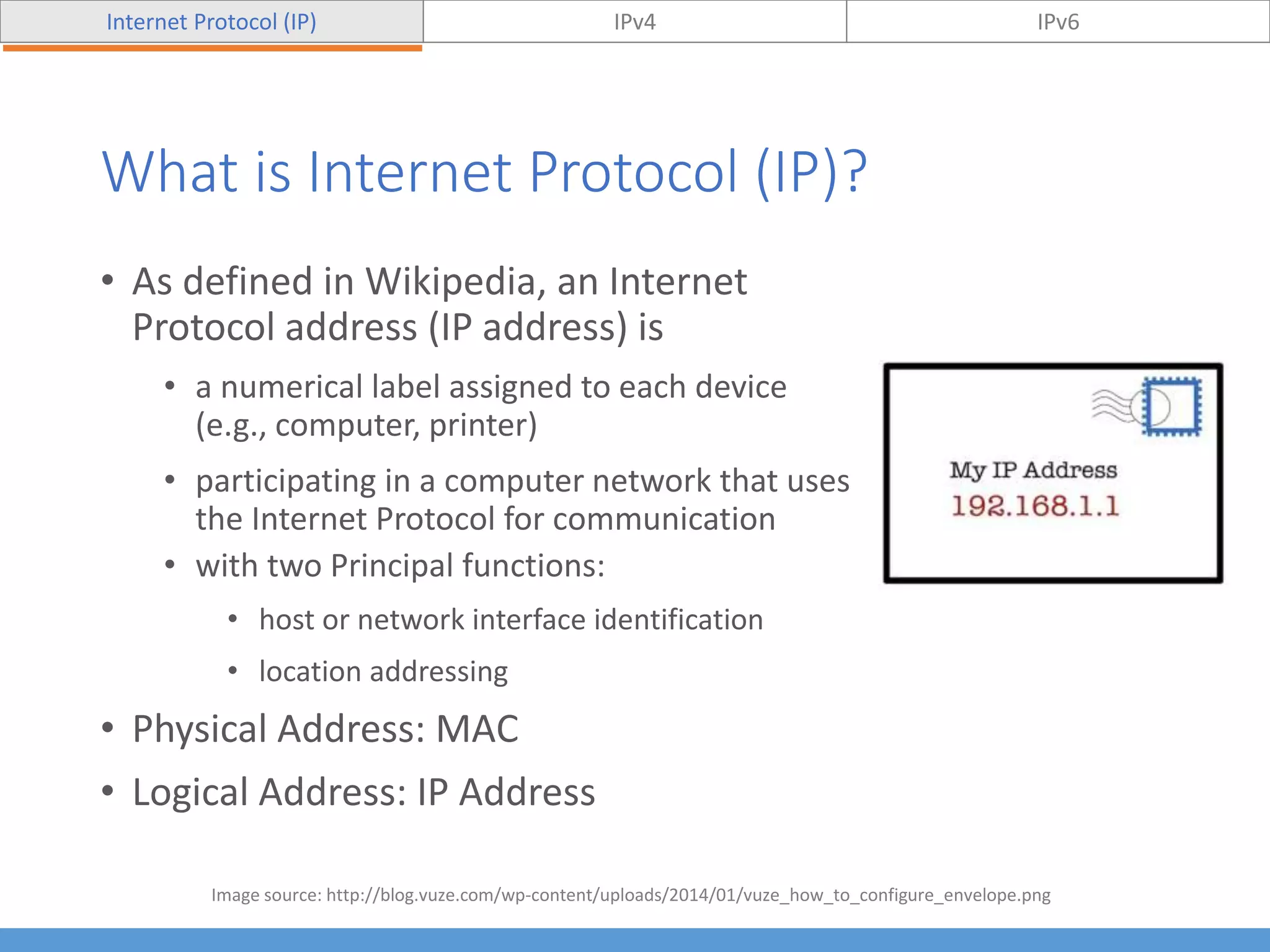
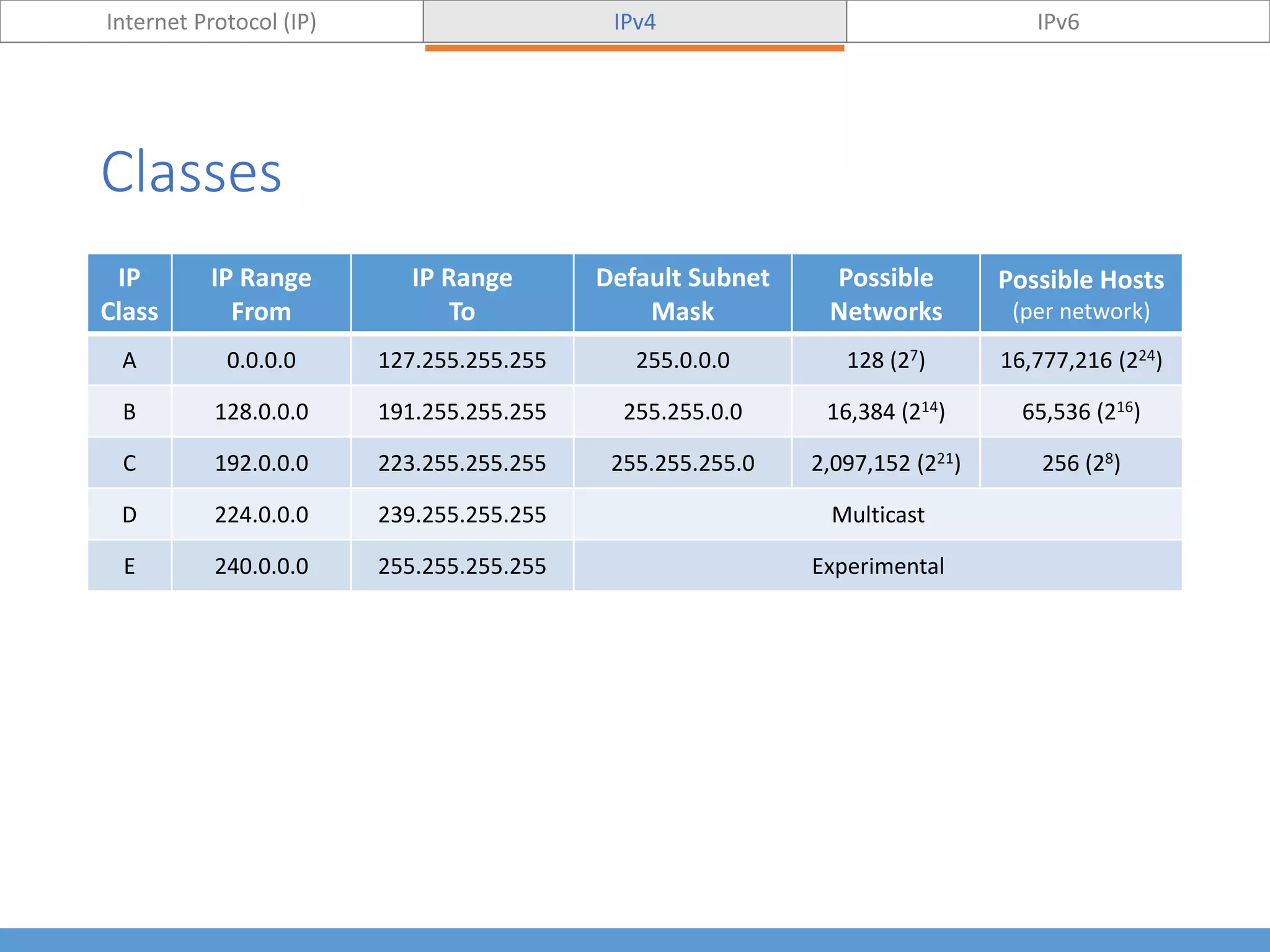
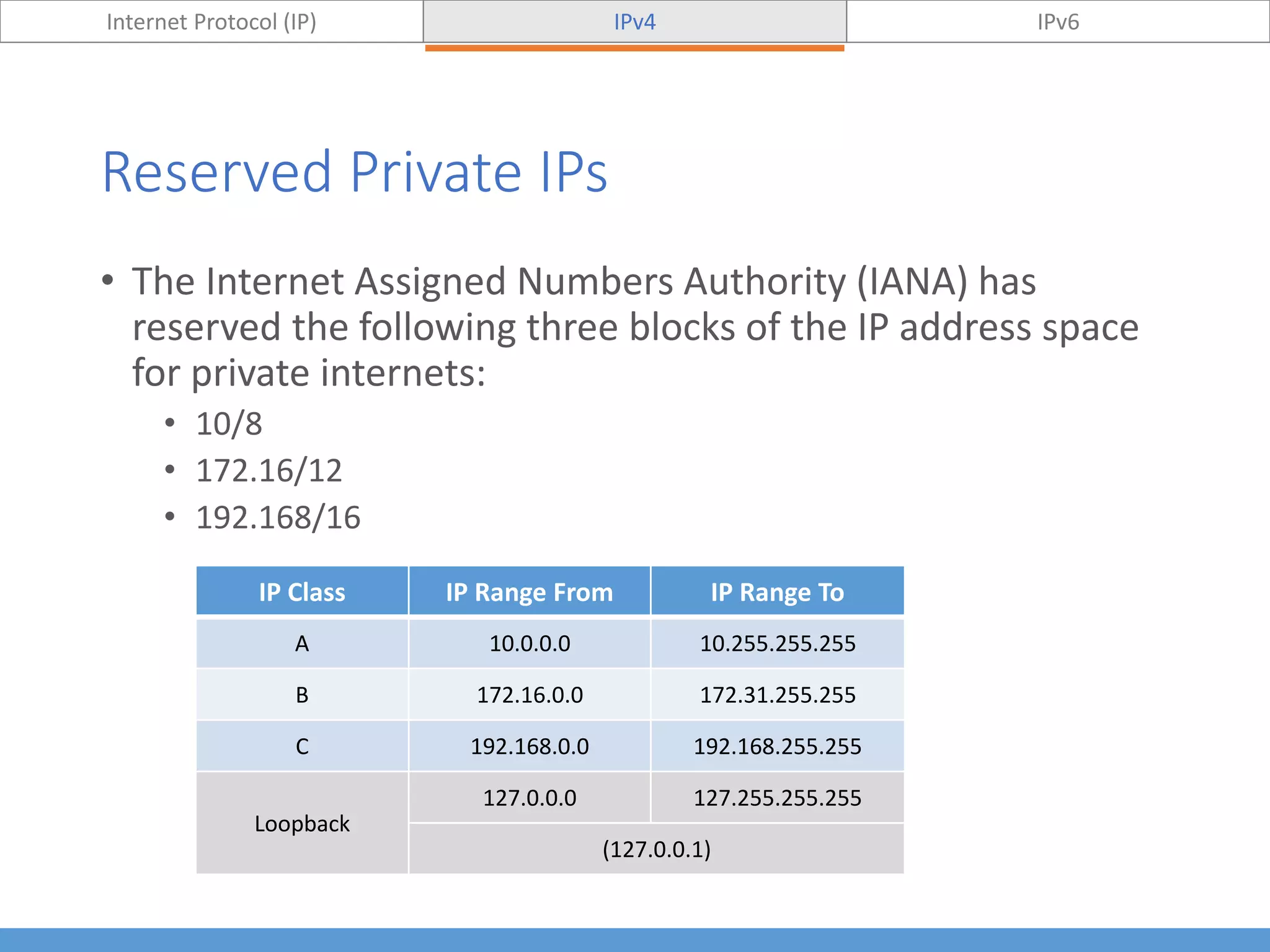
