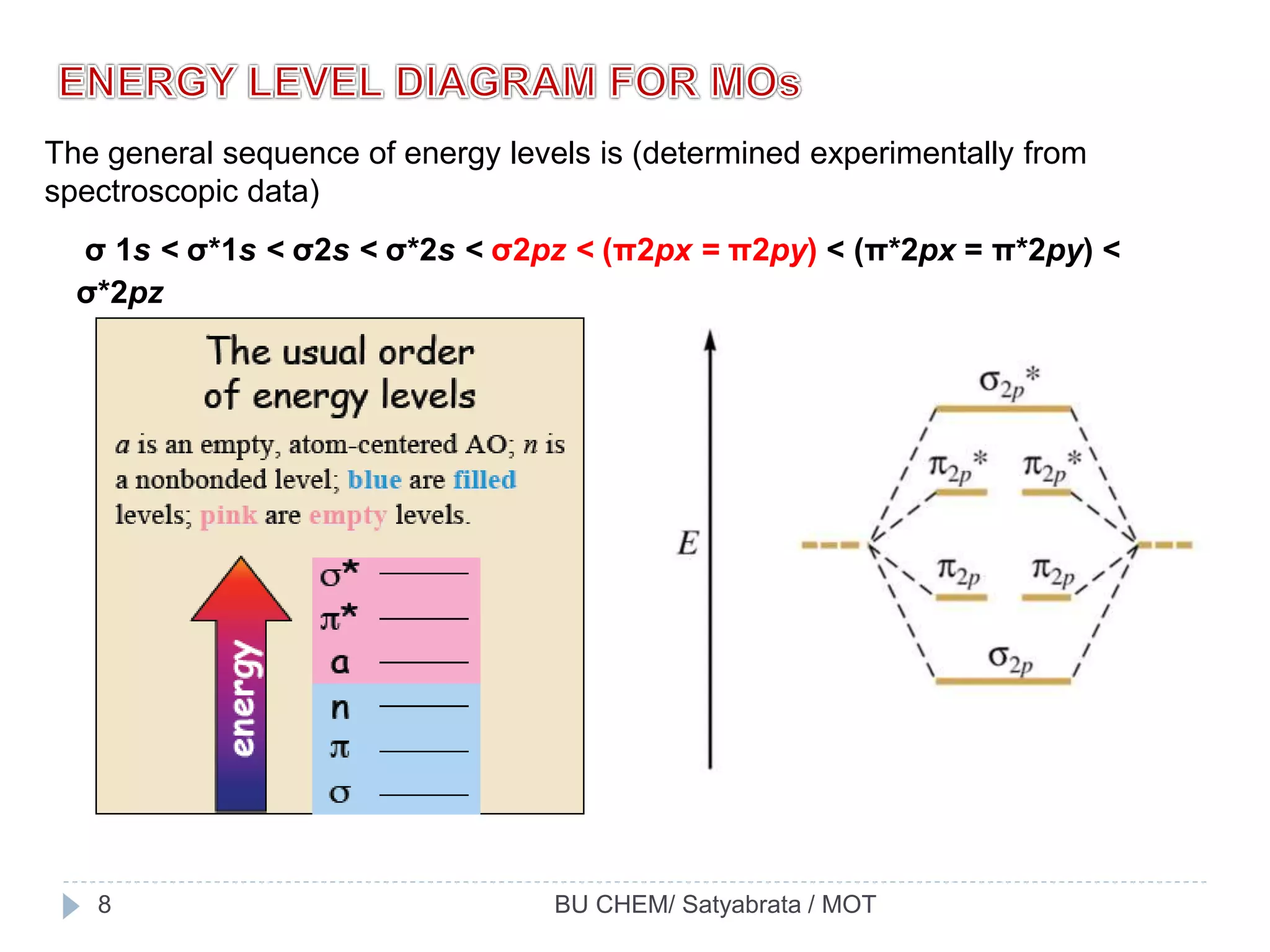
The document discusses molecular orbital theory (MOT), an approach to bonding in which orbitals encompass the entire molecule rather than being localized between atoms. MOT was put forward by Hund and Mulliken and later modified by Jones and Coulson. It addresses some of the drawbacks of valence bond theory, including explaining the paramagnetic nature of O2. MOT uses the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) approach and Hund's rule to determine molecular orbital configurations and energies.