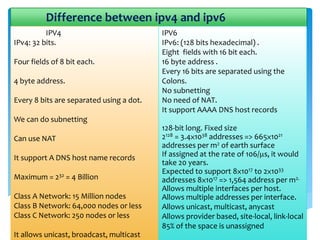
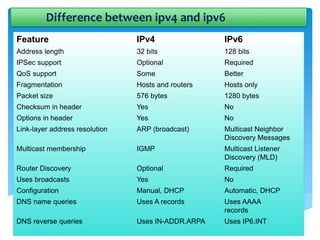
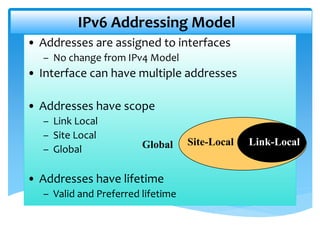
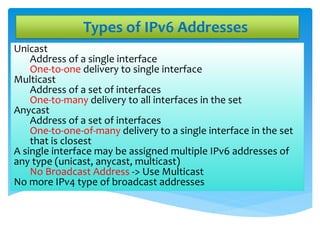
The document explains the differences between Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), including their address structures, the total number of available addresses, and management features. IPv4 provides 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses with features such as built-in security, flexible header formats, and support for various address types including unicast, multicast, and anycast. The transition to IPv6 is crucial due to the impending depletion of IPv4 addresses and offers a significantly larger address space for future internet connectivity.