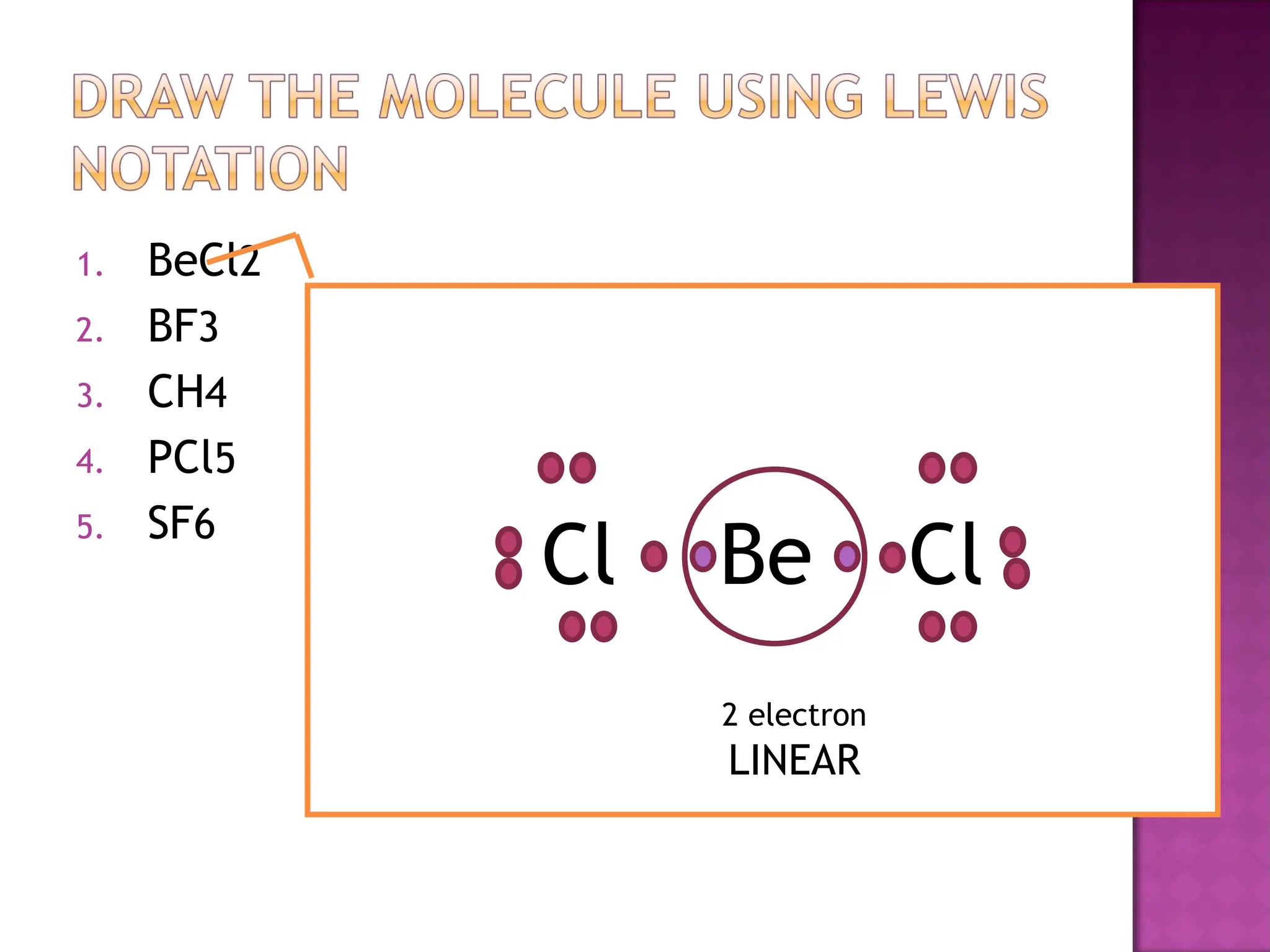
This document outlines the process for predicting molecular shapes based on the structure of atoms and the arrangement of electron pairs around a central atom. It details steps such as drawing Lewis structures and counting electron pairs to determine molecular geometry using VSEPR theory. Additionally, it includes a group activity for building molecular models to visualize these concepts.