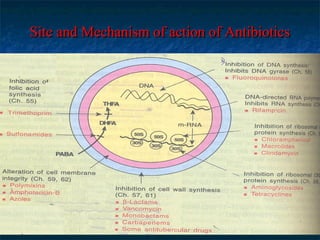
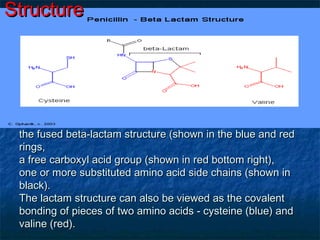
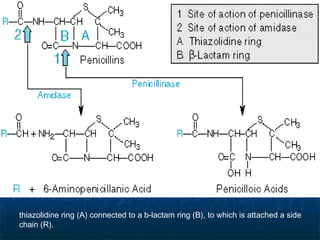
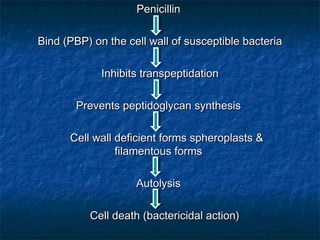
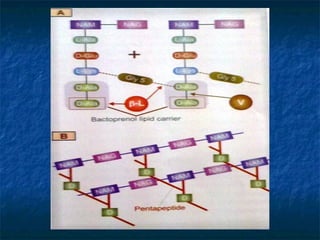
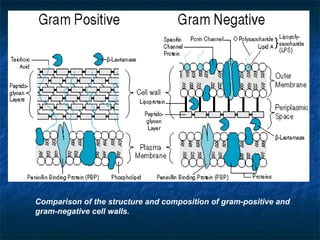
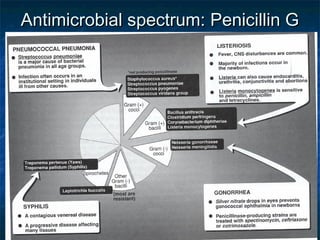
Penicillins are a group of antibiotics that are derived from the Penicillium mold. They work by inhibiting the final step of bacterial cell wall synthesis through binding to penicillin-binding proteins. This prevents cross-linking of peptidoglycan chains, leading to cell lysis. The first penicillin discovered was penicillin G, which is acid labile and used parenterally. Semisynthetic penicillins were later developed with better stability and absorption, including penicillinase-resistant penicillins effective against Staphylococcus. Extended-spectrum penicillins like ampicillin are also active against common gram-negative bacteria.