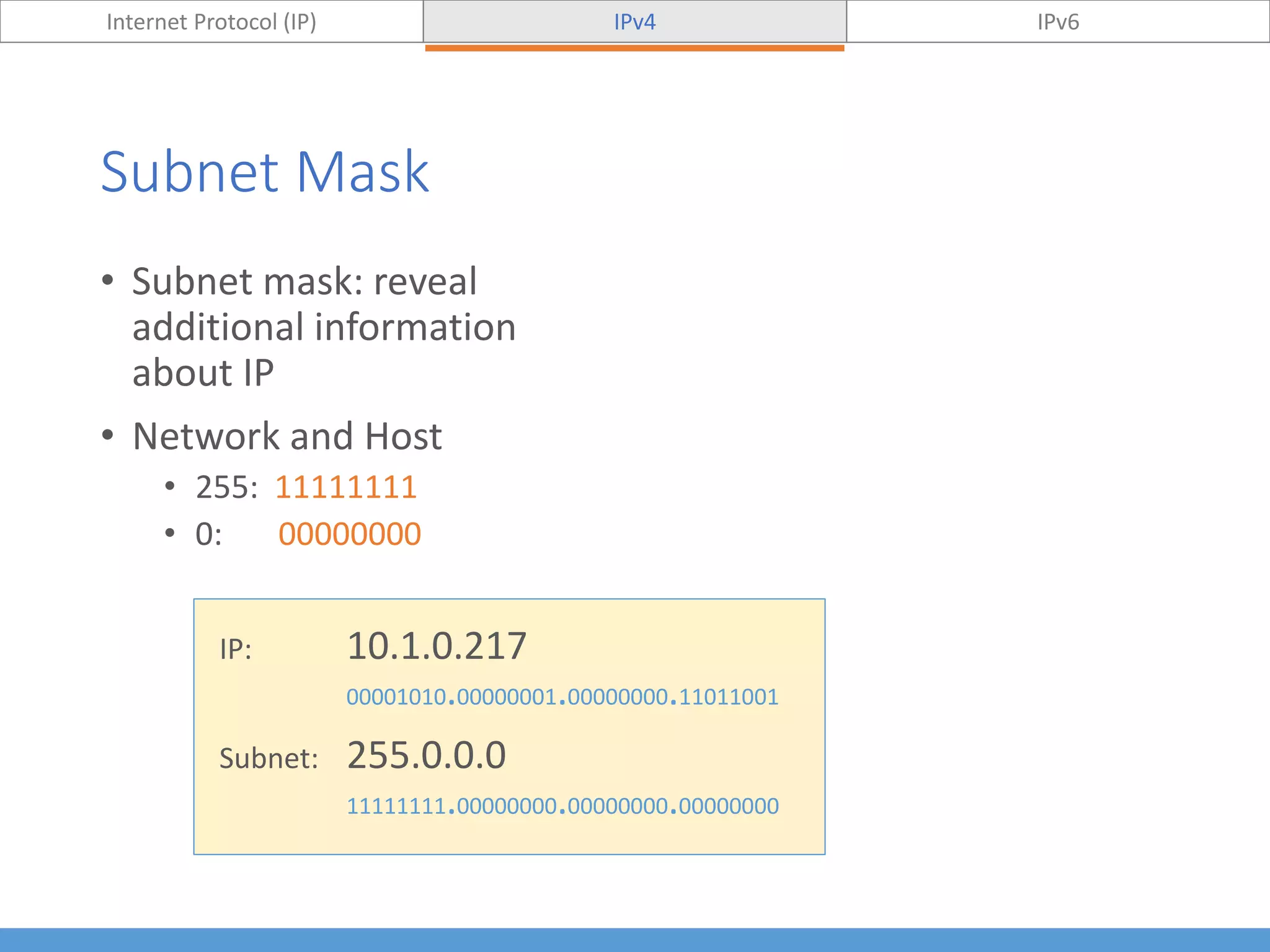
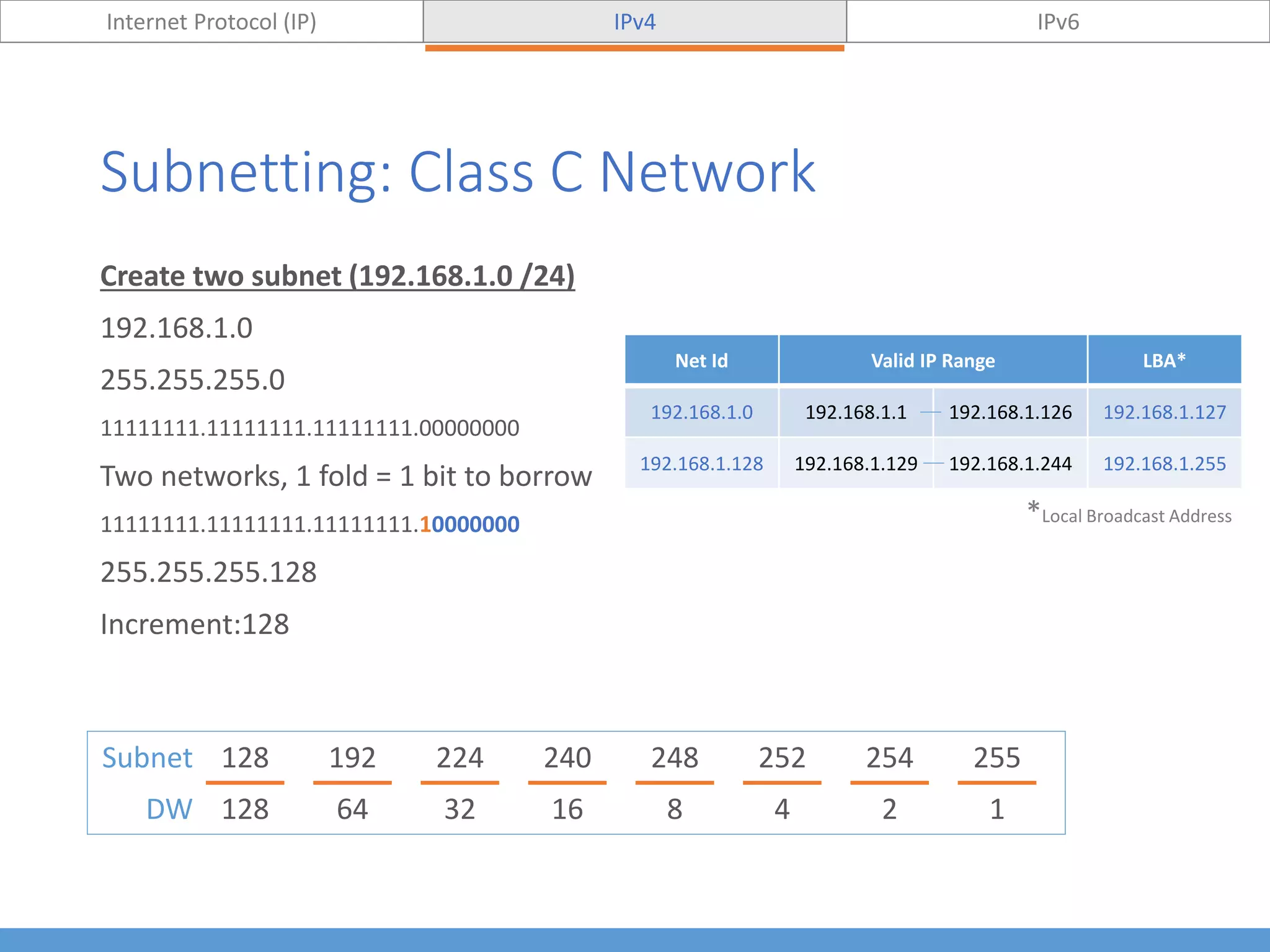
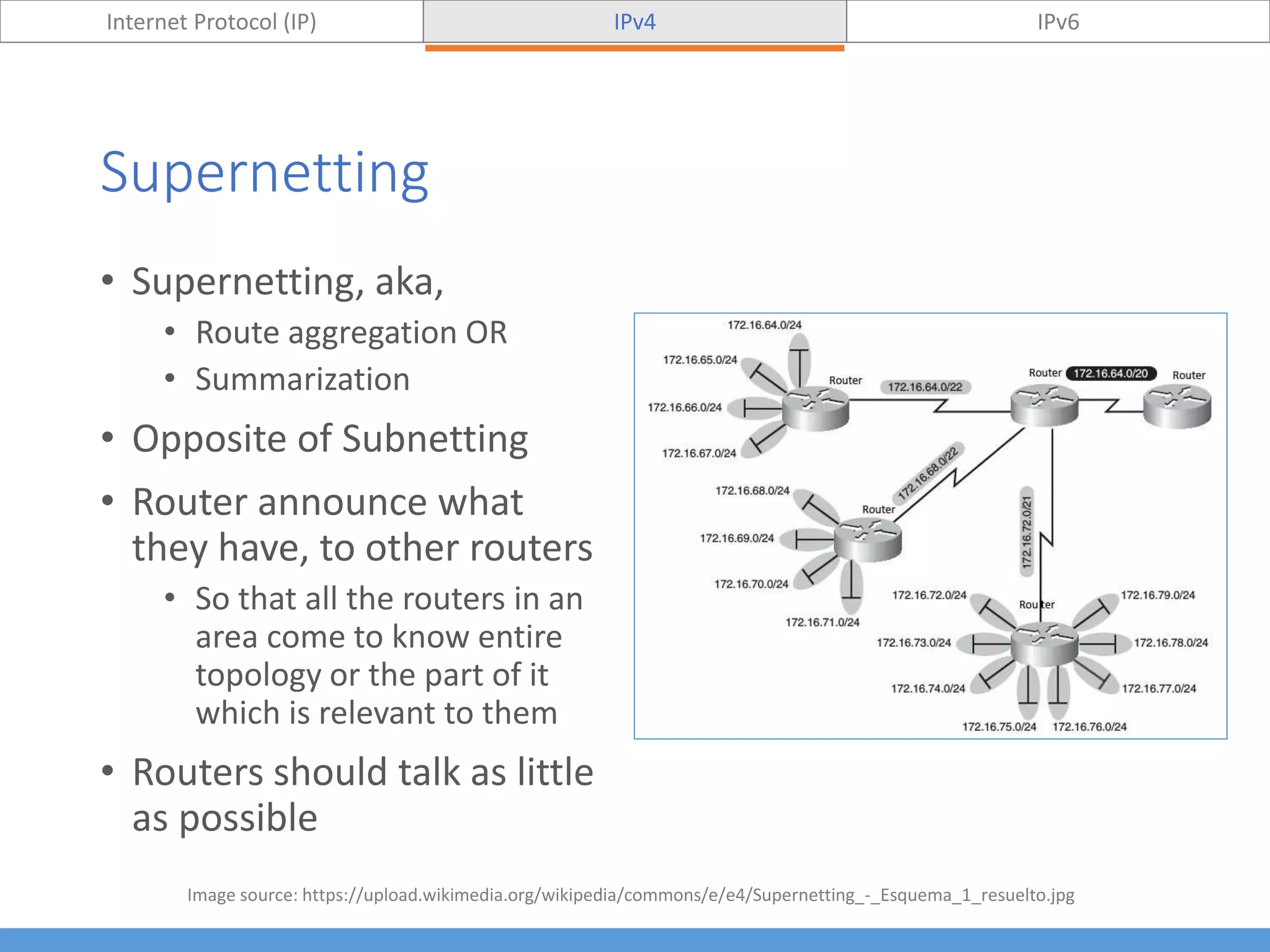
