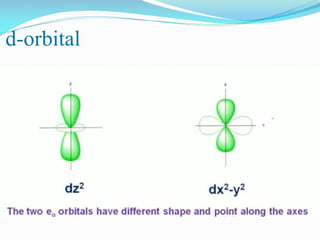
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on dπ-pπ bonds. It introduces that d-orbitals on third period elements can participate in bonding. The eg orbitals can form σ-bonds by overlapping with s and p orbitals, while the t2g orbitals can combine with p orbitals of the same character. However, free atom d-orbital energies are high, the orbitals are diffuse rather than compact, and promotion energies to d-orbital states are around 30-35 eV, making significant d-orbital contributions to bonding unlikely except in certain cases.