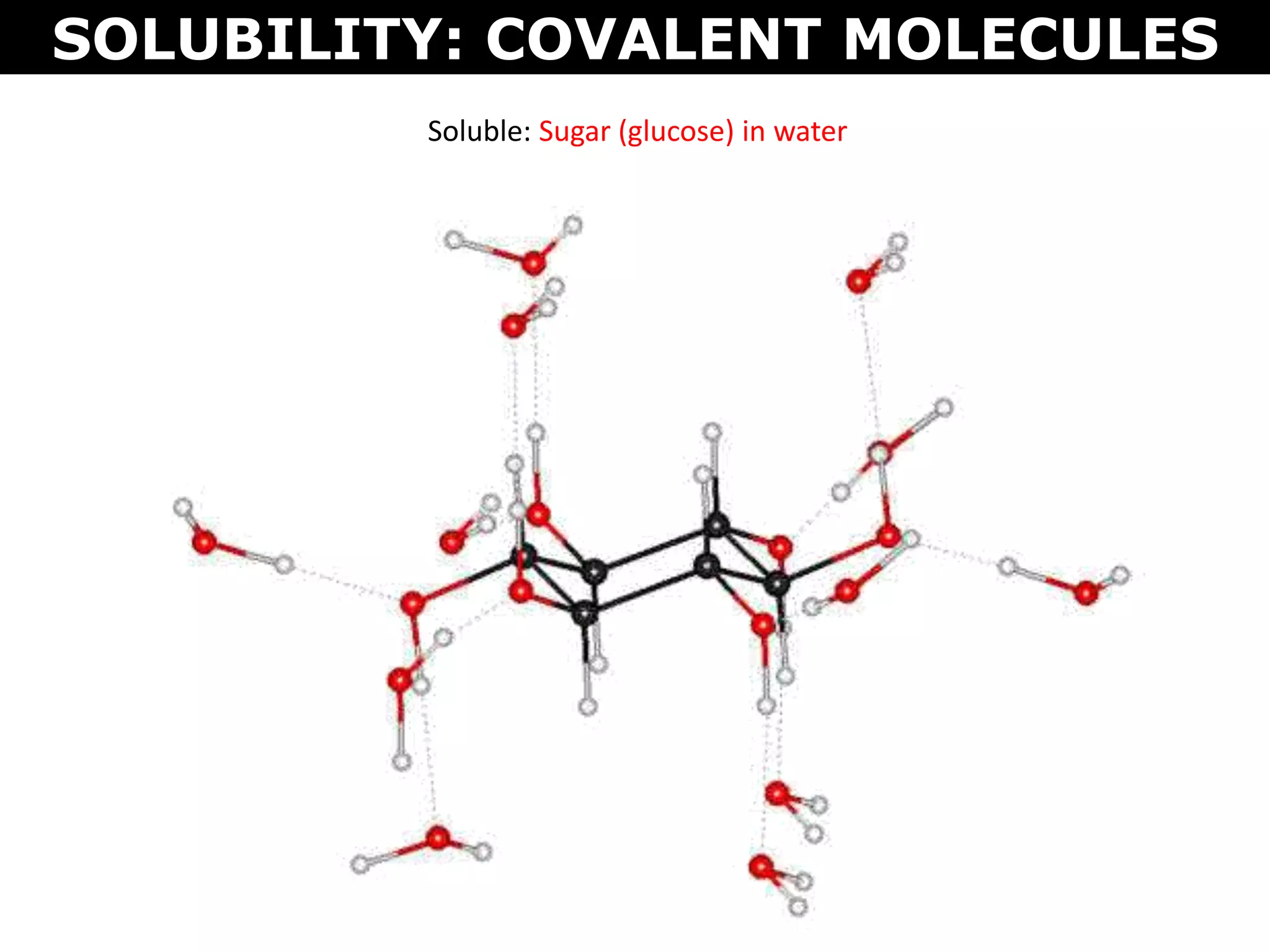
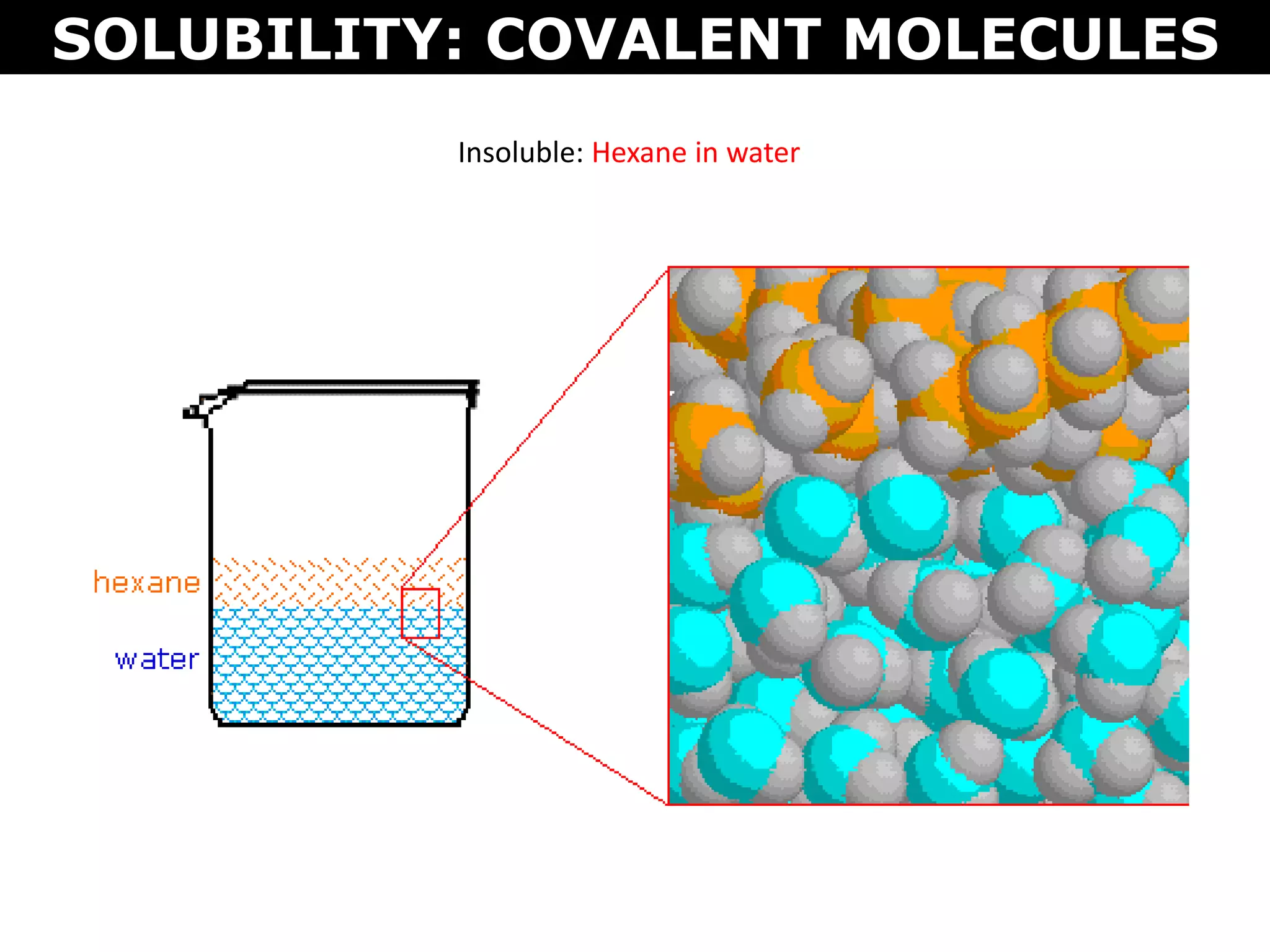
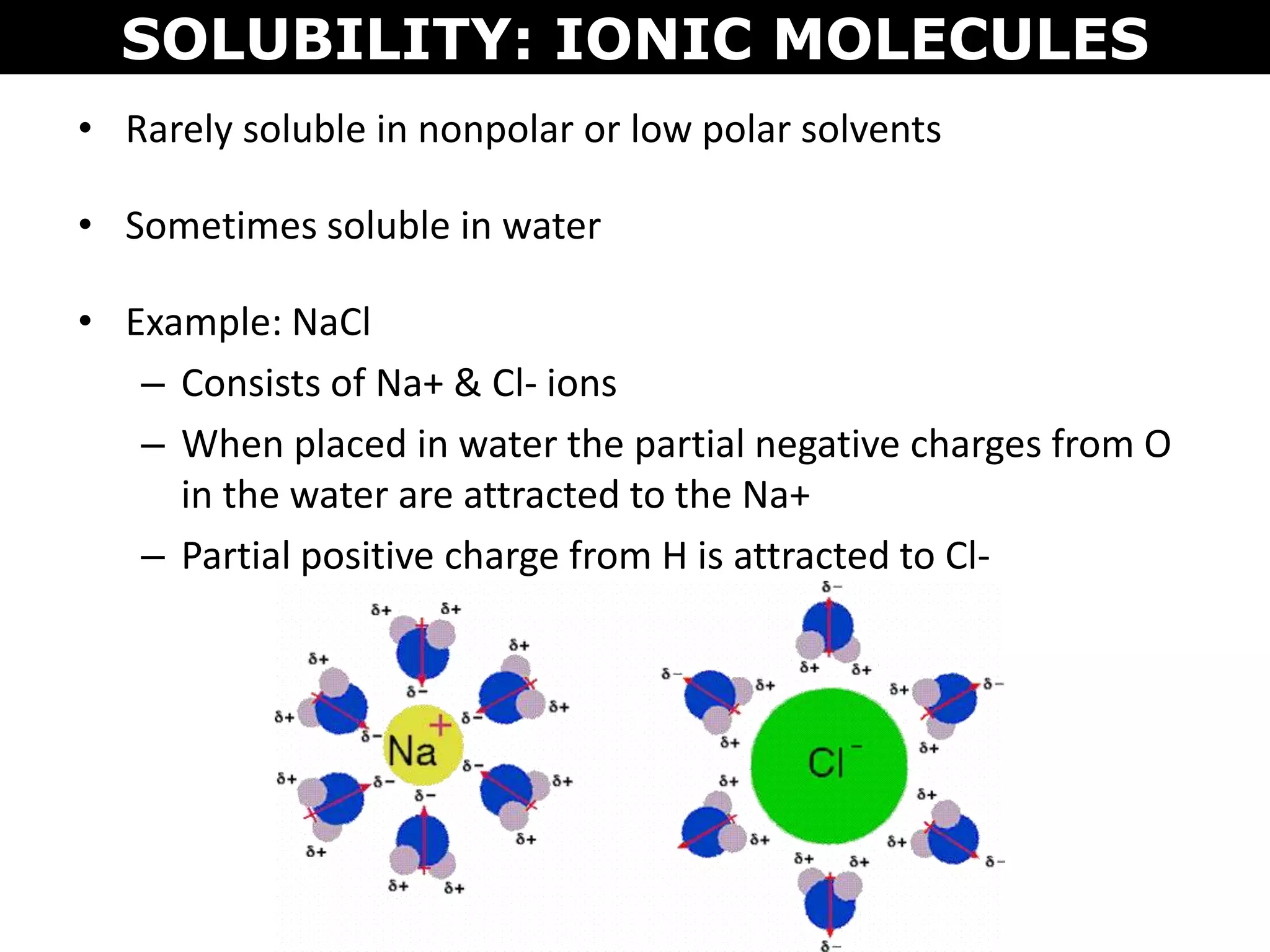
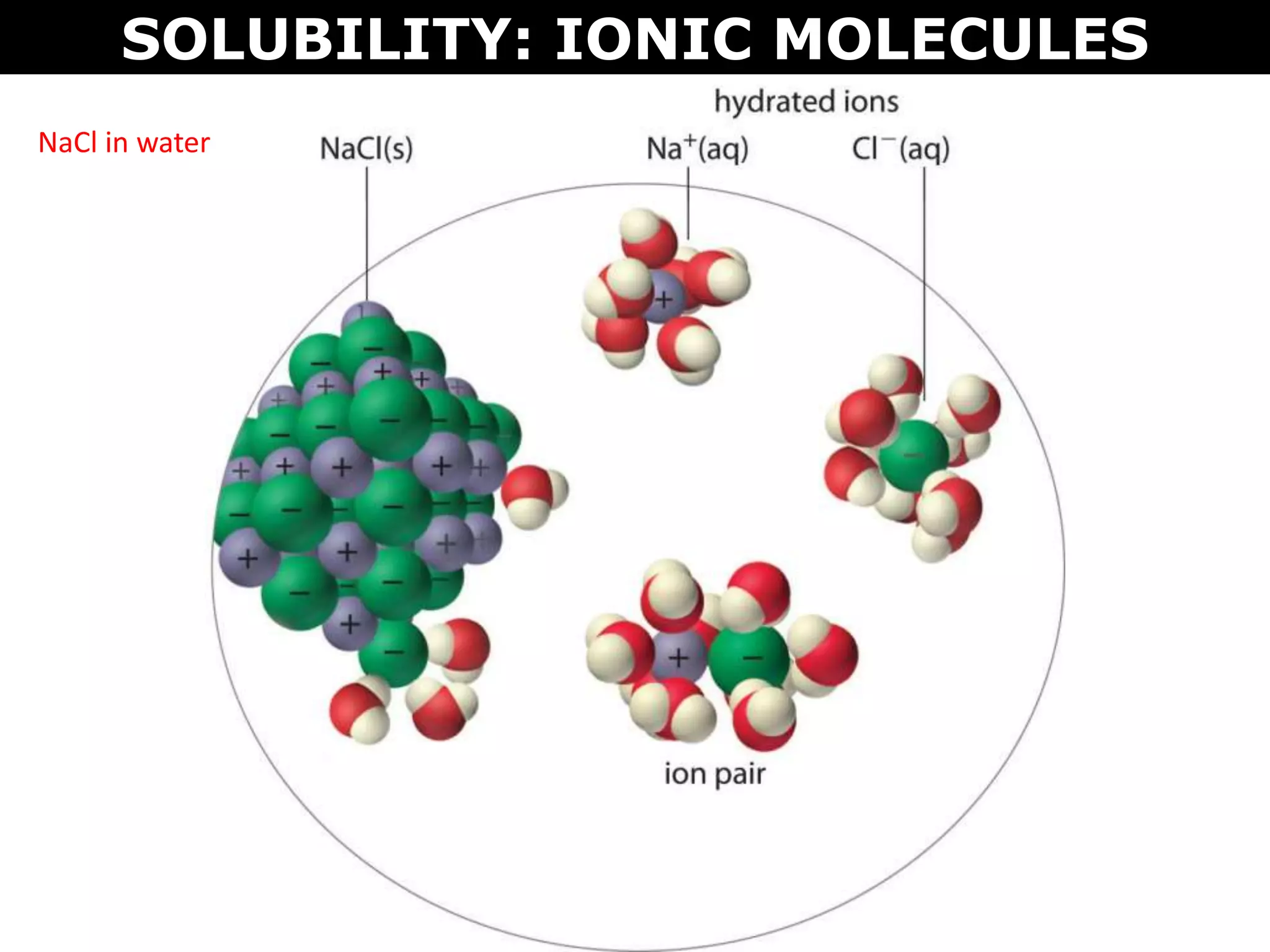
