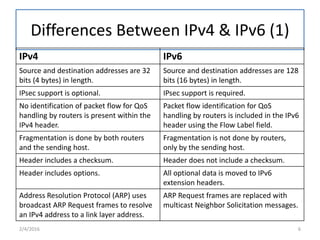
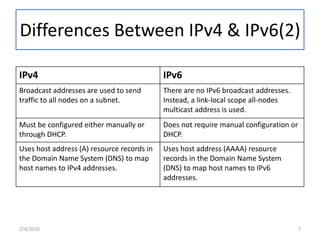
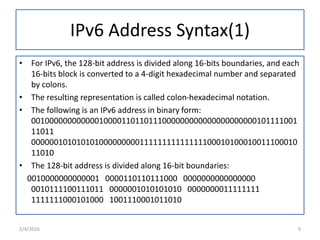
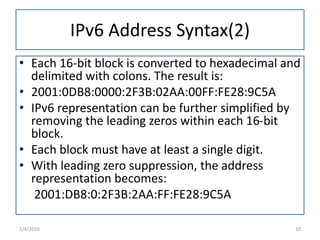
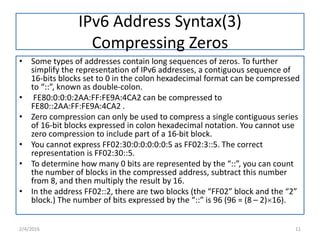
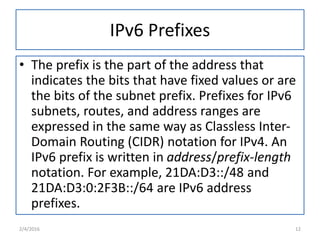
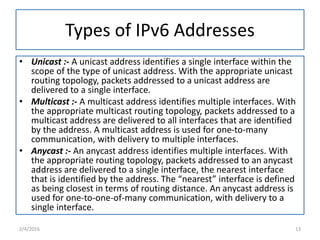
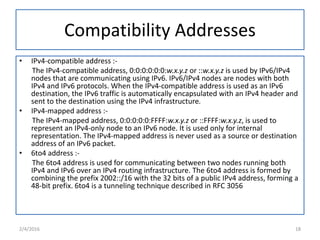
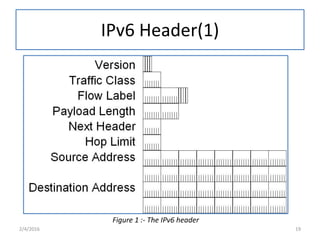
IPv6 was developed to replace IPv4 due to IPv4's limited address space and other issues. IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses compared to IPv4's 32-bit addresses, providing vastly more unique addresses. It also includes improvements in areas like security, quality of service, and extension headers. The transition from IPv4 to IPv6 is still ongoing, with strategies like running both protocols simultaneously, tunneling IPv6 traffic over IPv4, and translating headers to allow ongoing communication as adoption increases.