Embed presentation
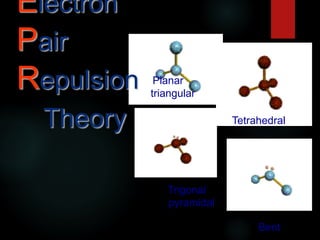
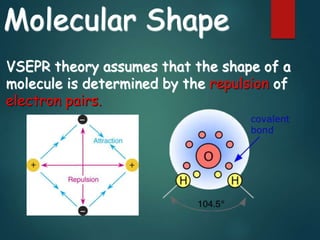

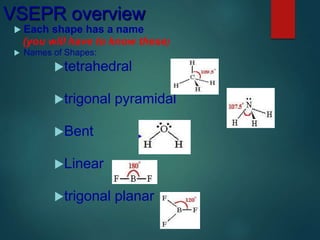
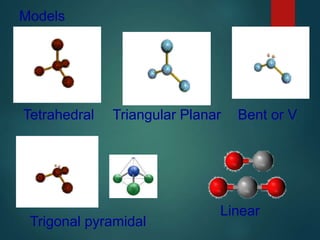
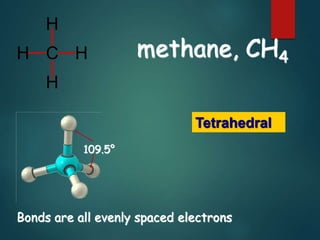
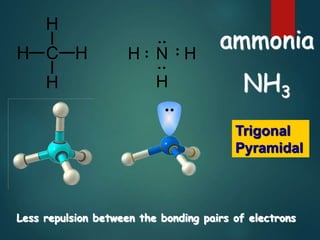
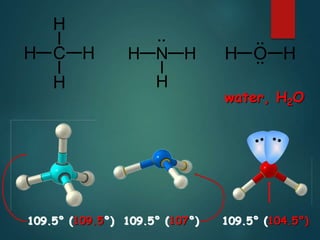
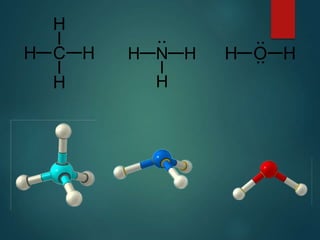
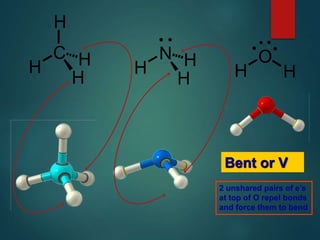
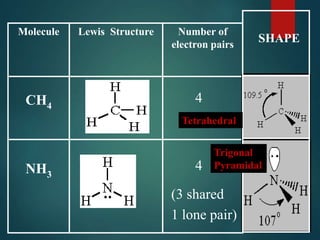
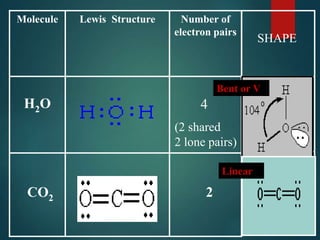
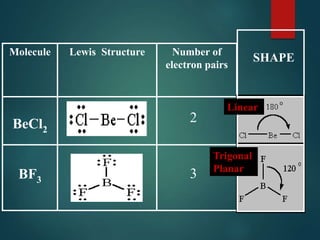
VSEPR theory predicts molecular shapes based on electron pair repulsion around a central atom. It assumes that electron pairs will maximize their distance from each other to minimize repulsion. Molecular shapes include tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal, bent, and linear based on the number of electron pairs. The theory uses Lewis structures to determine electron pairs from bonds and lone pairs, and predicts the shape that minimizes repulsion between these pairs.