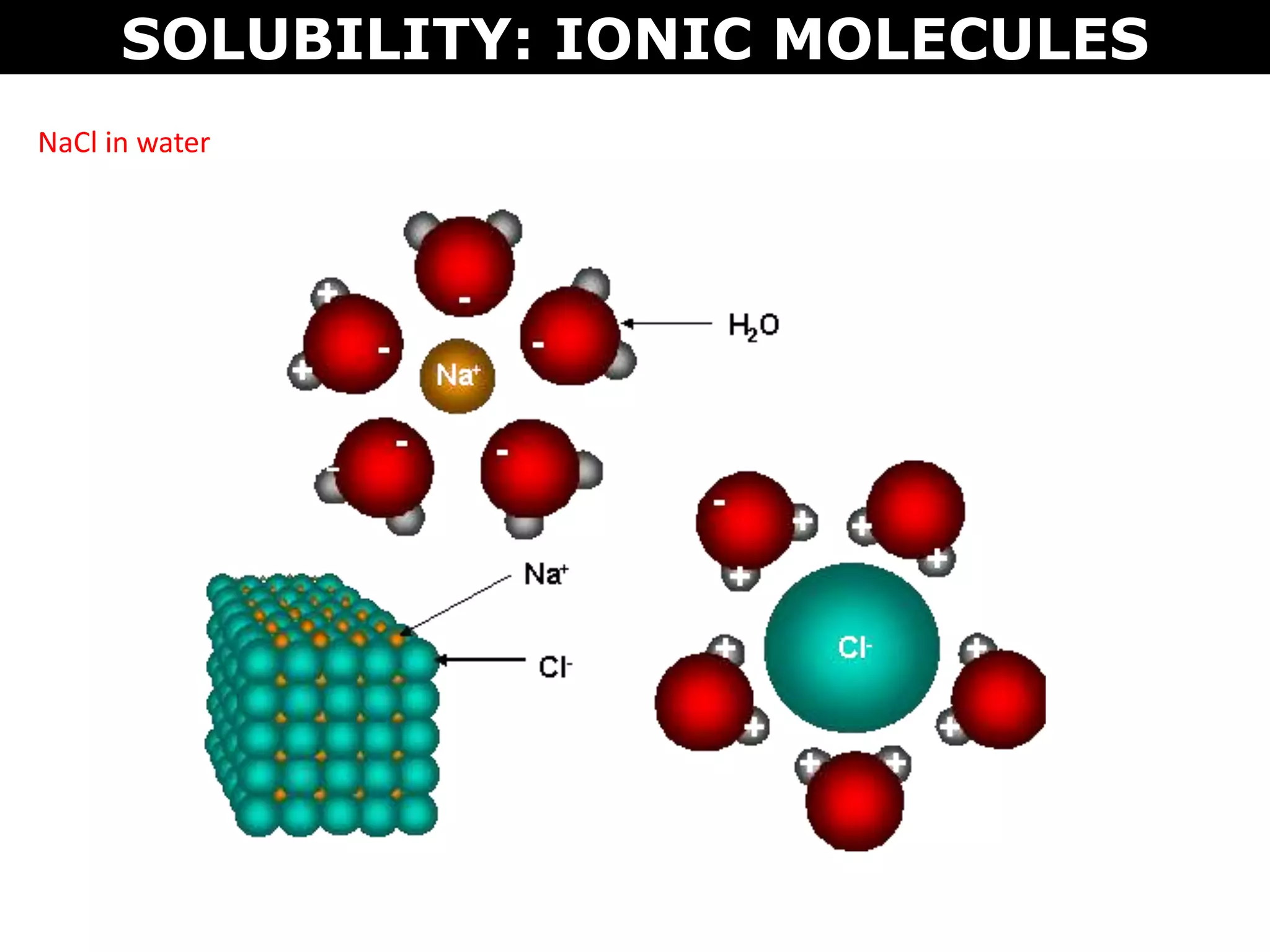
This document discusses intermolecular and intramolecular forces. It describes that intramolecular forces are the forces within a molecule that form covalent bonds. Intermolecular forces are the weaker forces between molecules and include London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding. London dispersion forces exist between all molecules and depend on the number of electrons. Dipole-dipole forces exist between polar molecules. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest intermolecular force and occurs when hydrogen is bonded to fluorine, oxygen, or nitrogen. Intermolecular forces influence properties such as melting point, boiling point, solubility, and surface tension.