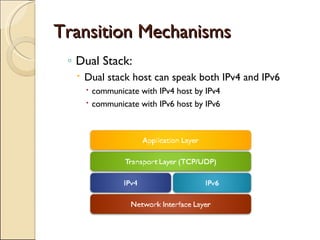
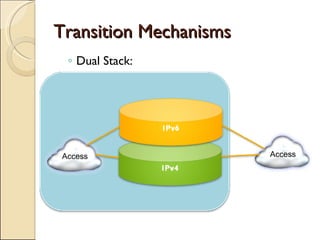
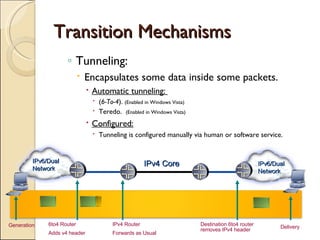
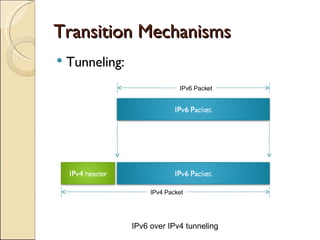
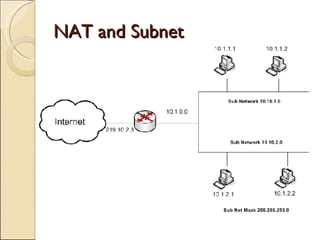
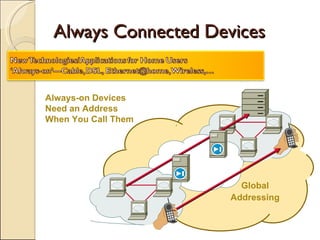
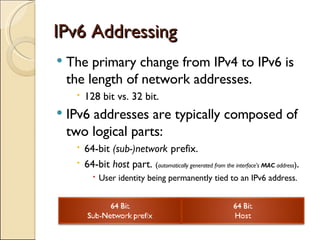
The document provides an overview of IPv6, including its key features and advantages over IPv4. It discusses IPv6 addressing formats and transition mechanisms from IPv4 to IPv6. IPv6 has a 128-bit address space compared to IPv4's 32-bit, allowing for many more addresses. It also supports features like autoconfiguration, mobility, and security that are improvements over IPv4. Transition techniques like dual stacking, tunneling, and translation allow IPv6 and IPv4 networks to interconnect during the transition period.










![IPv6 Addressing (cont.) IPv6 addresses in URL: In a URL the IPv6-Address is enclosed in brackets. http://[2001:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e:0370:7344]/ https://[2001:0db8:85a3:08d3:1319:8a2e:0370:7344]:443/ ‘ A’ record of DNS(IPv4) www.talals.net A 203.178.141.212 ‘ Qaud A’ “AAAA” record of DNS(IPv6) www.talals.net AAAA 3ffe:501:4819:2000:5254:ff:fedc:50d2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipv6-1199817293938788-2/85/IPv6-14-320.jpg)