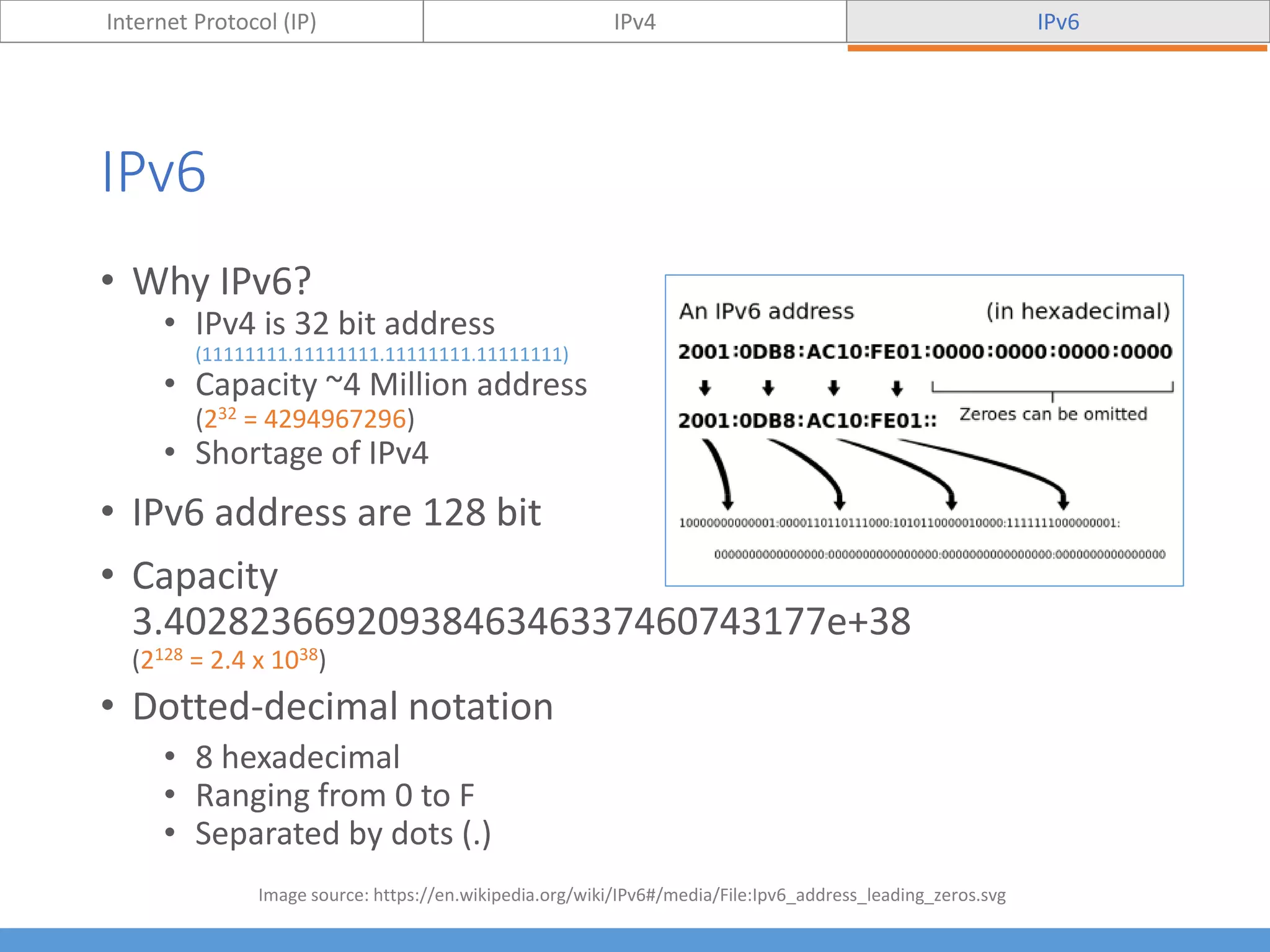
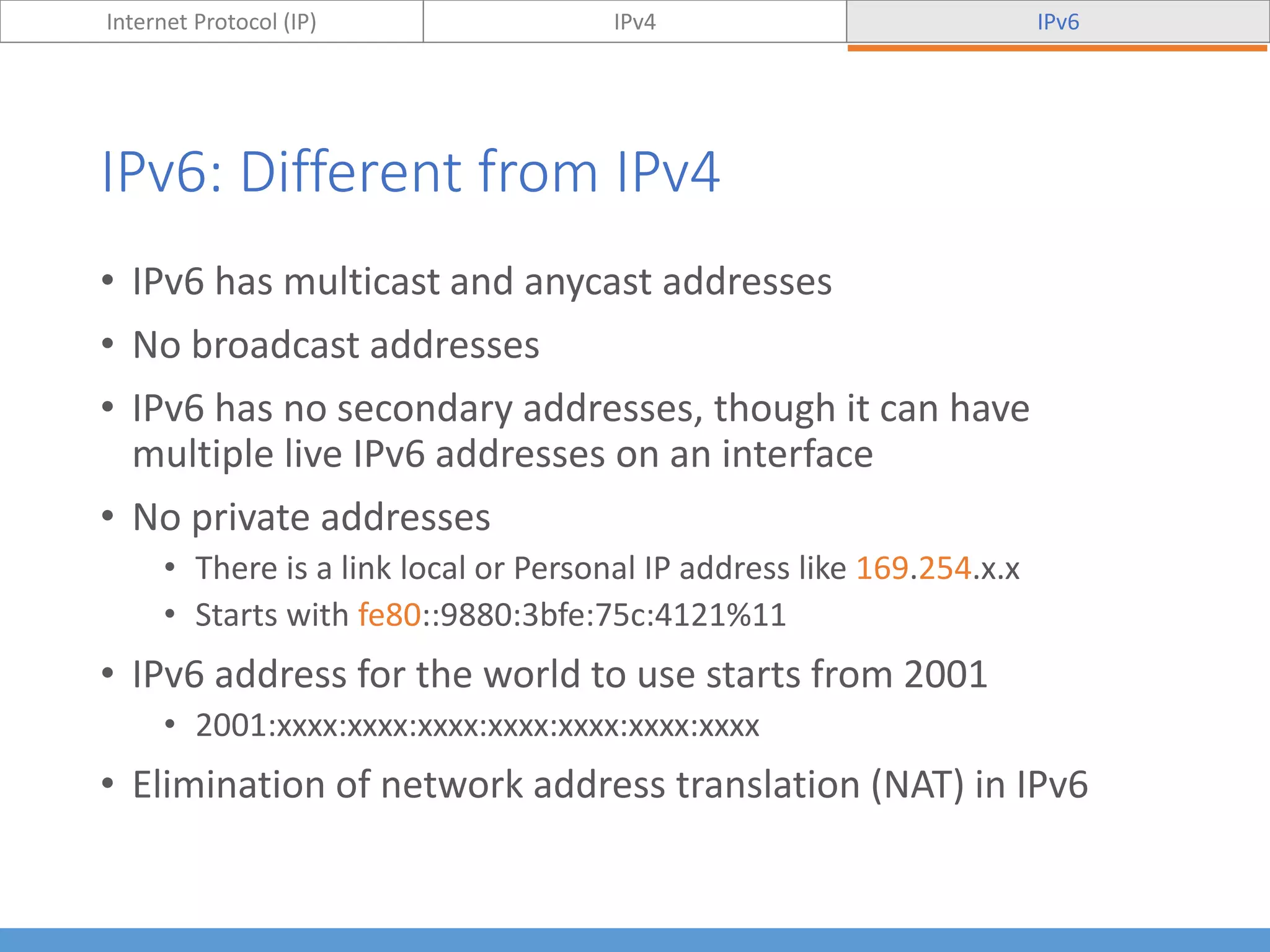
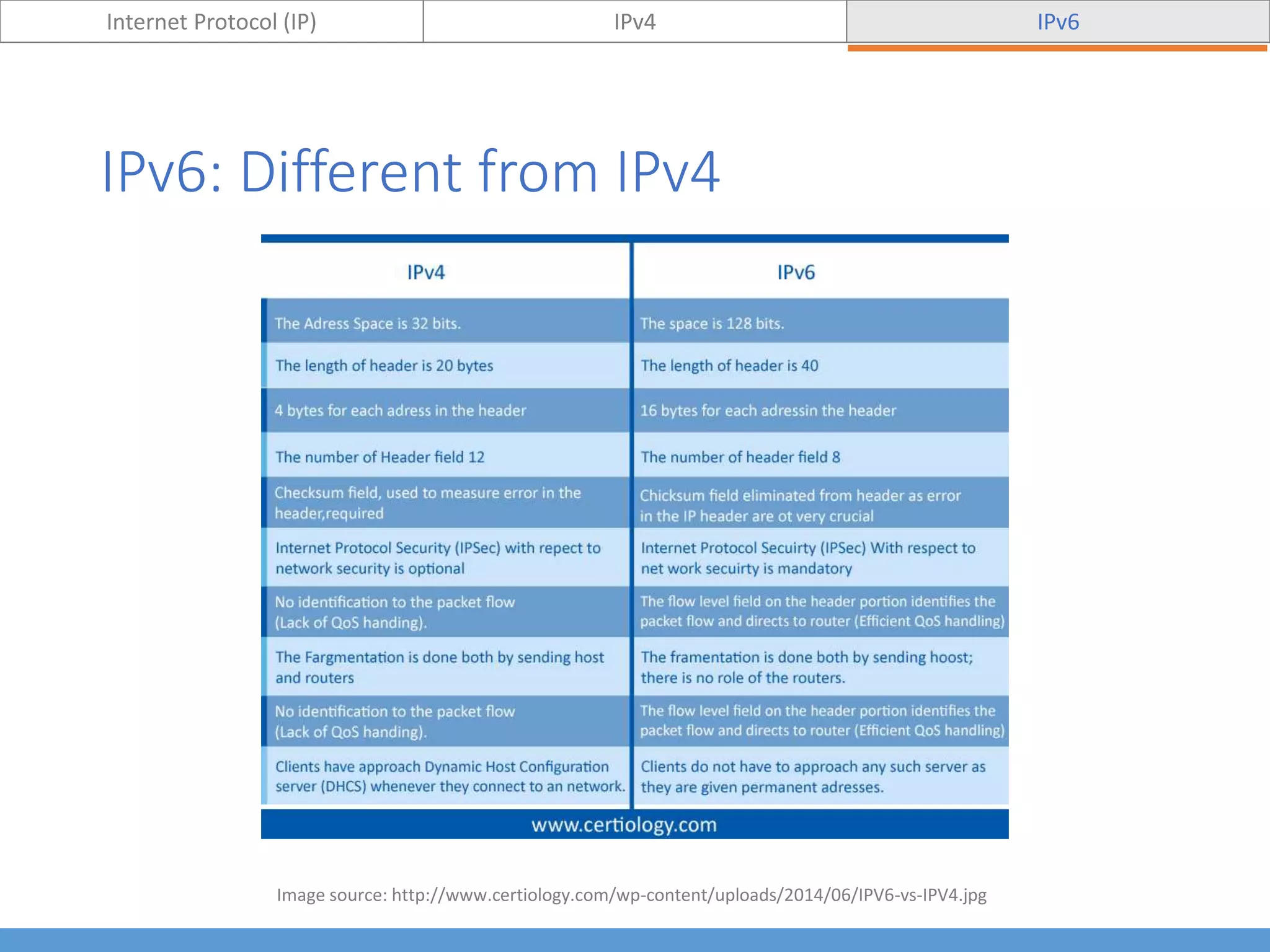
This document compares and contrasts IPv4 and IPv6. It begins by defining Internet Protocol (IP) and its purpose of identifying hosts and enabling location addressing. It then describes IPv4, including its 32-bit address structure, address notation, and class-based allocation that resulted in address exhaustion issues. The document also covers IPv6's 128-bit addresses that provide vastly more capacity to address this problem. Key differences between IPv4 and IPv6 are outlined, such as IPv6's elimination of NAT. The concepts of subnetting, supernetting, and private address ranges are also introduced to optimize IPv4 network design.