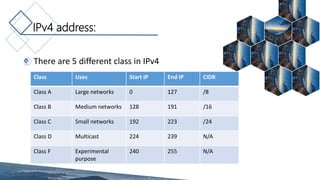
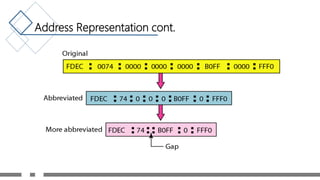
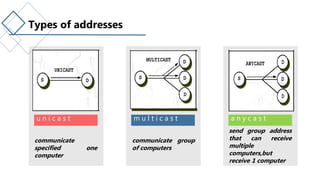
The document discusses IP addresses and the differences between IPv4 and IPv6. It defines what an IP address is, its uses, and the classes and addressing in IPv4. It describes problems with IPv4 like limited address space. It then defines IPv6 addressing which uses 128-bit addresses written in hexadecimal, and types of IPv6 addresses. It lists advantages of IPv6 like larger address space and built-in security. Tables compare features of IPv4 and IPv6 like address space, header fields, and representation.