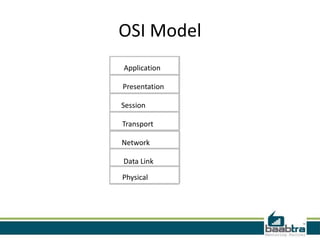
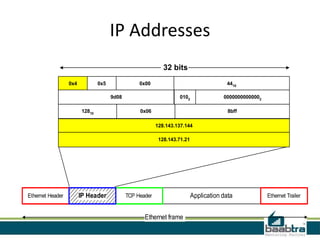
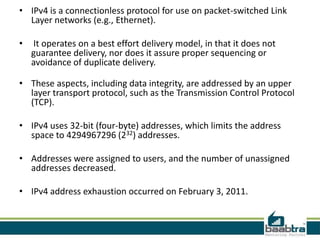
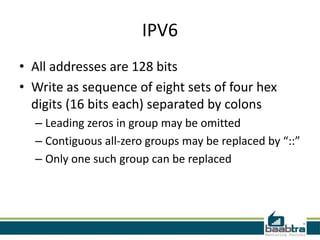
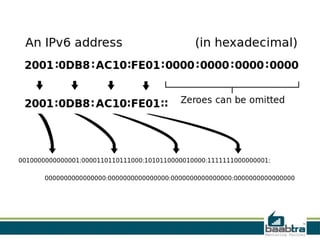
This document provides information about IP addresses and Internet Protocol versions 4 and 6. It defines an IP address as a unique identifier for devices on a TCP/IP network. IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses to allow for many more available addresses. The document also describes how IP addresses are structured and assigned, either statically or dynamically through DHCP. It notes that IPv6 deployment is increasing to address IPv4 address exhaustion issues.